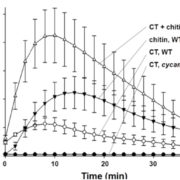
Cellotriose Induces Increases in Cytoplasmic Calcium
Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: On The Inside, Research, Research BlogThe root-colonizing endophytic fungus Piriformospora indica, which was originally isolated from the rhizosphere of two woody shrubs in the Indian Thar Desert, colonizes the roots of a broad host range, including the model plant Arabidopsis. P. indica does not cause pathogenic symptoms, but promotes root…
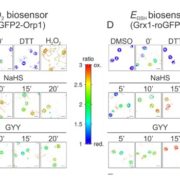
Hydrogen Sulfide’s Role in Stomatal Closure
Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: On The Inside, Research, Research Blog Hydrogen sulfide (H2S) is an important gaseous signaling molecule in plants that participates in stress responses, development, and stomatal closure. In plants, H2S is enzymatically produced by cysteine desulfhydrase in the catalyzed conversion of cysteine to pyruvate, H2S, and NH3+. In Arabidopsis…
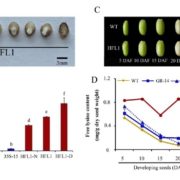
Serotonin Accumulation in High-Lysine Rice
Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: On The Inside, Research, Research BlogThe nutritional quality of cereals often suffers from a deficiency in essential amino acids, especially lysine. Recently, High Free Lysine (HFL) rice (Oryza sativa) has been genetically engineered. The free lysine content in the mature endosperm of two HFL transgenic lines (HFL1 and HFL2) is increased…
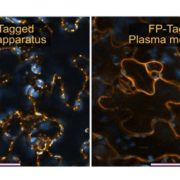
Update: Monitoring Polysaccharide Dynamics in the Plant Cell Wall
Blog, Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: UpdatesBy Catalin Voiniciuc, Markus Pauly, and Björn Usadel
All plant cells are surrounded by complex walls that play a role in growth and differentiation of tissues. Walls provide mechanical integrity and structure to each cell, and represent an interface with neighboring cells and the environment (Somerville…
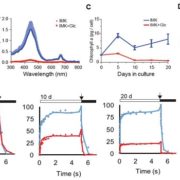
Glucose-Induced Trophic Shift in an Endosymbiotic Dinoflagellate
Blog, Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: On The Inside, Research, Research BlogDinoflagellates in the genus Symbiodinium have the ability to enter into endosymbiotic associations with corals, providing the metabolic basis for the highly productive and biologically diverse coral-reef ecosystems, as well as with other cnidarians, including sea anemones and jellyfish. The Symbiodinium-coral…
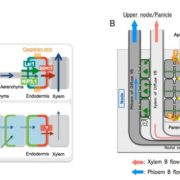
Boron Transport in Rice
Blog, Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: On The Inside, Research, Research BlogBoron (B) is an essential micronutrient for plant growth and development. Its major physiological function is to maintain the structure of the cell wall by crosslinking pectic polysaccharides through borate-diol bonding of two rhamnogalacturonan II molecules. B is immobile in most plant species. Therefore,…
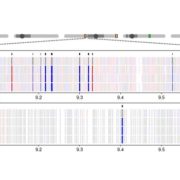
Epigenetic Divergence Associated with Heterosis
Blog, Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: On The Inside, Research, Research BlogHeterosis refers to the tendency of a crossbred individual to show qualities superior to those of both parents. The phenomenon has been exploited extensively in agricultural breeding for decades and has improved crop performance enormously. Despite its commercial impact, knowledge of the molecular basis…

Mineral Deposits in Ficus Leaves
Blog, Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: On The Inside, Research, Research BlogMineral deposits occur in many, but not all plant leaves. In those leaves that do have minerals, the mineral type, morphology and the distributions within the leaves are under strict control. In fact, mineralization in certain leaves is a well-preserved trait throughout evolution, indicating that such…

Anthocyanins on Demand
Blog, Plant Physiology: On The Inside, Research, Research BlogAnthocyanins are vacuolar pigments derived from the phenylpropanoid pathway that are produced in many different plant species. The role of anthocyanin accumulation under stress in vegetative tissues is probably linked to the scavenging of reactive oxygen species (ROS). Anthocyanins are powerful antioxidants…

