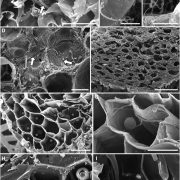
Insights into a Vascular Plant–Fungal Symbiosis
Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: On The InsideThe land invasion by plants more than 500 million years ago was facilitated by the formation of mutualistic symbioses with fungi, through which the earliest plants gained access to mineral nutrients in exchange for photosynthetically fixed carbon (C). It was long hypothesized that this ancient mycorrhiza-like…
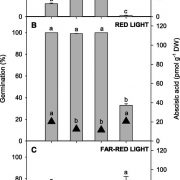
Smoke and Lettuce Seed Germination
Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: On The InsideWildfire smoke contains certain potent bioactive compounds (butenolides) that play a major role in regulating the germination of many plant species, predominantly grasses and shrub species from fire-prone ecosystems but also many non-fire-dependent plants such as rice (Oryza sativa), wild oats (Avena…
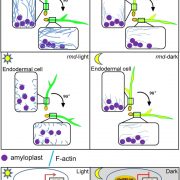
Actin Binding Protein and Negative Gravitropism
Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: On The InsideGravity is a key determinant in orienting plant stems for proper growth and development. An intact and dynamic actin cytoskeleton is thought to be important for plants to respond to gravity; however, pharmaceutical treatment and mutant analyses have yielded conflicting results. In Arabidopsis (Arabdopsis…
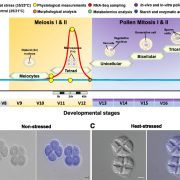
Heat Stress: Two New Insights
Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: On The InsideHigh temperatures caused by climate change are predicted to decrease cereal productivity in many parts of the world. Yield losses due to rising temperatures have already been reported for major cereal crops including maize (Zea mays), wheat (Triticum sp.), and rice (Oryza sativa). These cereals together…
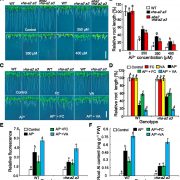
Vacuolar H+-ATPase Regulates Al Resistance
Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: On The InsideIn acidic soils, phytotoxic levels of active aluminum (Al) are released from Al-containing minerals when the pH drops to 5 or lower. These active Al forms, primarily Al3+, often threaten root vitality and inhibit primary root elongation, thus limiting the acquisition of nutrient elements and water necessary…

Stories Plantarum E5: Upside Down and Underground Transcript
Blog0 Comments
/
Image Description: Graphic is a white rectangle with a green border that says "Stories Plantarum Ep. 5 Upside Down and Underground" over the Stories Plantarum logo, an icon of an open book with a plant growing from it. On the left side is an image of the Demogorgon from Netlfix's Stranger Things. On…
Saffron Red Pigment Is Stored in Vacuoles through Active Transport
Research, The Plant Cell, The Plant Cell: In a NutshellDemurtas et al. developed a high-throughput approach to identifying vacuolar transporters and used it to explore transport of crocins in saffron. Plant Cell https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.19.00193
By Olivia C. Demurtas and Giovanni Giuliano
Background: The saffron spice is made of dried stigmas from…

A rice transcription factor controls grain length through cell number
Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: News and Views, ResearchProviding around 20% of global calories, rice (Oryza sativa) is one of the most important staple crops (Global Rice Science Partnership (GRiSP), 2013). With consumption particularly increasing in sub-Saharan Africa, the Middle East and Latin America, it is vital to increase rice yields to supply the…
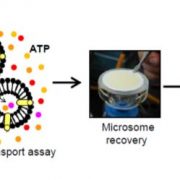
The ABCCs of Saffron Transportomics
Research, The Plant Cell, The Plant Cell: In BriefSaffron spice is prized for its aroma, flavor, and color. The latter derives from highly concentrated apocarotenoid glycosides called crocins. Accumulation of specialized metabolites like crocins often requires their sequestration in the vacuole to prevent cellular toxicity, feedback inhibition of…

