Powering Epigenetics through the 1C Pathway
Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: News and ViewsBy Lisa Smith and Nathan Butler
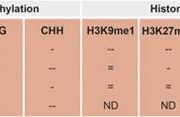
Epigenetic modifications in plants repress transposable elements to maintain genome stability and facilitate adaptation to changing environmental conditions by regulating the expression of some genes. Furthermore, conditions such as disease stress can alter the epigenetic…
Natural Variation Reveals Interplay between C4 Biology and Water Use Efficiency
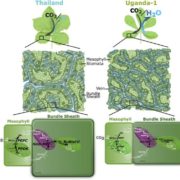
Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: News and ViewsThe year 2016 marked a half-century since the discovery of C4 photosynthesis, yet we still seek to elucidate many of the mechanisms underpinning the C4 cycle. Although C4 and C3 plants share molecular units involved in photosynthesis (Miyao, 2003; Kellogg, 2013), C4 plants have unique morphological traits…
Live-Cell Imaging of Mobile RNAs in Plants
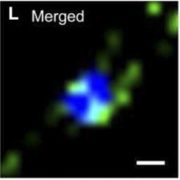
Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: News and ViewsOne of the most exciting findings in the past few decades is the discovery that individual mRNAs and noncoding RNAs can act as long-distance signaling messengers traveling cell to cell to distant sites in the plant. Numerous examples unveiled the involvement of endogenous RNAs as non-cell-autonomous…
Adjusting Boron Transport by Two-Step Tuning of Levels of the Efflux Transporter BOR1
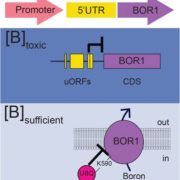
Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: News and ViewsBoron is an essential plant micronutrient with the narrowest optimal range in the soil of any micronutrient. At neutral pH, boron is present as uncharged boric acid, B(OH)3, which can freely penetrate membranes. Boron plays an important role in cross-linking cell wall components, but boron starvation…
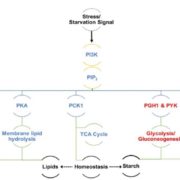
A Molecular Gatekeeper of Algal Biofuel Synthesis
Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: On The InsideAlgae undergo a complete metabolic transformation under stress by arresting cell growth, inducing autophagy, and hyper-accumulating biofuel precursors such as triacylglycerols and starch. However, the regulatory mechanisms behind this stress-induced transformation are still unclear. Understanding the signaling…
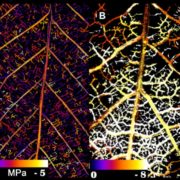
Low Xylem Vulnerability in Oaks
Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: On The InsideUnder conditions of drought stress, the continuous column of water in the plant xylem experiences increasing tension caused by declining water potential at the sites of evaporation. Eventually, air is drawn into the water transport system, forming embolisms in the xylem conduits. Although plants have…
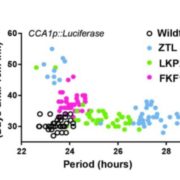
New Insights into the Molecular Biology of Plant Circadian Rhythms
Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: On The InsideThe circadian clock is an endogenous timekeeper that synchronizes essential biological processes with the outside world. Eukaryotic clocks rely on the ubiquitin proteasome system to target core clock factors for degradation. Altering clock protein degradation can change the period length of the clock.…
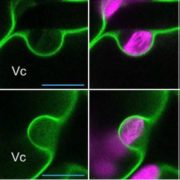
Selective Chloroplast Microautophagy
Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: On The InsideWhen plants are exposed to excessive light, photoinhibition occurs and chloroplasts become damaged. Photodamaged chloroplasts undergo vacuolar digestion through a poorly understood autophagic process called chlorophagy. In general, cell biologists recognize two types of autophagy: macroautophagy and…
ABA Biosynthesis Occurs in the Mesophyll
Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: On The InsideThe plant hormone abscisic acid (ABA) plays a critical role in enhancing plant survival during water deficit. While there is no doubt that ABA is a carotenoid derivative and that carotenoid cleavage occurs in the chloroplast, uncertainty remains about which tissues are responsible for synthesizing ABA.…

