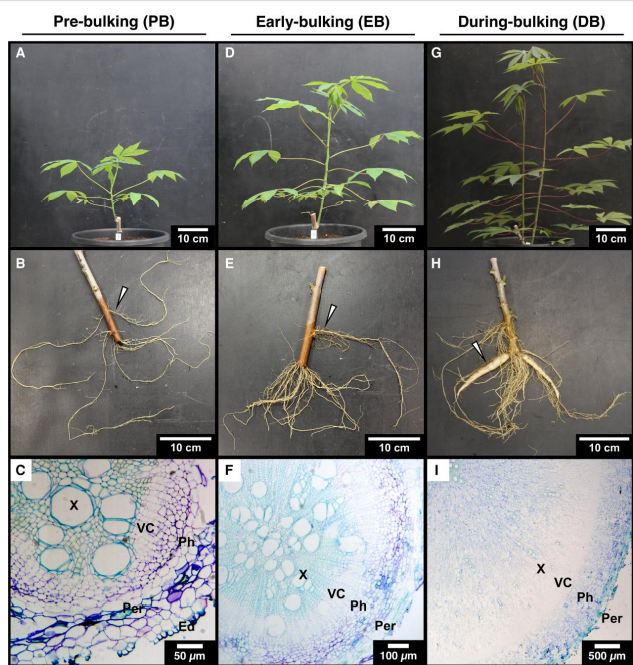
Phloem loading and subcellular transport drive carbon storage in cassava roots
Plant Science Research WeeklyCassava (Manihot esculenta) is a vital starchy crop essential for food security in Sub-Saharan Africa, South America, and Southeast Asia. A recent study on cassava by Rüscher et al. provides important insights into the plant’s sugar control mechanisms as the roots expand, produce large amounts of…
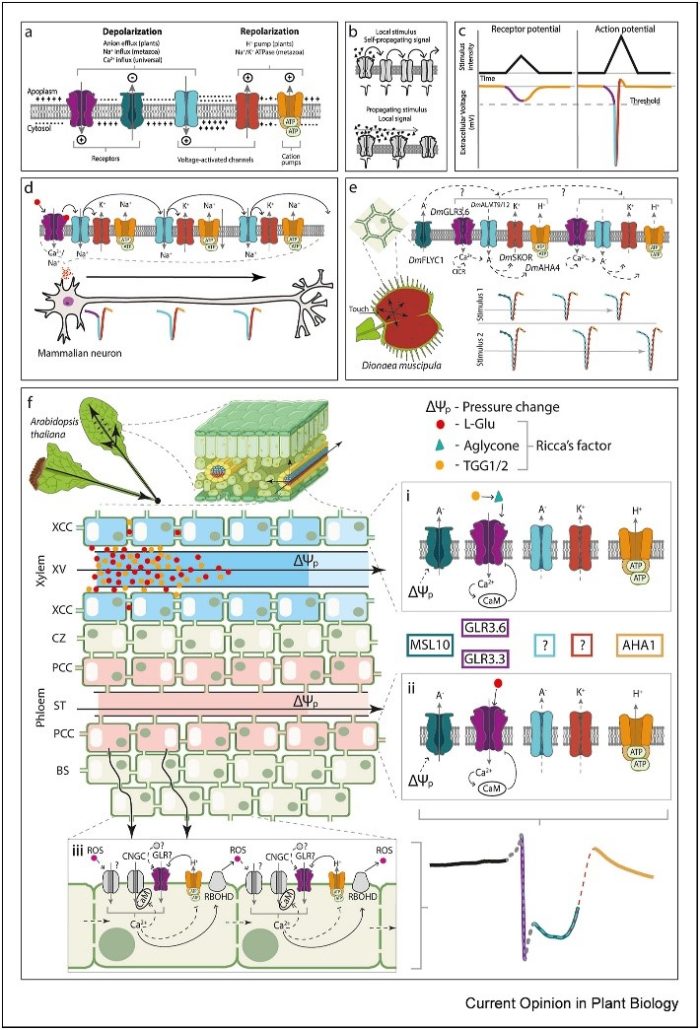
Review. Revisiting plant electric signaling: Challenging an old phenomenon with new discoveries
Plant Science Research WeeklyIn the electrifying world of plant signaling, a paradigm shift is underway as researchers dig