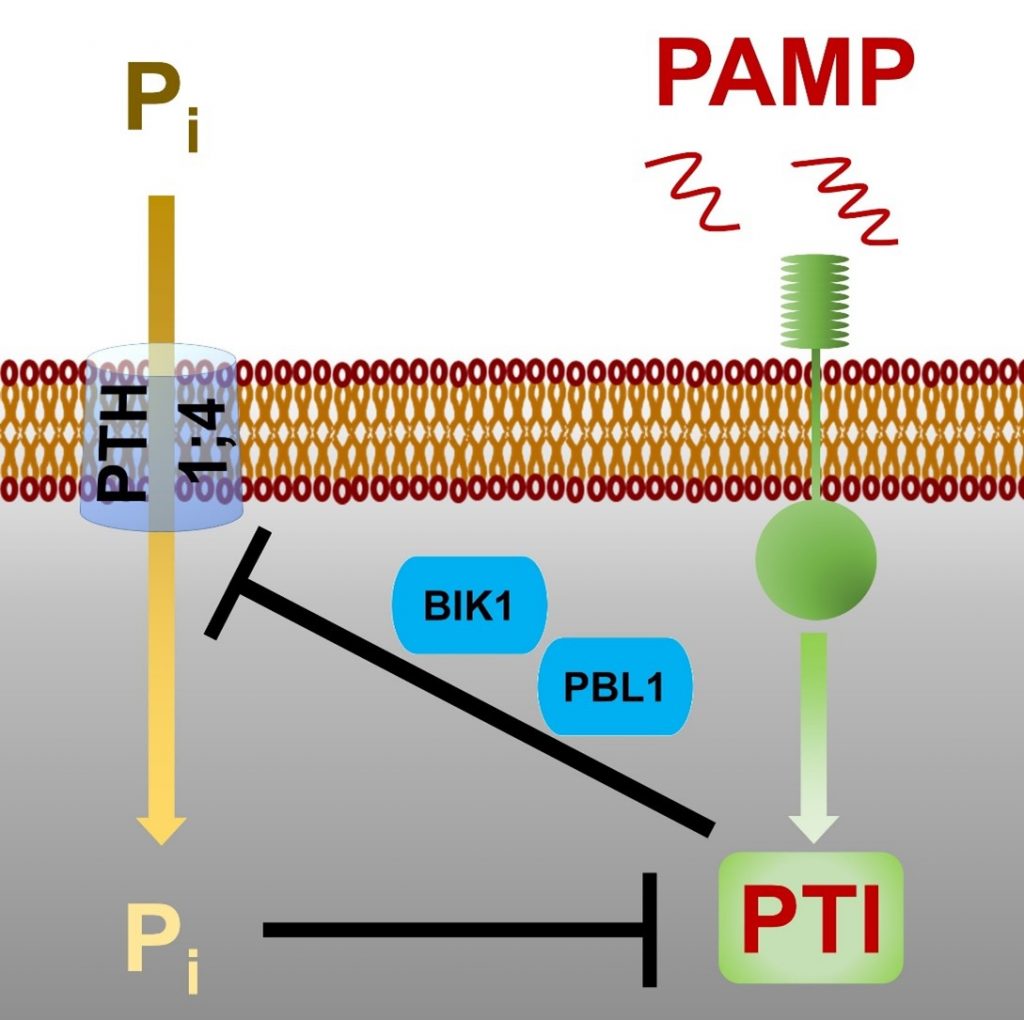
Crosstalk between phosphate transport and plant immunity (Curr. Biol.)
