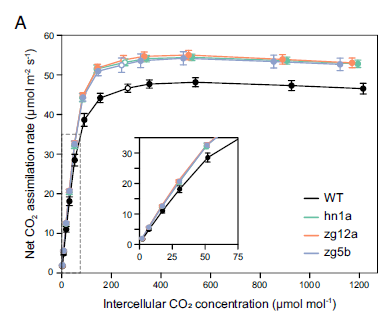
Boosting C4 photosynthesis and productivity by elevating Rubisco levels in sorghum and sugarcane
Plant Science Research WeeklyThe United Nations projects that by 2050, global food production must increase by 60% to meet growing demand, a goal that must be met under the pressures of global climate change and without further agricultural land expansion. With rising atmospheric CO₂ levels, Rubisco has emerged as the primary…
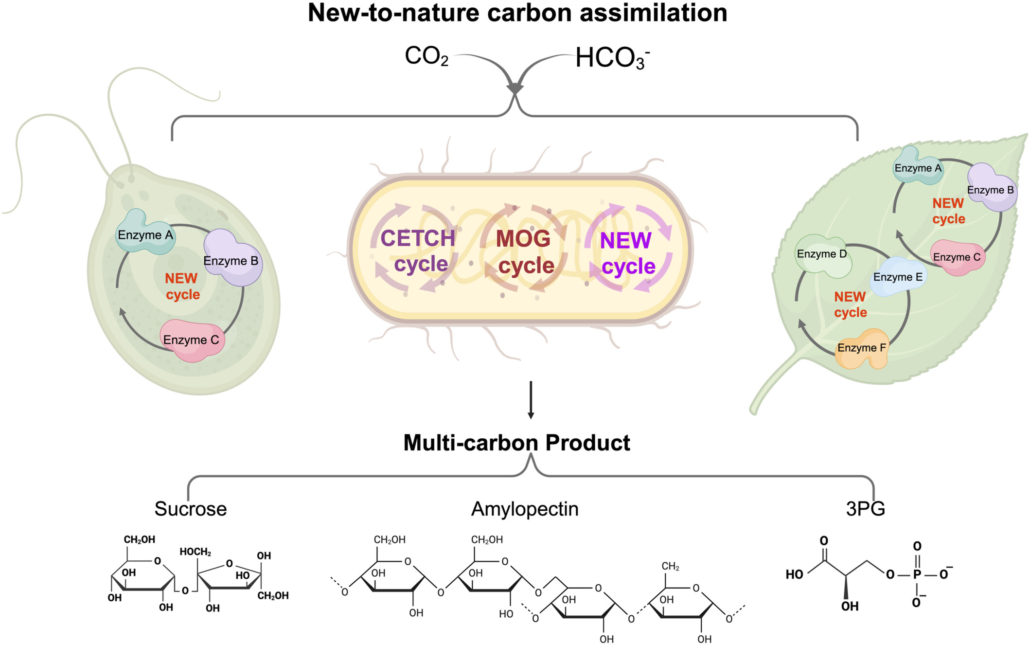
Review: Genetic engineering for carbon assimilation in plants
Plant Science Research WeeklyRubisco (Ribulose‐1,5‐bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase) is the central enzyme for photosynthesis, This enzyme poorly discriminates between CO2 and O2, which limits its efficiency. To work around this and make carbon assimilation more efficient, scientists have been employing different engineering…
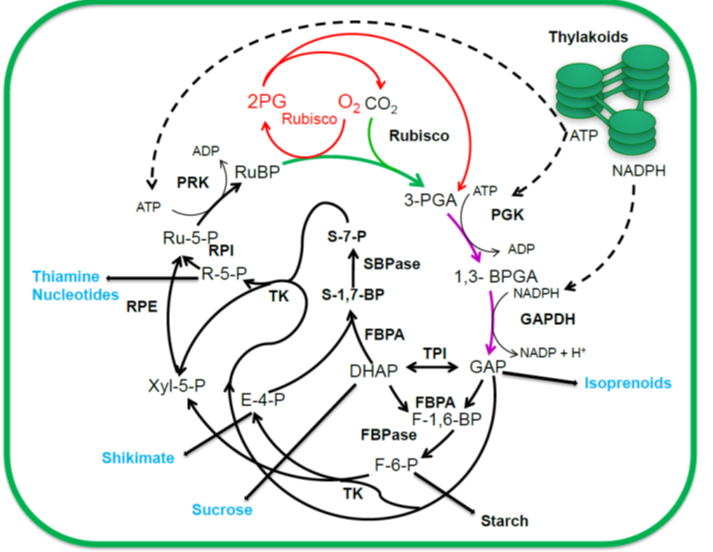
Review: Strategies to improve photosynthesis
Plant Science Research WeeklyPhotosynthesis is the process by which plants assimilate carbon by using light energy. However, with the solar energy conversion efficiency of many crop plants less than 1%, it is inefficient. Therefore, there is interest in manipulating photosynthesis for increased efficiency. Here, Croce et al. identifying…
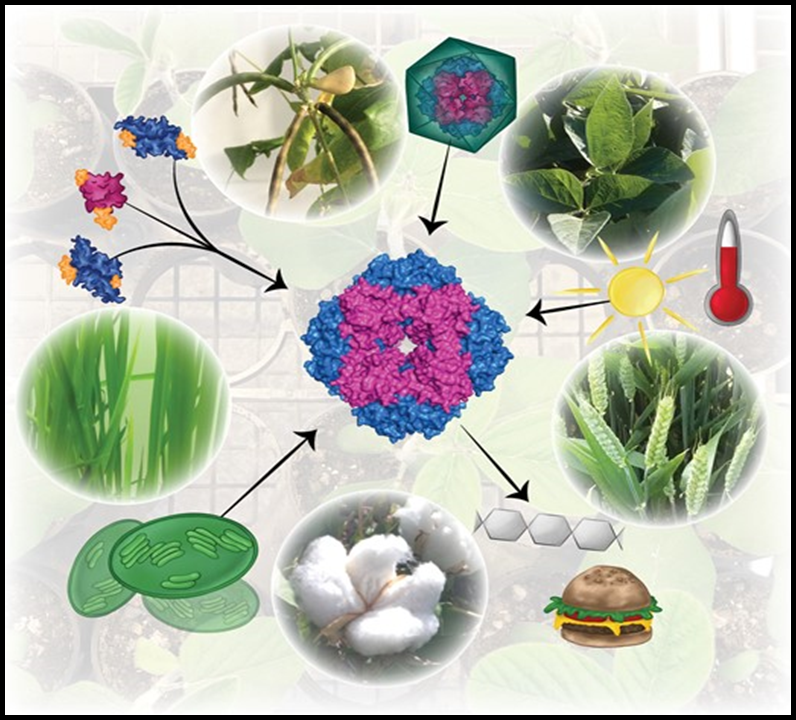