into the intricate mechanisms of action potentials (APs) and slow wave potentials (SWPs). Departing from conventional neurophysiological dogma in the animal kingdom, this review by Barbosa-Caro and Wudick illuminates…
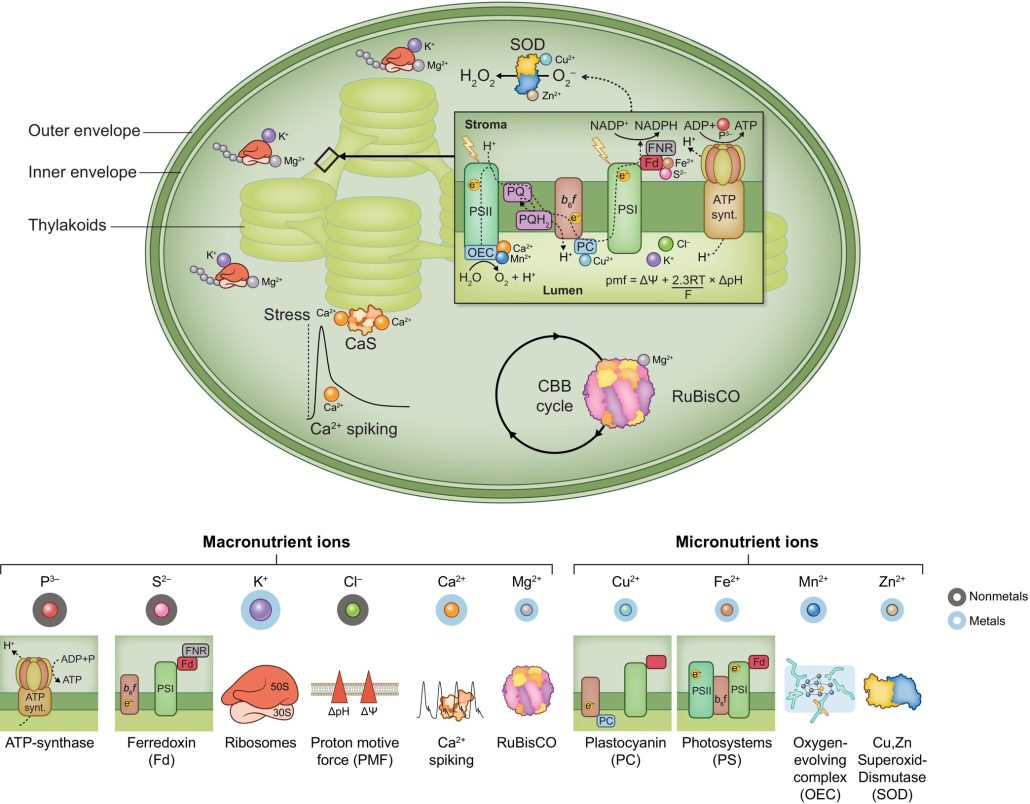
Review: Chloroplast ion homeostasis
Plant Science Research WeeklyHealthy plants require access to several mineral nutrients, which are usually taken up in ionic form. The details of nutrient uptake, distribution, and function have been painstakingly revealed over several decades. In this excellent new Tansley Review, Kunz et al. provide an overview of ion homeostasis…
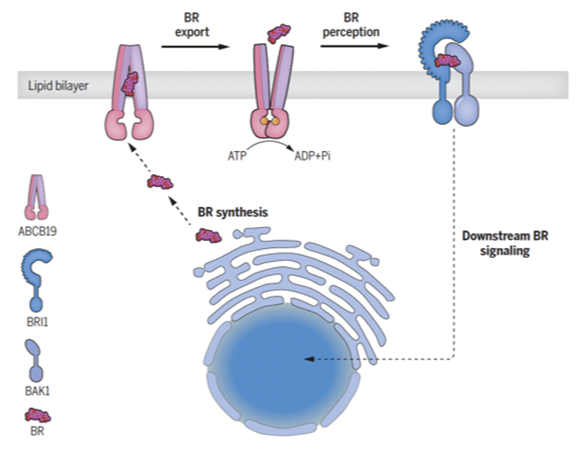
How do plants export brassinosteroids?