Plant Science Research WeeklyPlants have evolved signaling cascades to survive biotic and abiotic stresses, and recent studies have shown that there is crosstalk between many of these pathways. In a recent study, Dindas et al. developed a micro-electrode-based system to detect active inorganic phosphate (Pi) transport in Arabidopsis…
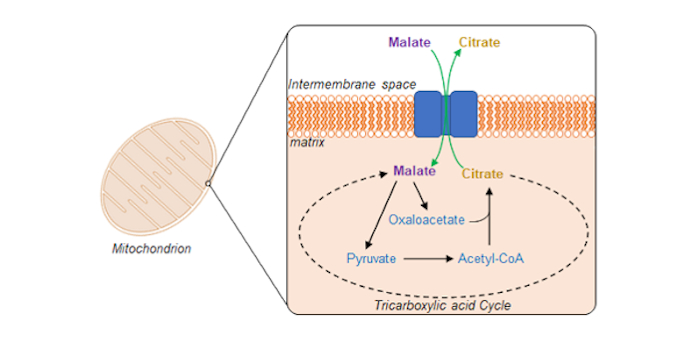
Swapping citrate for malate by plant mitochondria
The Plant Cell: In a NutshellLee et al. unravel a mitochondrial transporter responsible for selectively exporting citrate in exchange for malate. Plant Cell (2021)
By Chun Pong Leea, Marlene Elsässerb, Philippe Fuchsb,c, Ricarda Fenskea, Markus Schwarzländerb, A. Harvey Millara
aARC Centre of Excellence in Plant Energy Biology,…
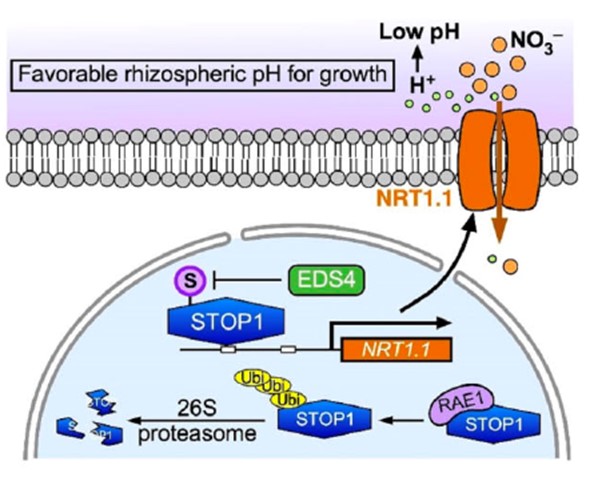
STOP1-NRT1.1: a new module to optimize nitrogen and growth in acidic media for plants (Plant Cell)
Plant Science Research WeeklyAcidic soils often negatively impact plant growth, yet the application of fertilizers containing urea or ammonia have the effect of acidifying soils. In a recent paper, Ye and colleagues investigated how nitrate uptake through the nitrate transporter NITRATE TRANSPORTER 1.1 (NRT1.1) can mitigate some…
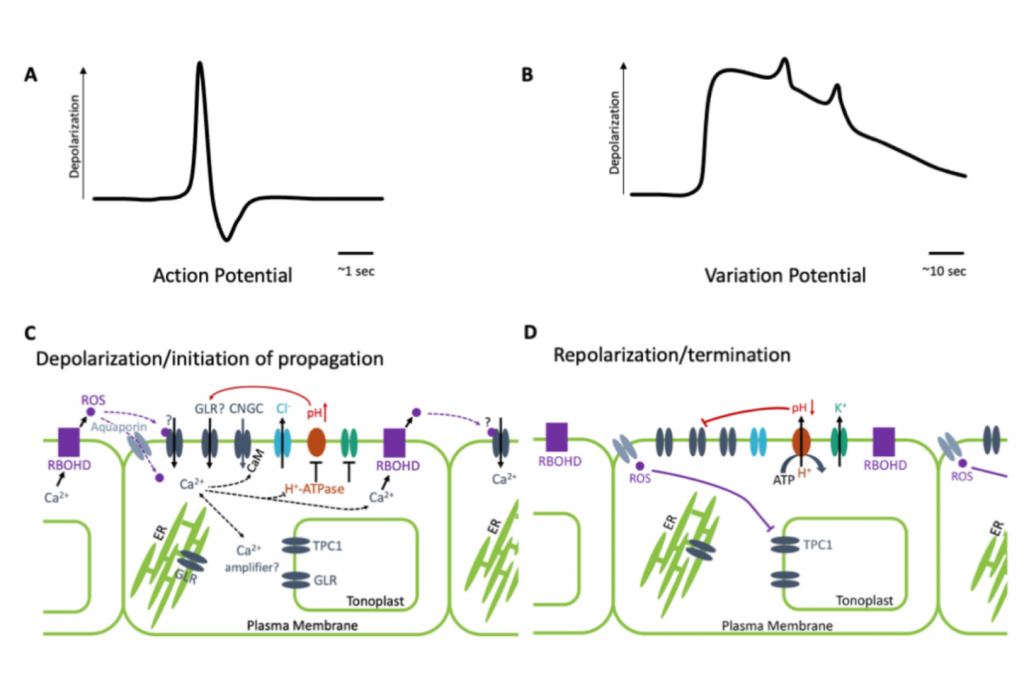
Review. The Fast and The Furious: Rapid long-range signaling in plants (Plant Physiol)
