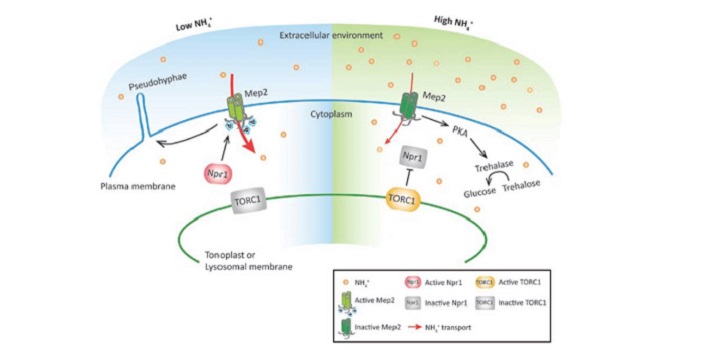
Review: Ammonium as a signal for physiological and morphological responses ($)
0 Comments
/
Ammonium is one of the major forms in which nitrogen is assimilated. Besides being a nutrient, it also acts as signal that affects gene expression and root system architecture. Some ammonium-induced genes are also induced by low pH (ammonium acidifies the apoplast), whereas others are specifically induced…
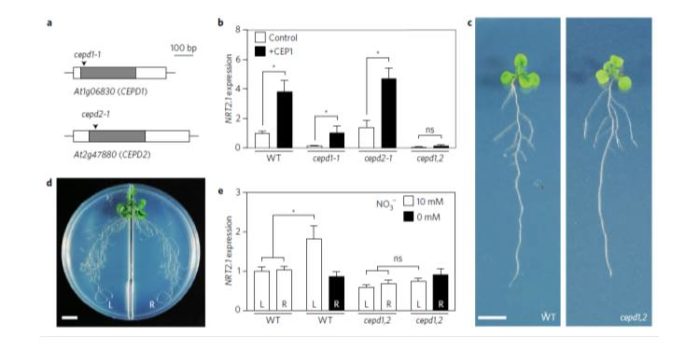
Shoot-to-root mobile polypeptides involved in systemic regulation of nitrogen acquisition ($)
To balance nutrient uptake (usually from heterogeneous sources) with nutrient demand, plants use a root-shoot-root signaling pathway. Previously, a root-to-shoot mobile peptide C-TERMINALLY ENCODED PEPTIDE (CEP) was shown to translocate from N-starved roots to the shoot, where it interacts with a leucine-rich…
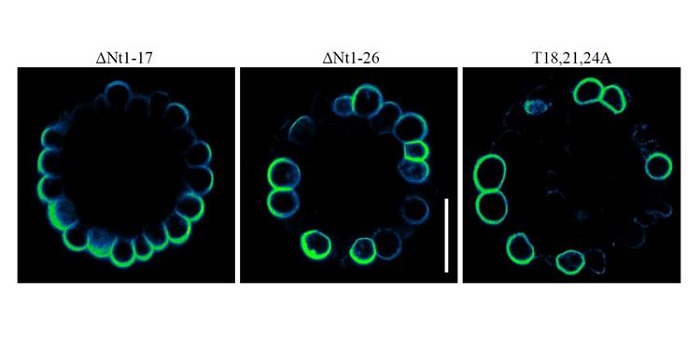
Threonine Phosphorylation Regulates Polar Localization of the Boric Acid Transporter NIP5;1 in Root Cells
IN BRIEF by Gregory Bertoni gbertoni@aspb.org
Proper localization of proteins in the plasma membrane is critical for proper functioning of plant cells, but the underlying mechanisms are poorly understood (Łangowski et al, 2016). This is especially true for transporter proteins that move necessary…
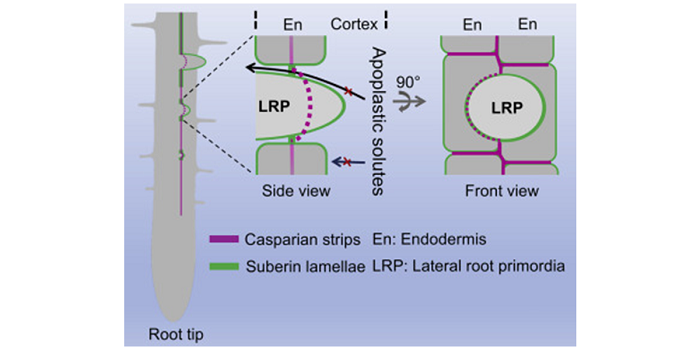
Role of LOTR1 in Nutrient Transport ($)
Casparian strips, named after the German botanist Robert Caspary who discovered them, are a cellular feature found in the roots of all higher plants. They are ring-like lignin polymers deposited in the middle of anticlinal cell walls (parallel to the root radius) between endodermal cells. Along with…
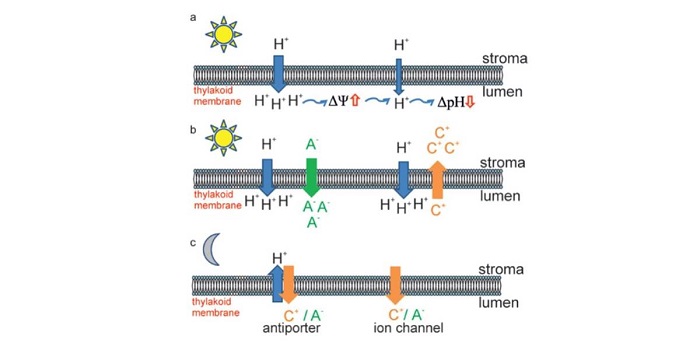
Review: Impact of the ion transportome of chloroplasts on the optimization of photosynthesis ($)
