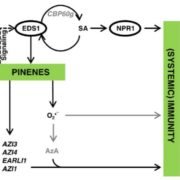
Secrets of the Forest: Volatiles First Discovered in Pine Trees Propagate Defense Signals Within and Between Plants
0 Comments
/
Systemic acquired resistance (SAR)—a plant-wide heightened state of defense following localized exposure to a pathogen—is characterized by increased salicylic acid (SA) and ROS levels and elevated expression of pathogenesis-related genes. SAR depends on ENHANCED DISEASE SUSCEPTIBILITY1 (EDS1), which…
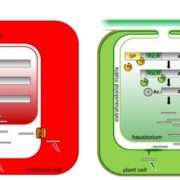
An Emerging Paradigm? RxLR Cleavage Before Effector Secretion
Eukaryotic pathogens are responsible for devastating plant diseases that threaten food supplies globally – think potato blight caused by the oomycete Phytophora infestans, rice blast caused by the fungus Magnaporthe oryzae, and wheat stem rust caused by the fungus Puccinia graminis f. sp. tritici.…

Technology Turbocharges Functional Genomics
Obtaining genomics and other –omics datasets is now routine and widely used across all biological systems, including plants. As a consequence, a wide range of plant species are being interrogated at the genome, epigenome, transcriptome, translatome, and proteome level, leading to new hypotheses about…
Division of labor during apical hook formation
Soon after dicots germinate, the hypocotyl arches into a hook-like structure that protects the shoot apical meristem as the seedling grows through the soil. Once the seedling emerges from the ground and senses light, the hypocotyl straightens. The asymmetric growth that results in apical hook formation…
The Long Non-coding RNA ELENA1 Functions in Plant Immunity
Once seen as potential sequencing artifacts, long, non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs, >200 nucleotides) have gained recognition as important regulatory factors. LncRNAs are transcribed from a variety of genomic locations (introns, intergenic spaces, and coding regions) from the sense or antisense strand (reviewed…
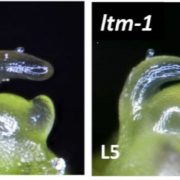
Meristem Doming and the Transition to Reproductive Development in Tomato
During vegetative growth, the shoot apical meristem (SAM) produces lateral organ primordia but remains roughly the same size, as WUSCHEL–CLAVATA signaling modulates the balance between cell division and differentiation. During the transition to reproductive growth in many species, the SAM expands in…
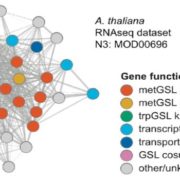
Chasing Scattered Genes: Identifying Specialized Metabolite Pathway Genes through Global Co-expression Analysis
Plants produce scores of specialized metabolites (SMs) to attract or repel the organisms around them and to cope with life in a variable environment. For thousands of years, we have been exploiting these compounds to feed, heal, and adorn us. Many more SMs remain to be discovered: the chemical constituents…
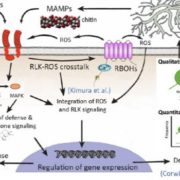
The Plant Cell Reviews Plant Immunity: Receptor-Like Kinases, ROS-RLK Crosstalk, Quantitative Resistance, and the Growth/Defense Tradeoff
Tender green leaves and tasty tubers, roots, and stems are vulnerable to a wide range of pathogens, pests, and herbivores. Perhaps it should not be surprising that they have evolved an equally wide range of defense mechanisms. This issue of The Plant Cell includes reviews of just a few of the many facets…
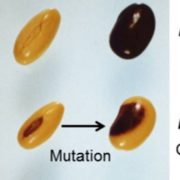
Saddle Up, Soybean Seed Pigments: Argonaute5 in Spatially Regulated Silencing of Chalcone Synthase Genes
Most soybean seeds you see, whether in bins at the store, or in train cars as a commodity crop, have a yellow seed coat that may have only a tiny fleck of dark pigment at the hilum, where the seed attaches to the pod. The predominant yellow color results from silencing of chalcone synthase (CHS) genes…

