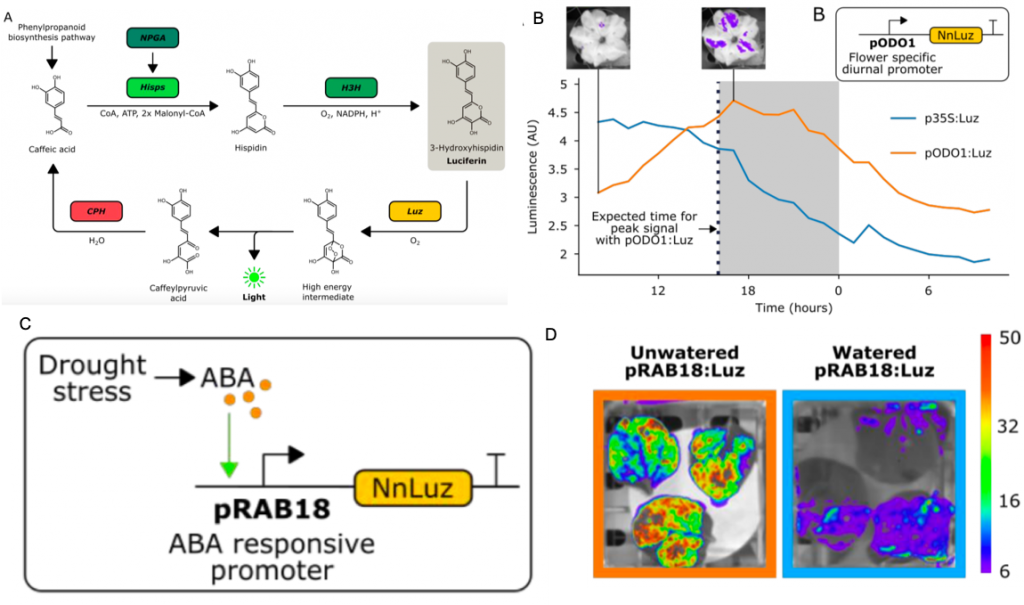
Versatile auto-luminescent luciferase-based reporters for spatiotemporal gene expression studies (eLIFE)
Plant Science Research WeeklyFirefly luciferase constructs are extensively used for gene expression studies but require a reaction with an exogenous substrate, so expression to some extent reflects tissue penetrance. Khakhar et al. designed customizable auto-luminescence constructs based on a fungal bioluminescence pathway (FBP)…
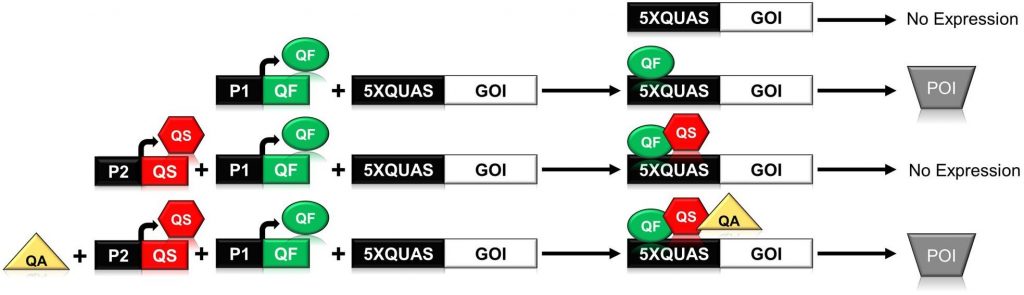
The Q-System as a synthetic transcriptional regulator in plants (Front. Plant Biol.)
Plant Science Research WeeklyThe ability to reliably induce a transgene has greatly enhanced the study of plant biology. Various chemical inducible system have worked robustly in plants, but plant synthetic biology is still lacking an efficient orthogonal (from outside) inducible system where multiple genes can be controlled at…
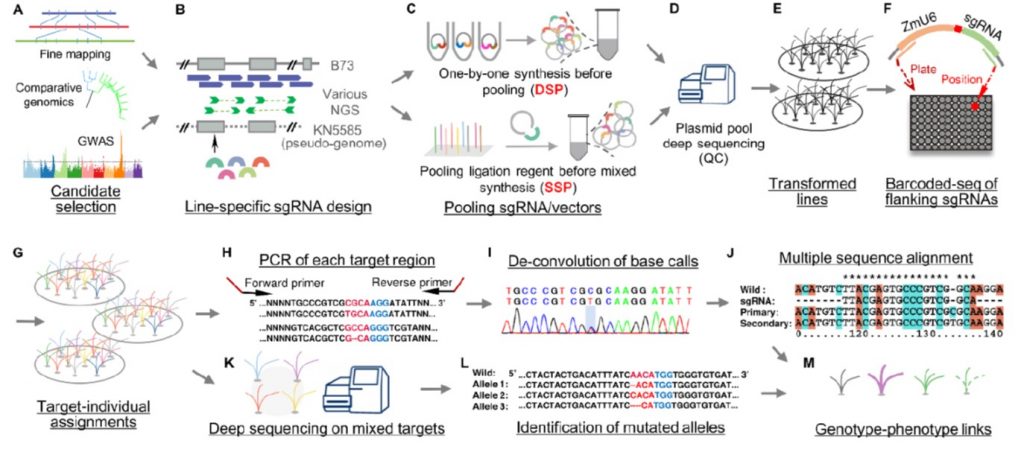
High-throughput CRISPR/Cas9 mutagenesis streamlines trait gene identification in maize (Plant Cell)
Plant Science Research WeeklyMaize has provided some fascinating mutants and developmental insights, but its genomic complexity has made it more difficult (for example as compared to rice) to identify agronomically important genes. Liu et al. describe a new high-throughput method to integrate forward- and reverse-genetics to identify…

