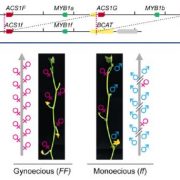
Copious cucurbits coming up! Function of the Female locus in cucumber gynoecy
Blog, Research, The Plant Cell, The Plant Cell: In BriefIf you’ve ever grown cucumbers (Cucumis sativus) at home, you know that at some point over the summer, those cucumbers will probably produce a bounty of fruit and only your trusted pickle recipe will help manage the massive number of cucumbers. Rather than being overwhelmed commercial growers want…
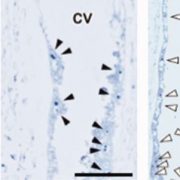
EMFasizing the conserved function of Polycomb in rice endosperm development
Blog, Research, The Plant Cell, The Plant Cell: In BriefF1 plants resulting from crosses between parents of different strains often exhibit improved fitness, known as heterosis, or also hybrid vigor. Hybrids are heavily used in modern agriculture and could be part of the solution to address the challenge of feeding an ever-growing world population. However,…
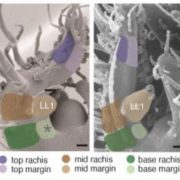
Marginal differences play a central role in complex leaf development
Blog, Research, The Plant Cell, The Plant Cell: In BriefDevelopment involves a delicate patterning of cell division and differentiation in three dimensions. This is beautifully illustrated in leaves, where three axes are visible: proximo-distal (from base to tip), medio-lateral (from the midvein to the margin/edge of the blade) and adaxial-abaxial (from upper…
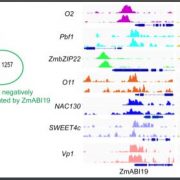
A Hub of Hubs: The Central Role of ZmABI19 in the Regulatory Network of Maize Grain Filling
Blog, The Plant Cell, The Plant Cell: In BriefCereal grains accumulate large amounts of proteins and starch and are a major source of dietary calories for humans and animals. In maize (Zea mays), most of the storage compounds are synthesized during the grain-filling period of kernel development. Several key transcription factors (TFs) that regulate…
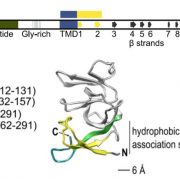
Hold Me, Fold Me...or Not!
Blog, Research, The Plant Cell, The Plant Cell: In BriefIt's not just human relationships that may require a chaperone to prevent inappropriate interactions. Numerous proteins in organisms from Escherichia coli to us, especially hydrophobic membrane proteins, also require chaperones in aqueous environments to prevent inappropriate interactions such as aggregation…
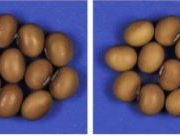
Slice and Dice: DCL2 Mediates the Production of 22-nt siRNAs That Influence Trait Variation in Soybean
Blog, Research, The Plant Cell, The Plant Cell: In BriefIn plants, small interfering RNAs (siRNAs) serve as key regulators of gene expression. While 24-nucleotide (nt) siRNAs are produced by DCL3 and mediate transcriptional silencing of transposons and pericentromeric chromatin through RdDM (Borges and Martienssen, 2015), 22-nt siRNAs are processed by DCL2…
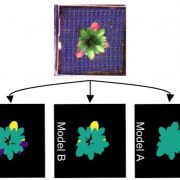
Got Rosettes? Phenotype Them Fast, Accurately, and Easily with ARADEEPOPSIS!
Blog, Research, The Plant Cell, The Plant Cell: In Brief“Deep learning” is a buzz term that seems to be cropping up in plant biology research these days. Originally reserved, perhaps, for computer nerds rather than us biology ones, deep learning is a type of machine learning used in the field of artificial intelligence. Modeled on the human brain, deep…
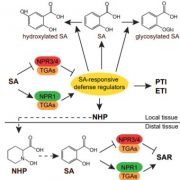
Zones of Defense? SA Receptors Have it Under Control
Blog, Research, The Plant Cell, The Plant Cell: In BriefThe constant evolutionary arms race with pathogens has equipped plants with a layered immune system. As the first line of defense, membrane-localized pattern recognition receptors perceive microbe-associated molecular patterns and activate pattern-triggered immunity (PTI). In parallel, R proteins –…

How to Eat One’s Feelings: Autophagy and Phosphatidylinositol 3-Phosphate
Blog, Research, The Plant Cell, The Plant Cell: In BriefMoving around taught me two essential skills, only one being relevant here: how to put up wallpaper, and how critical it is to label boxes to help the moving company drop them at their intended location. Now think of a cell: the boxes are vesicles, their contents are proteins and metabolites, and the…