Plant Science Research WeeklyIf you’ve ever wondered how plants grow, survive, and adapt to their dynamic environment, the secret lies in their vast array of chemical messengers, also called phytohormones. Brassinosteroids are important hormones that are crucial for plant development and defense against environmental stresses.…
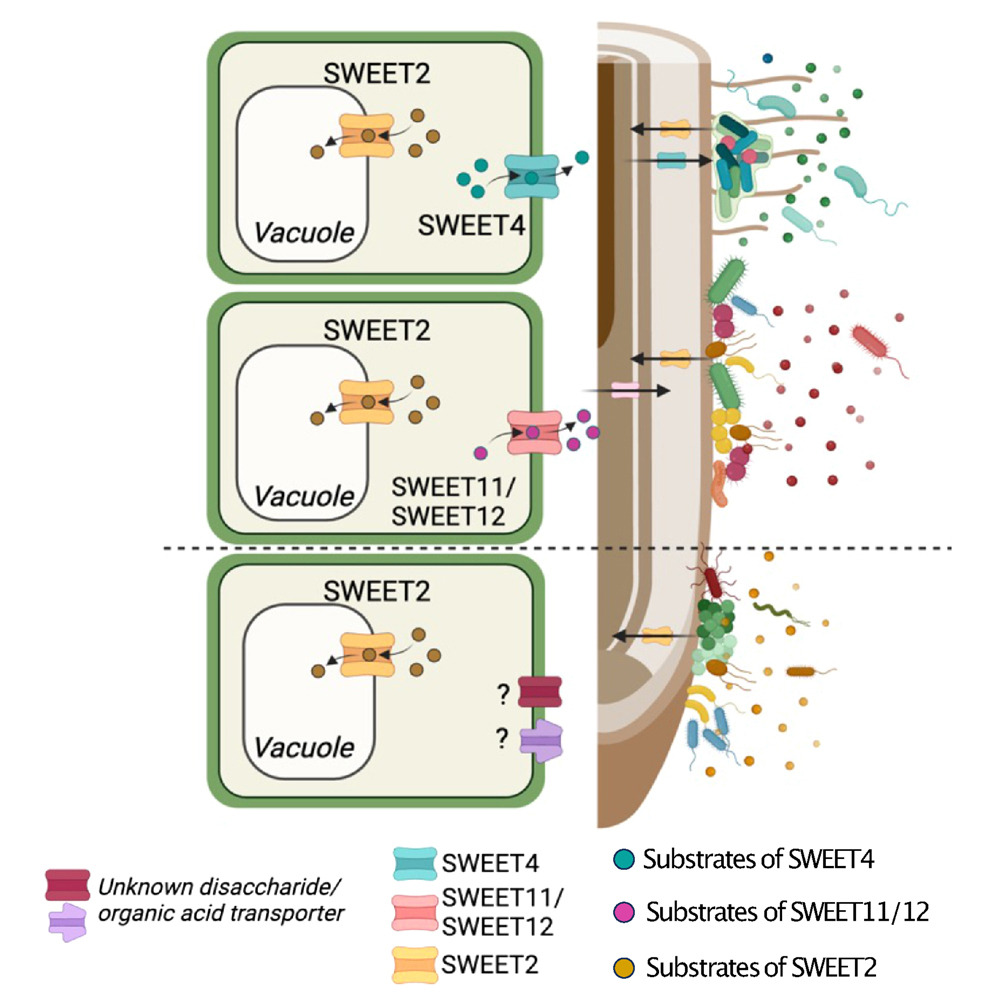
SWEET sugar transporters orchestrate distribution of microbiota along the root longitudinal axis
Plant Science Research WeeklyPlant roots are functionally distinct along the longitudinal axis due to different cell types and diverse metabolic states. Root-secreted metabolites are involved in the assembly of complex microbial communities, yet the relationships between root-metabolites and organization of root microbiota at the…
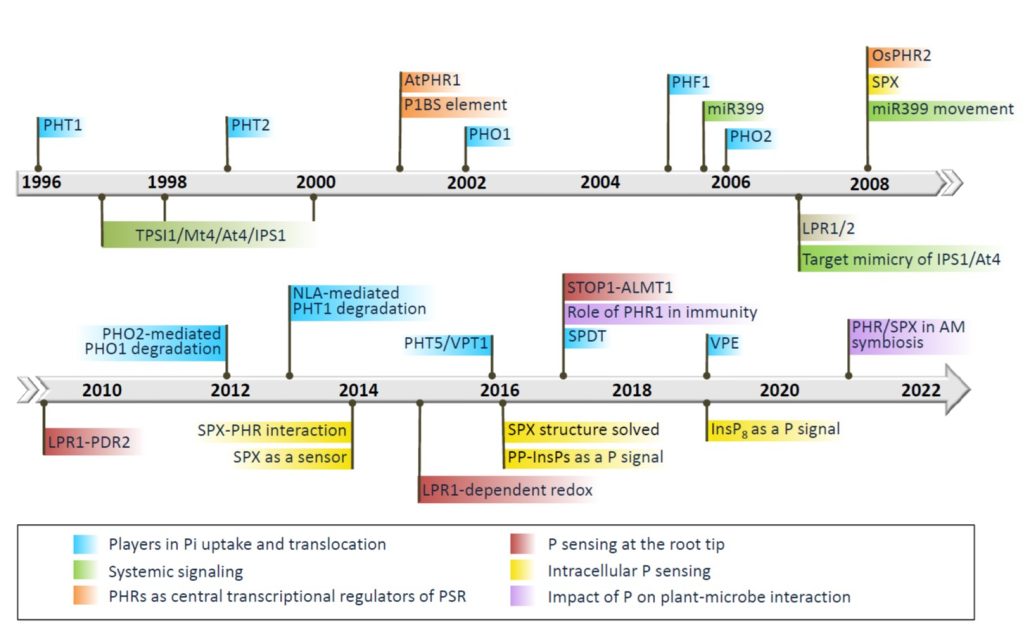
Review. Milestones in understanding phosphorus uptake, transport, sensing, use, and signaling
