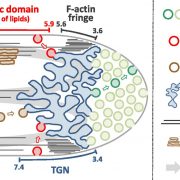
Apical Membrane Traffic In Pollen Tube Tips
Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: On The InsidePollen tubes elongate very rapidly at rates of several micrometer per minute and strictly in one direction: this process involves the intense local secretion of cell wall material at the tube tip. Consequently, there is a massive incorporation into the plasma membrane (PM) of excess membrane material…
Cutin Synthesis and Deposition
Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: On The InsideThe waxy cuticle that covers the aerial parts of leaves, fruits, and nonlignified stems of land plants is chemically heterogeneous, with lipids representing between 60% to 80% of the cuticle, depending on the plant organ and species. These lipids can be polymerized, represented by cutin, or non-polymerized,…
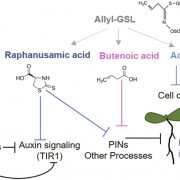
Allyl-GSL Catabolites and Root Development
Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: On The InsideIn order to survive attacks by pathogens and herbivores, plants have developed a variety of defense mechanisms and resistance strategies, including the production of defensive chemicals. Such defense chemicals, however, can have detrimental effects on growth or can introduce ecological costs by attracting…
Root Foraging under Low Nitrogen Depends on Brassinosteroids
Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: On The InsidePlant root systems alter their architecture upon encountering spatial heterogeneity in the nutrient concentrations of the soil. For example, when roots are subjected to decreasing N availability that causes mild N deficiency, lateral root emergence increases moderately, whereas elongation of primary…

Melatonin Represses Oil and Anthocyanin Accumulation in Seeds
Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: On The InsideMelatonin is a highly conserved bioactive molecule present in all plant species. It is produced from serotonin through two consecutive enzymatic steps. Serotonin is converted into either N-acetylserotonin by serotonin N-acetyltransferase (SNAT) or into 5- methoxytryptamine by caffeic acid O-methyltransferase…
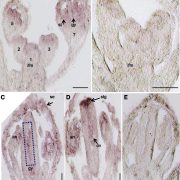
Role of Cell Wall Invertase in Ovule Development
Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: On The InsideApart from its well-known function in Suc unloading, cell wall invertase (CWIN), an enzyme that catalyzes the hydrolysis of Suc into Fru and Glc, also plays a role in sugar signaling and plant development. As an example of CWIN playing a role in plant development, Liao et al. (10.1104/pp.20.00400)…
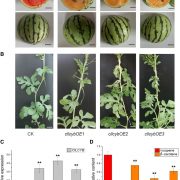
How Cultivated Watermelon Derived its Red Flesh
Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: On The InsideModern cultivated watermelons (Citrullus lanatus) are sweet tasting and tender, with intensely colored flesh that ranges in hue from yellow to deep red. These colors are produced by the accumulation of various carotenoids in the flesh cells. Red-fleshed watermelons that accumulate lycopene in their flesh…
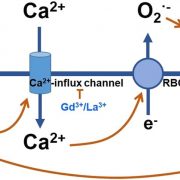
Hydrogen Gas Regulates Cadmium Uptake
Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: On The InsideCadmium (Cd) is a toxic heavy metal that is relatively mobile in the soil and has become a serious worldwide environment problem. Cd is easily taken up by plant roots where it can be loaded into the xylem and transported to above-ground tissues. Cd accumulation in the shoot inhibits plant growth and…
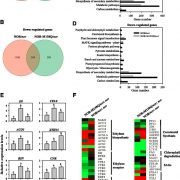
Sulfoxidation of NON-RIPENING Affects Tomato Fruit Ripening
Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: On The InsideTranscription factors (TFs) can be subject to multiple posttranslational modifications (PTMs) that affect protein stability, subcellular localization, interactions with corepressors and activators, and DNA binding activity of TFs, thereby influencing their regulatory activities on target genes. Recent…