Plant Science Research WeeklyPlants possess a complex series of local and systemic signaling networks driven by multiple stimuli. They translate this information into plant-wide response to coordinate their physiology and development. Here, Johns et al. review these communication pathways, which function across different scales…
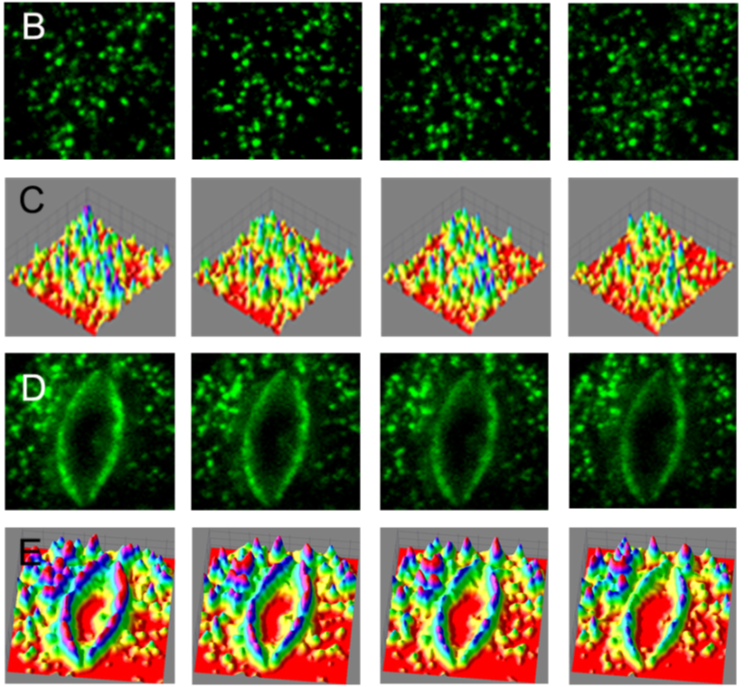
In vivo single-particle tracking of the aquaporin AtPIP2;1 in stomata reveals cell type-specific dynamics (Plant Physiol)
Plant Science Research WeeklyBacteria can exploit the stomatal pores to gain entry into plant leaves. Previous studies have demonstrated that guard cells close in response to flagellin, an effect that is described as stomatal immunity. Like ABA-induced stomatal closure, this involves the movements of ions and water from the guard…
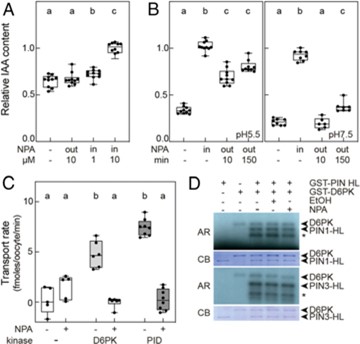
NPA directly binds to and inhibits PIN transporters (PNAS)
Plant Science Research WeeklyN-1-naphthylphthalamic acid (NPA) inhibits polar auxin transport (PAT). Though used for over six decades, the precise mechanism by which it inhibits PAT is still unclear. A new study by Abas and colleagues now suggests that NPA directly associates with and inhibits the activity of PIN-FORMED (PIN) transporters.…
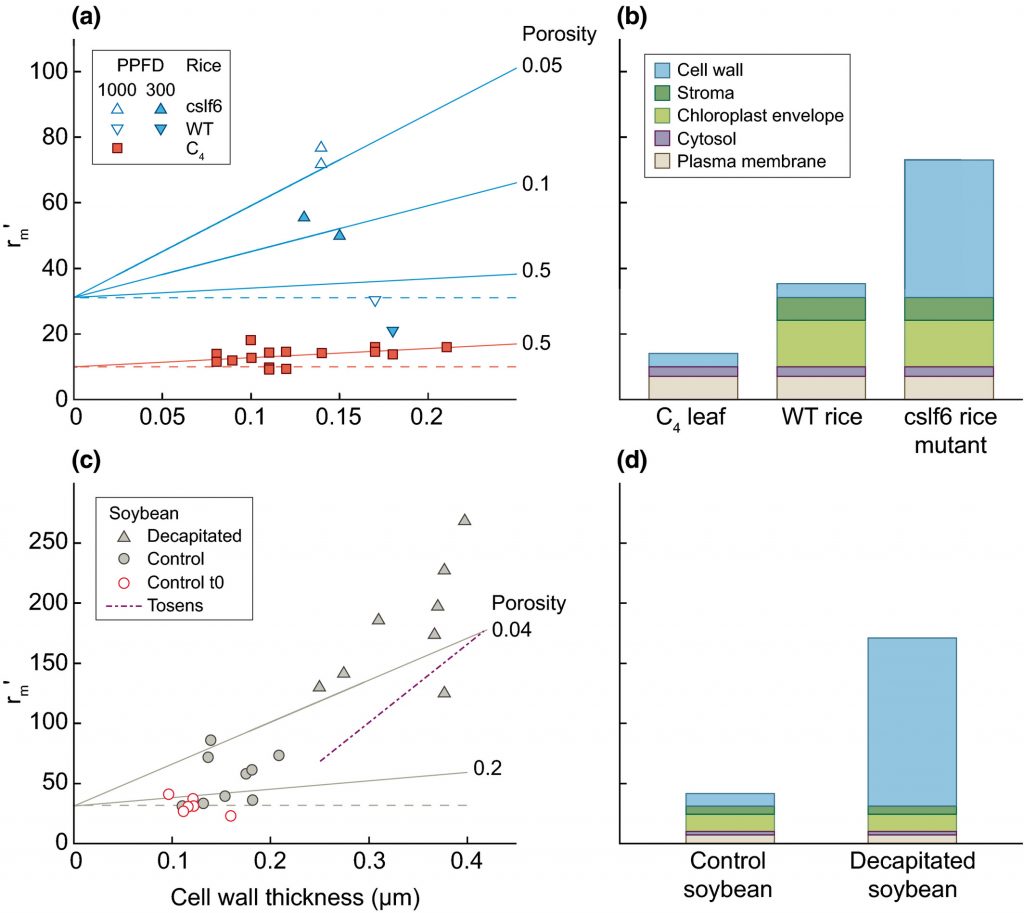