Special issue: Rubisco and its regulation
Plant Science Research WeeklyRubisco (ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase) catalyzes the fixation of atmospheric carbon from CO2 to molecules used for biosynthesis and energy production. Several studies have focused on understanding the nature, complexity, activity, and regulation of Rubisco due to its key role in the production…
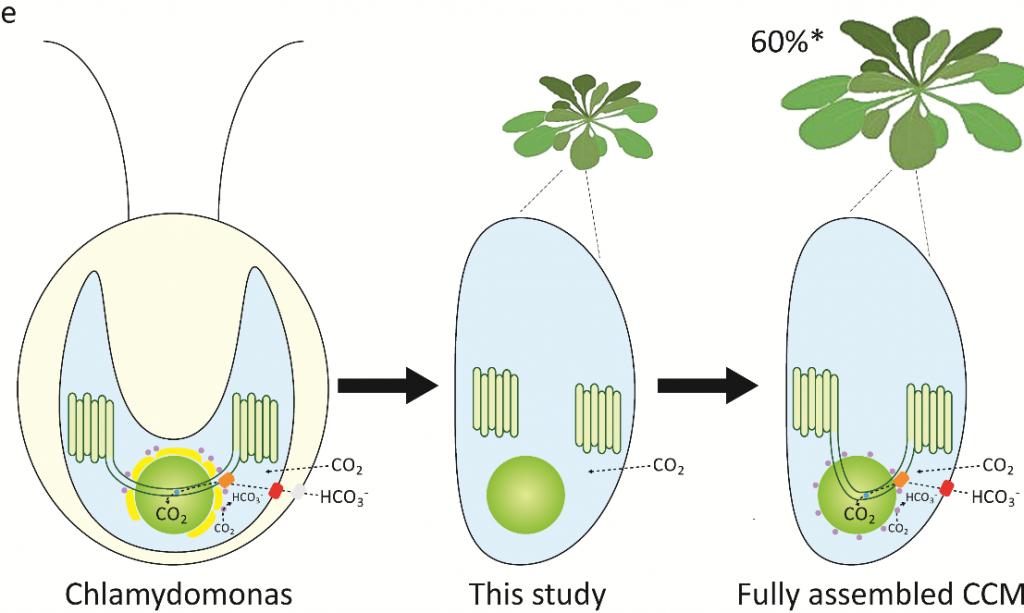
Condensation of Rubisco into a proto-pyrenoid in higher plant chloroplasts (bioRxiv)
Plant Science Research Weekly
Rubisco is a major enzyme in assimilating CO2 during photosynthesis. The efficiency of CO2 assimilation is compromised by a low ratio of CO2/O2, especially in C3 plants like rice, wheat and soybean. Algae sequester Rubisco as a condensate in a microcompartment called a pyrenoid within the chloroplast…
The dependency of red Rubisco on its cognate activase for enhancing plant photosynthesis and growth (Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA)
Plant Science Research WeeklyThe rate of carboxylation by Rubisco versus the rate of the competing oxygenation reaction limits photosynthesis in some conditions, so many researchers are investigating ways to enhance Rubisco. Rubisco is not limited to green plants but can be found in other lineages including red algae and photosynthetic…
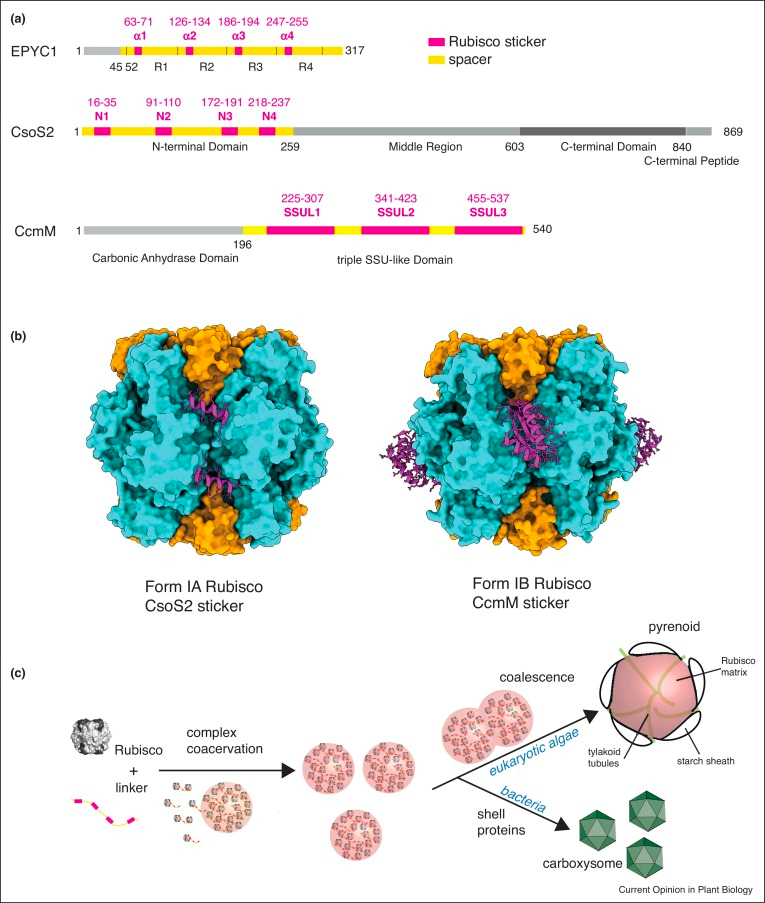
