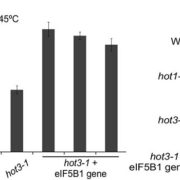
Some Like it HOT: Protein Translation and Heat Stress in Plants
Blog, Research, The Plant Cell: In BriefThe ability to acclimate to high temperatures that are normally lethal is common to virtually all organisms on the planet. A short exposure to milder heat stress informs organisms that they should ready themselves in case they experience even warmer conditions. Acquired thermo-tolerance in plants is…
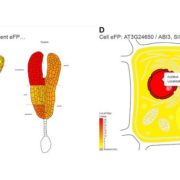
So Much Data, So Little Time: ePlant Steps into the Breach for Plant Researchers
Blog, Research, Research Blog, The Plant Cell, The Plant Cell: In Brief0 Comments
/
The ever-increasing amount of data available to researchers has come with similarly increasing cognitive loads in efforts to use these data. Even when data sets are stored in well-curated databases, it can be time-consuming to master the specific tools harbored at each site and cumbersome to move between…
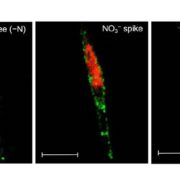
An Emerging Model Diatom to Study Nitrogen Metabolism
Blog, Research, Research Blog, The Plant Cell, The Plant Cell: In BriefCarbon and nitrogen metabolism are intricately linked in all organisms and are tightly regulated to maintain growth, homeostasis, and other cellular activities. In plants and algae, photosynthesis provides both carbon skeletons and the reductant needed for assimilation of inorganic NO3¯ by nitrate reductase…
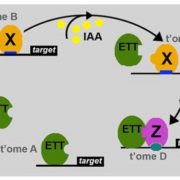
A Genome-wide Approach to Understanding a Non-Canonical ARF
Blog, Research, Research Blog, The Plant Cell, The Plant Cell: In BriefThe canonical auxin-response pathway in plants begins with auxin sensing by F-box proteins, triggering degradation of AUX/IAA proteins that act as transcriptional repressors via their interaction with sequence-specific DNA-binding AUXIN RESPONSE FACTORS (ARFs; reviewed in Weijers and Wagner, 2016). Recently,…
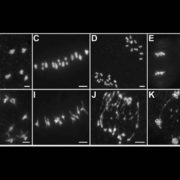
Crossover Guard: MEICA1 Prevents Meiotic Mishaps
Blog, Research, Research Blog, The Plant Cell, The Plant Cell: In BriefDuring meiosis, recombination between allelic sequences on pairs of homologous chromosomes forms crossovers; these crossovers help make sure that the homologs segregate accurately (reviewed in Zhang et al., 2014). However, cells must suppress recombination between non-allelic sequences, as ectopic recombination…

Exploring Maize Leaf Architecture from Different Angles
Blog, Research, The Plant Cell, The Plant Cell: In BriefOrnamental grasses with a sprawling growth habit may be welcome in the garden, but grasses such as maize (Zea mays) give the highest yields when they exhibit upright leaf architecture, allowing them to be planted at high density while maximizing their exposure to sunlight. The maize leaf is composed…

BEN, ROB, and the Making of a Petunia Flower
Research, Research Blog, The Plant Cell, The Plant Cell: In BriefA lot of effort goes into making a flower. Suites of genes must function in the right place at the right time. If not, stamens might grow where sepals should be, and so on, yielding homeotic mutant flowers. In general, flower parts are arranged in four concentric whorls of organs, including (from outside…
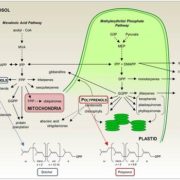
The Who, What, and Where of Plant Polyprenol Biosynthesis Point to Thylakoid Membranes and Photosynthetic Performance
The Plant Cell, The Plant Cell: In BriefIsoprenoids are a huge group of compounds that include primary metabolites such as carotenoids, chlorophylls, and hormones, as well as a plethora of specialized secondary metabolites. In addition to their importance in the physiology of plants (and of other kingdoms of life), isoprenoids have drawn attention…
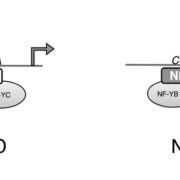
CONSTANS Companion: CO Binds the NF-YB/NF-YC Dimer and Confers Sequence-Specific DNA Binding
Blog, Research, The Plant Cell, The Plant Cell: In BriefOne of the central players in the complex regulation of flowering, CONSTANS (CO) functions as a center for integration of the various signals that determine the timing of flowering. As output, CO regulates the expression of FLOWERING LOCUS T (FT) and other genes (reviewed by Shim et al., 2017). CO contains…