In photosynthesis, light energy generates proton motive force (pmf) across the thylakoid membrane. The establishment and maintenance of pmf involves numerous membrane transporters as well as other ions. Szabò and Septea review how various ions (including K+, Na+, Fe2+, Cu+, Mn2+, Ca2+, Cl–) contribute…
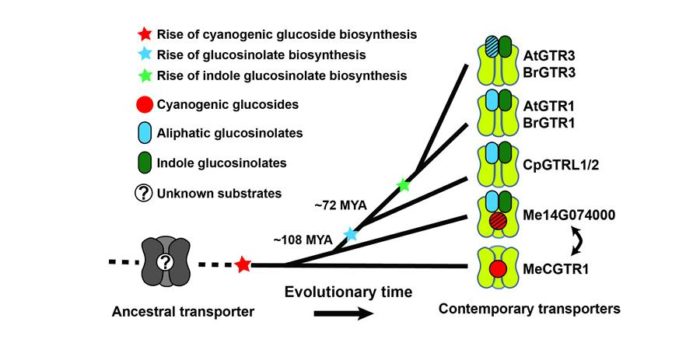
Origin and evolution of transporter substrate specificity within the NPF family
Which arose first during evolution- a metabolite molecule or a transporter that could move it across a membrane? Jørgensen et al. studied transporters for glucosinolate defense molecules in Brassicales species. Glucosinolates are derived from the broad class of cyanogenic glucosides, and glucosinolates…

Heteroblastic Development of Transfer Cells: A Role for MicroRNA
Transfer cells (TCs) play critical roles in membrane transport of solutes at various sites within plants and between plants and their environment. This transport capacity is conferred by inward wall protuberances that extend into the cell lumen. These ingrowths function to enhance the area of surrounding…
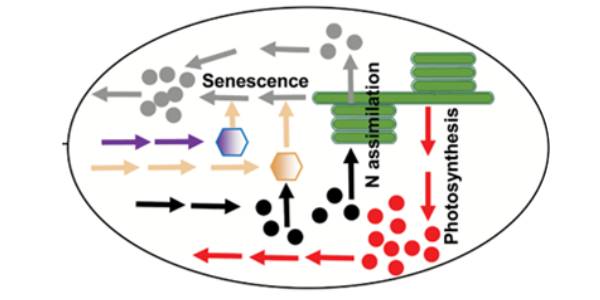
Review: Source-sink interactions in plants ($)
With populations increasing globally, improving crop yield potential is one of the major challenges to the plant biologist, complicated by the changing climate. A better understanding of the source (material producer or exporter, e.g., leaves) – sink (material importer or consumer, e.g., roots, growing…
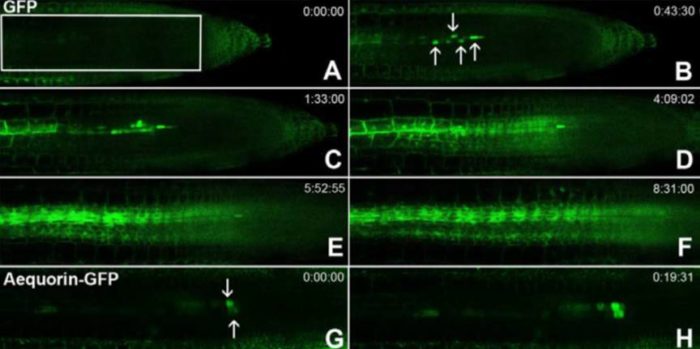
Phloem unloading in Arabidopsis roots
It is well known that long distance transport and movement of molecules is enabled by phloem, but the precise mechanism of loading/unloading of phloem mobile compounds is not known. In this article, Ross-Elliott et al. used a combination of approaches (non-invasive imaging, 3D-electron microscopy, and…