Review: Biomolecular condensates in photosynthesis and metabolism ($) (Curr. Opin. Plant Biol.)
Plant Science Research WeeklyBiomolecular condensates are membraneless organelles with the capacity to spatially concentrate biomolecules. Liquid-liquid phase separation (LLPS) is one mechanism of condensate formation in which demixing of macromolecules leads to separation into dense and light phases. Photosynthetic organisms like…

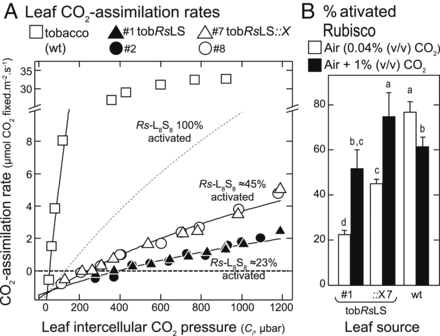
Small subunits can determine enzyme kinetics of tobacco Rubisco expressed in Escherichia coli (Nature Plants)
Plant Science Research Weekly
Rubisco is the enzyme responsible for the fixation of CO2 to ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate (RuBP) during photosynthetic reactions. However, this enzyme has some functional issues, such as a slow catalytic turnover rate and sensitivity to temperature and CO2, and it catalyzes a competing oxygenation process…

Back to where it came from: chloroplast expression of both Rubisco subunits helps functional enzyme analysis
Blog, Research, The Plant Cell, The Plant Cell: In BriefRubisco catalyzes the key carboxylation step in photosynthetic CO2 fixation and is probably the most abundant protein on Earth. The enzyme is famous for inefficient catalysis and the habit of binding oxygen instead of CO2 in one out of every four binding events, leading to photorespiration reactions…

