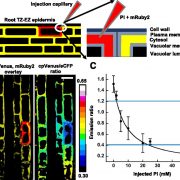
On the Inside: Spatial Dynamics of Pi Distribution in Roots
Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: On The InsideThe availability of inorganic phosphate (Pi) often limits plant growth and crop productivity. The signaling mechanisms governing Pi starvation responses in plants include responses to external Pi concentrations to modify the root system architecture and responses to internal Pi concentrations to maintain…
On the Inside: Characterization of a Ribosome Biogenesis Factor
Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: On The InsideThe structure and biogenesis of the eukaryotic 80S ribosome are similar in all eukaryotes, as are the ribosomal RNAs (rRNAs) and ribosomal proteins involved in these processes. The biogenesis of the 80S ribosome in eukaryotes is best characterized in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Indeed, the individual…
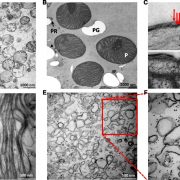
On the Inside: The Origins of Euglena gracilis’s Middle Plastid Envelope Membrane
Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: On The InsideThe plastids of Euglena gracilis, a freshwater photosynthetic flagellate, are embedded by three membranes. These membranes are an evolutionary vestige of the secondary endosymbiotic event that occurred between a phagotrophic eukaryovorous euglenid and a Pyramimonas-related green alga. The plastids…
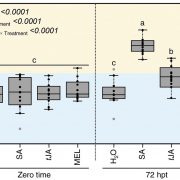
On the Inside: Citrus Greening Disease and Melatonin
Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: On The InsideMelatonin has diverse effects on plant growth and development and has been implicated in tolerance to abiotic stresses such as drought, salinity, freezing, and high temperature. The protective role of melatonin against biotic stresses in plants, however, remains unclear. Huanglongbing (HLB), popularly…
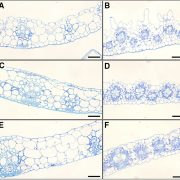
On the Inside: Sodium Sequestration by a Turfgrass
Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: On The InsideAbout 20% of irrigated land is considered saline, with the amount of saline soils increasing worldwide. This trend is alarming due to the high salt sensitivity of most crop species. Yield reduction in crops in saline soils amounts to losses in the order of 12 to 27.3 billion US dollars annually. Thus,…

On the Inside: Non-Stomatal Water Loss by Tomato Fruits
Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: On The InsideIn land plants, water is lost primarily by transpiration through stomata. However, when the aerial tissues begin to dry, the stomata close, and transpiration, much reduced, occurs mostly from the apoplast of epidermal cells. The hydrophobic cuticle that coats the epidermis of aerial organs provides the…
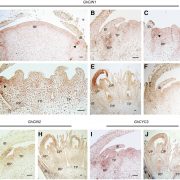
On the Inside: Molecular Regulation of Asteraceae Inflorescence Development
Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: On The InsideThe reproductive structures of the Asteraceae (the sunflower family), the largest family of flowering plants, are among the most complex within the flowering plants. The species in this family develop head-like inflorescences that resemble flowers. In many Asteraceae flowers, the hermaphroditic disc…
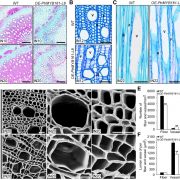
On the Inside: Feedback Regulation of Wood Formation in Poplar
Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: On The InsideWood formation is controlled by a number of MYB family transcription factors, which may act as transcriptional activators or repressors. Secondary wall associated NAC domains (SNDs) and vascular-related NAC domains are master regulators controlling the expression of downstream transcription factors,…
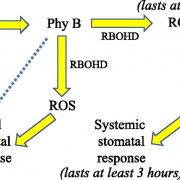
On the Inside: Phytochrome B and Systemic Reactive Oxygen Species Waves
Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: On The Inside
Several recent studies have revealed that reactive oxygen species (ROS)waves propagate through plants, originating at the treated, stimulated, or stressed local tissue and spreading within minutes to the entire plant. ROS waves regulate and coordinate systemic metabolic, molecular, and physiological…

