
Plastid stress signaling alters cell cycle progression (Cell Reports)
Plant Science Research Weekly
The chloroplast is in constant communication with the nucleus via so-called retrograde signaling. This signaling, which can take many molecular forms, is important for maintaining chloroplast function. In this paper by Duan et al. we learn that interfering with plastid DNA replication, either through…
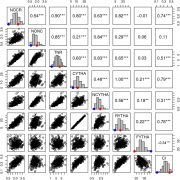
Multiple QTL mapping in autopolyploids: A random-effect model approach with application in a hexaploid sweetpotato full-sib population (Genetics)
Plant Science Research WeeklyGene mapping and QTL identification for the improvement of important traits have not been fully explored in an autopolyploid species like sweetpotatoes (2n=6x=90) due to its genetic complexity. Most sweet potato QTL mapping efforts have relied on models used for diploid species, leading to low density…
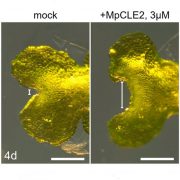
Molecular regulation of meristem development in liverworts (Curr. Biol.)
Plant Science Research WeeklyPlants grow through meristems, pools of undifferentiated cells that produce and develop into all varieties of cell types. Flowering plants such as Arabidopsis regulate meristematic cell division through CLAVATA3/EMBRYOSURROUNDING REGION-related (CLE) peptide signaling, but the molecular mechanisms in…
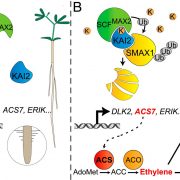
The karrikin signaling regulator SMAX1 controls Lotus japonicus root and root hair development by suppressing ethylene biosynthesis (Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA)
Plant Science Research Weekly
KARRIKIN INSENSITIVE 2 (KAI2) and MORE AXILLARY GROWTH 2 (MAX2) form an important hormone receptor complex and mediate several developmental responses in the karrikin signaling pathway. The proteolytic degradation of the suppressor of MAX2 (SMAX1) is a major step in this pathway. Carbonnel et al.…
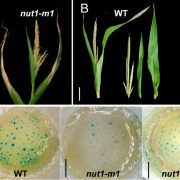
A protoxylem-specific NAC transcription factor modulates heat and drought stress in maize (PNAS)
Plant Science Research Weekly
Excessive heat and water deficit coincide with flowering and result in developmental defeats such as male floral organs browning, infertile pollen, and failure in fertilization: a syndrome known as “tassel blasting” in maize. The genetic pathway underlying tassel blasting is not well characterized.…
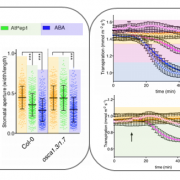
The calcium-permeable channel OSCA1.3 regulates plant stomatal immunity (Nature)
Plant Science Research Weekly
In plants, the perception of environmental threats induces a peak of calcium ions (Ca2+) in the cytosol that triggers signal transduction pathways leading to stomatal closure as defense response. In Arabidopsis, the mechanosensitive Ca2+ channel OSCA1 regulates water transpiration in response to…
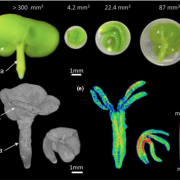
The process of seed maturation is influenced by mechanical constraints (New Phytol.)
Plant Science Research WeeklyDeveloping organs need to sense their surroundings to modulate their growth. In the case of embryos, their development is physically limited by the embryo sac; thus, they must assess the space they have available for growing and modulate their growth accordingly. In this paper, Rolletschek et al. report…
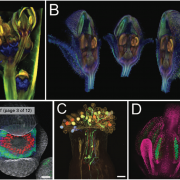
Plant Science Research Weekly: September 4, 2020
WWR Full PostReview. Imaging flowers: a guide to current microscopy and tomography techniques to study flower development
Flowers bear the reproductive organs and determine the reproductive success of plants by producing fruits and seeds. Flowers usually include four whorls of organs: sepals, petals, stamen…
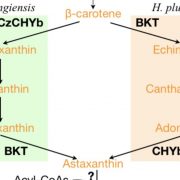
An Alternative Route for Astaxanthin Biosynthesis in Green Algae
Blog, Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: News and Views, ResearchTianhu Sun
ORCID ID: 0000-0002-2513-1387
Plant Breeding and Genetics Section, School of Integrative Plant Science, Cornell University, Ithaca, New York 14853
[email protected]
Astaxanthin is the reddish carotenoid pigment that gives color to shrimp, salmon, and flamingo. However, these animals…