Plant Science Research WeeklyPhosphorus (P) is an essential nutrient and critical component of nucleic acids, phospholipids, and other molecules. Yang et al. provide a historical (since 1996) overview of the processes controlling its uptake and use. Plants take up P from the rhizosphere primarily in the form of orthophosphate (Pi).…
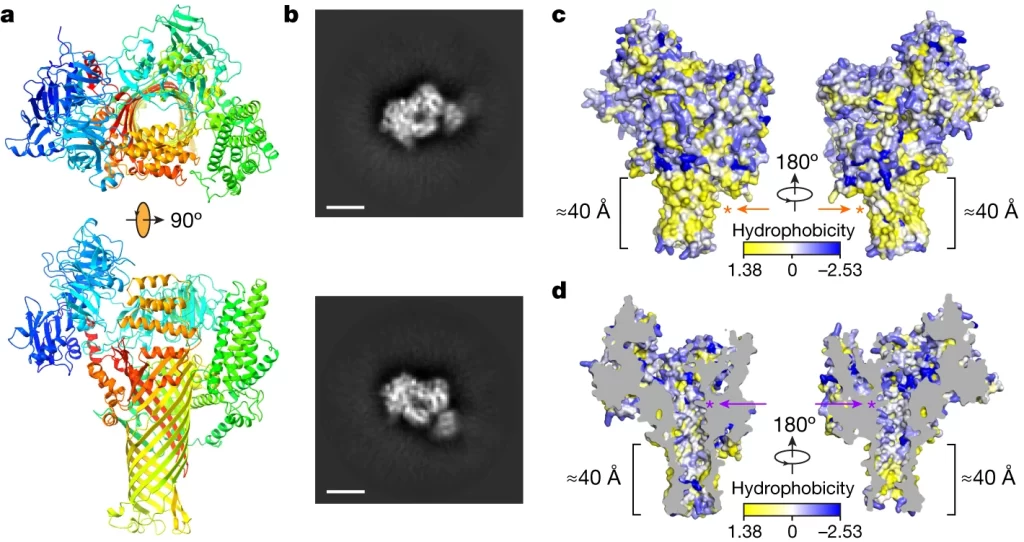
Bacterial pathogens deliver water- and solute-permeable channels to plant cells
Plant Science Research WeeklyWhat do you do when you’ve identified a gene that you know is important, but you don’t know how it functions? Usually, you can get hints from homology searches, overexpression studies, or the identification of protein domains, but sometimes those approaches don’t work. That’s where the story…
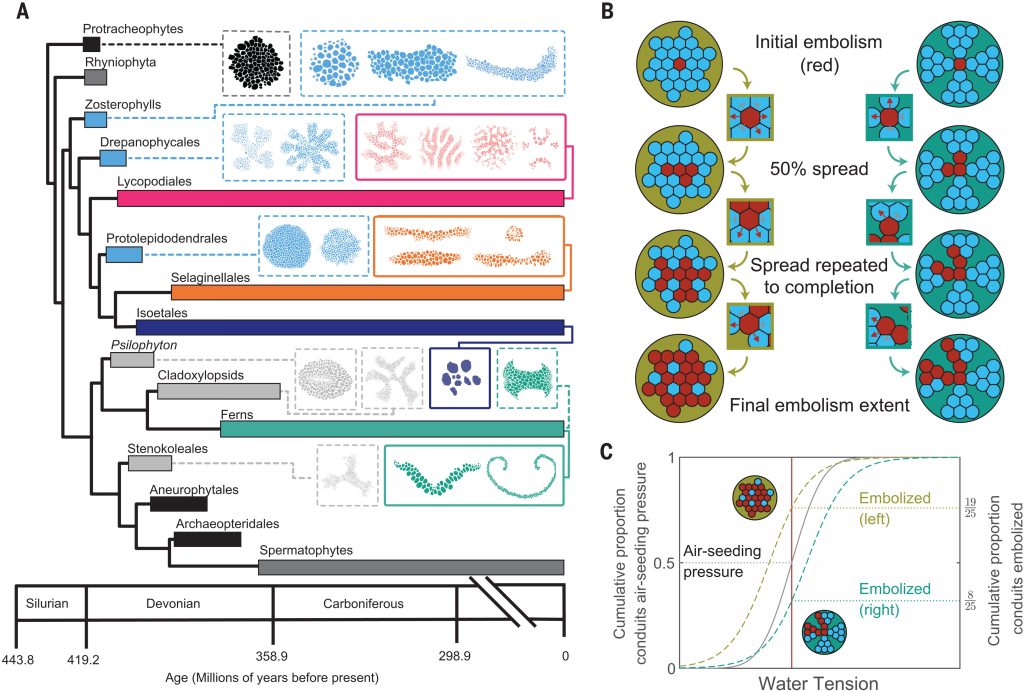