Review: Mesophyll conductance: walls, membranes and spatial complexity (New Phytol.)
Plant Science Research WeeklyThere’s been a lot of talk lately about how to improve the carboxylation efficiency of Rubisco, but of course this also depends on how much CO2 reaches the enzyme within the chloroplasts. To do so, it needs to pass through several distinct barriers: the boundary layer to reach the leaf surface, the…

Identification of a unique ZIP transporter involved in zinc uptake via the arbuscular mycorrhizal fungal pathway (bioRxiv)
Plant Science Research WeeklyLast week, PSRW presented two review papers regarding host plant interactions with microbial populations, particularly for plant nutrient intake. Watt-Williams et al. utilize such knowledge for their paper, performing an RNA-seq dataset to identify a novel zinc transporter in Medicago truncatula. Zinc…
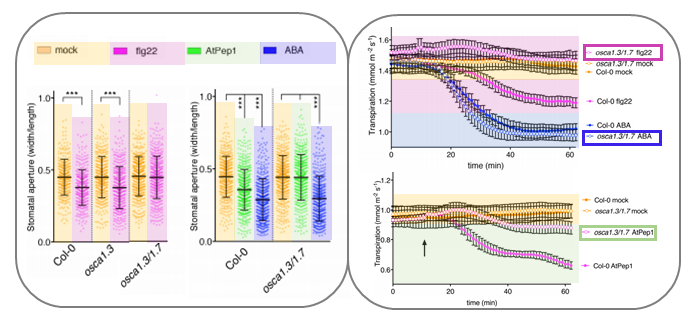
The calcium-permeable channel OSCA1.3 regulates plant stomatal immunity (Nature)
Plant Science Research Weekly
In plants, the perception of environmental threats induces a peak of calcium ions (Ca2+) in the cytosol that triggers signal transduction pathways leading to stomatal closure as defense response. In Arabidopsis, the mechanosensitive Ca2+ channel OSCA1 regulates water transpiration in response to…

