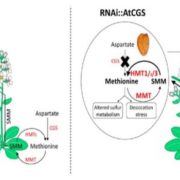
A Possible Strategy for Increasing Methionine Titer in Seeds
Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: On The Inside, Research0 Comments
/
Methionine is a nutritionally essential sulfur-containing amino acid found at low levels in plants and in their seeds. It often limits the nutritional value of crop plants as a source of dietary protein for humans and animals. In plants, methionine plays key roles in protein synthesis and mRNA translation,…
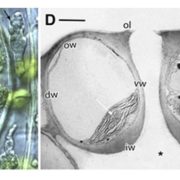
Plant Physiology Focus Issue on Stomata published
Blog, Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: Editorials, ResearchThe June 2017 issue of Plant Physiology is a Focus Issue on stomata; here is the editorial overview to this issue by Michael R. Blatt, Plant Physiology, Editor-in-Chief, and Tim J. Brodribb and Keiko U. Torii, Plant Physiology Editors.
Small Pores with a Big Impact
The guard cells surrounding stomatal…
Solar UV-B Inhibits Growth of Maize Leaves
Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: On The Inside, ResearchGrowth inhibition is one of the most consistent plant responses to Ultraviolet-B (UV-B) exposure; this radiation, both as part of the solar spectrum in the field and from UV-B lamps in controlled environments. In this work, Fina et al. (10.1104/pp.17.00365) demonstrate that the UV-B levels…
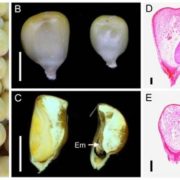
Vitamin B6 Is Essential for Maize Embryogenesis
Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: On The Inside, ResearchVitamin B6 is synthesized de novo in plants, fungi, archeae, and most eubacteria, but not in animals, including humans, which have to obtain it from dietary sources. Vitamin B6 is an essential cofactor for a range of biochemical reactions and a potent antioxidant. In plants, it plays important roles…
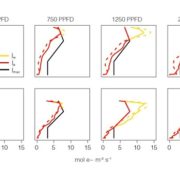
Light Direction, Absorption, and Photosynthesis
Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: On The Inside, ResearchPlant photosynthesis generally increases with irradiance until light saturation occurs. The directional quality of light, however, can affect its penetration and absorption within a leaf. For example, increasing the angle of incidence (from perpendicular) at which light intersects the leaf surface decreases…
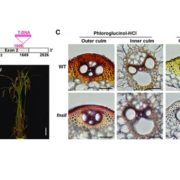
A Flavone Synthase that Alters Lignin
Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: On The Inside, ResearchLignin, a ubiquitous phenylpropanoid polymer found in the cell walls of vascular plants, is derived primarily from oxidative couplings of monolignols (p-hydroxycinnamyl alcohols). By filling up spaces between cell wall polysaccharides (cellulose and hemicelluloses), lignin confers increased mechanical…
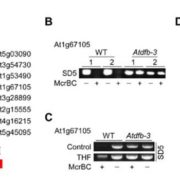
Folate, DNA Methylation and Flowering Time
Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: On The Inside, ResearchTetrahydrofolate (THF) and its derivatives, collectively termed folates, are a group of essential B-complex vitamins that have long been recognized as necessary nutrients to support normal cell differentiation and growth. Folates function as co-enzymes in one-carbon transfer reactions and play a central…
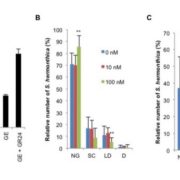
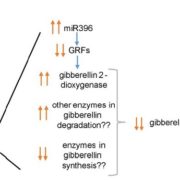
Strigolactone-Gibberellin Cross Talk
Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: On The Inside, ResearchStrigolactones Root parasitic weeds, such as broomrape (Orobanche spp.) and witchers weed (Striga spp.), are harmful plants in sub-Saharan Africa, the Middle East, and Asia that maintain seed dormancy in the absence of host plant. Both parasitic plant species require germination stimulants released from…
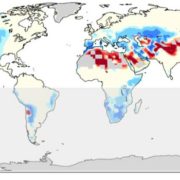
Update: Stomatal function across temporal and spatial scales: deep-time trends, land-atmosphere coupling and global models
Blog, Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: Updates, Research, Research BlogBy Peter J Franks, Joseph A Berry, Danica L. Lombardozzi, and Gordon B Bonan
The colonization of land by plants and their interaction with biogeochemical and atmospheric processes transformed continental climate and hydrology. Stomata, which evolved to optimize the biological economics of plant carbon…