Hydraulic failure as a primary driver of xylem network evolution in early vascular plants (Science)
Plant Science Research WeeklyThe earliest terrestrial plants had relatively small, simple forms. The evolution of water-conducting cells provided opportunities for increased size. However, water movement by tension (driven by evaporation) can fail when the water column breaks and is blocked by an air bubble called an embolism. Looking…
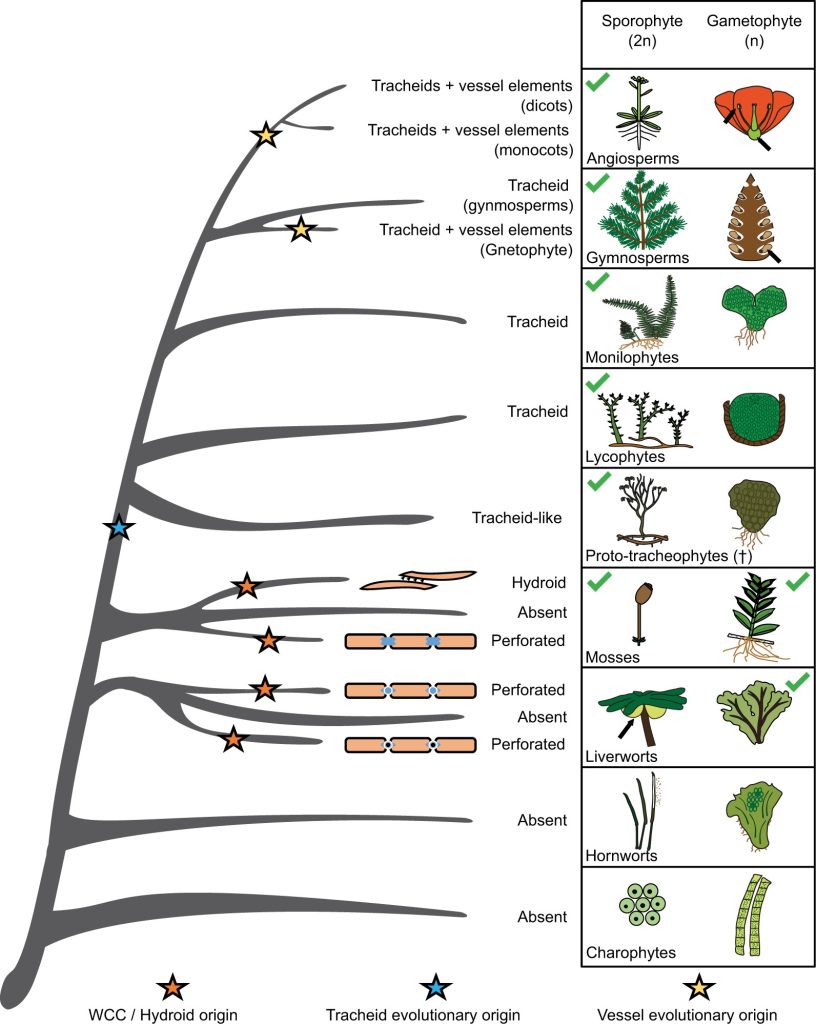
Review: Deep origin and gradual evolution of transporting tissues: Perspectives from across the land plants (Plant Physiol)
Plant Science Research WeeklyThe development of vascular plants (tracheophytes) was a major innovation during the evolution of land plants. The classic view is that the evolution of transporting tissues is distinct to tracheophytes, but Woudenberg and Renema et al. discuss an alternative hypothesis where this was a gradual process…