Base-editing-mediated artificial evolution of OsALS1 in planta to develop novel herbicide-tolerant rice germplasms (Mol. Plant)
Plant Science Research WeeklyThe trait of herbicide tolerance allows farmers to use chemical means to eliminate weed competitors. Acetolactate synthase (ALS) is an enzyme targeted by more than 50 different herbicides. In order to generate novel herbicide tolerance traits, Kuang et al. used a base-editing artificial evolution approach,…
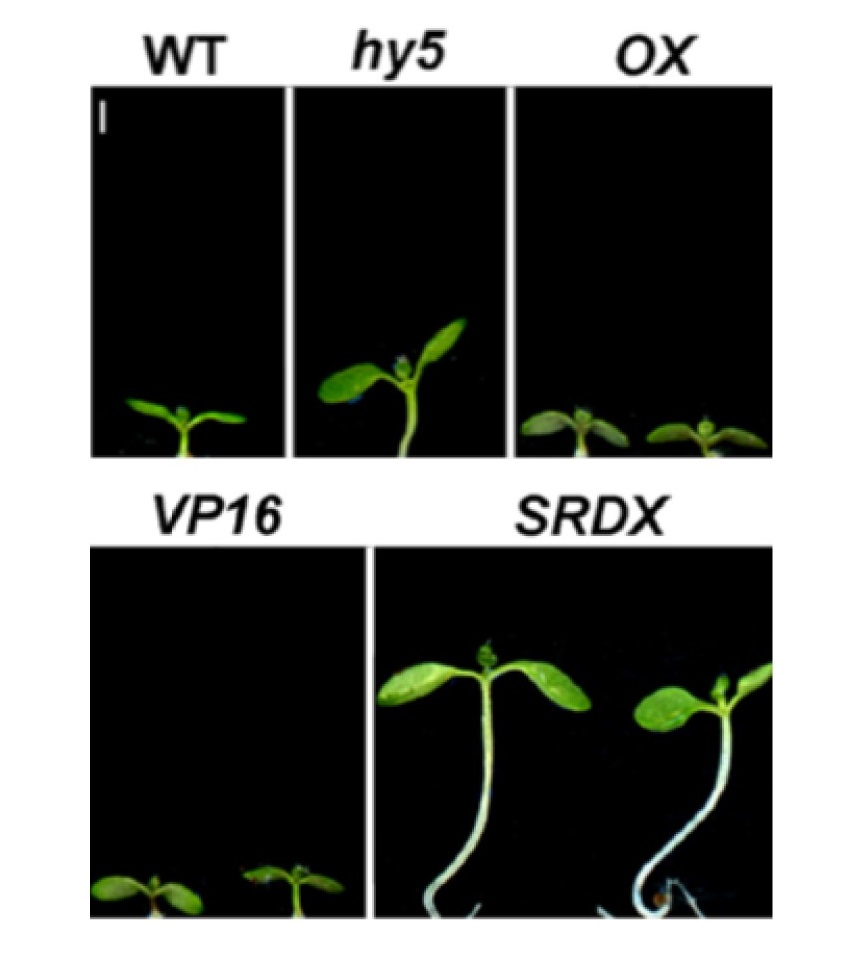
Chimeric activators and repressors define HY5 activity and reveal a light-regulated feedback mechanism (Plant Cell)
Plant Science Research WeeklyPlants take cues from the environment and decide when and how to regulate growth. When light is limiting, etiolated growth allows plants to reach the soil surface and gain access to light. After light perception, plants de-etiolate and go through a series of morphological and genetic changes. HY5 is…
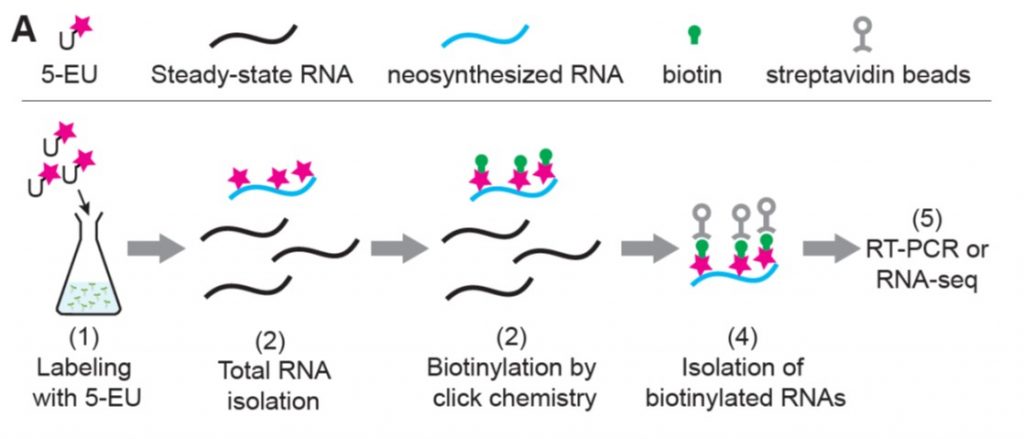
Metabolic labeling of RNAs uncovers hidden features and dynamics of the Arabidopsis transcriptome (Plant Cell)
Blog, Plant Science Research WeeklyThe ability to directly sequence RNAs (RNA-seq) has revolutionized our understanding of gene expression, but it can miss or underestimate short-lived RNAs. Several methods have been developed to identify newly-synthesized mRNAs to provide a snapshot of transcription as it happens. Szabo present Neu-seq,…
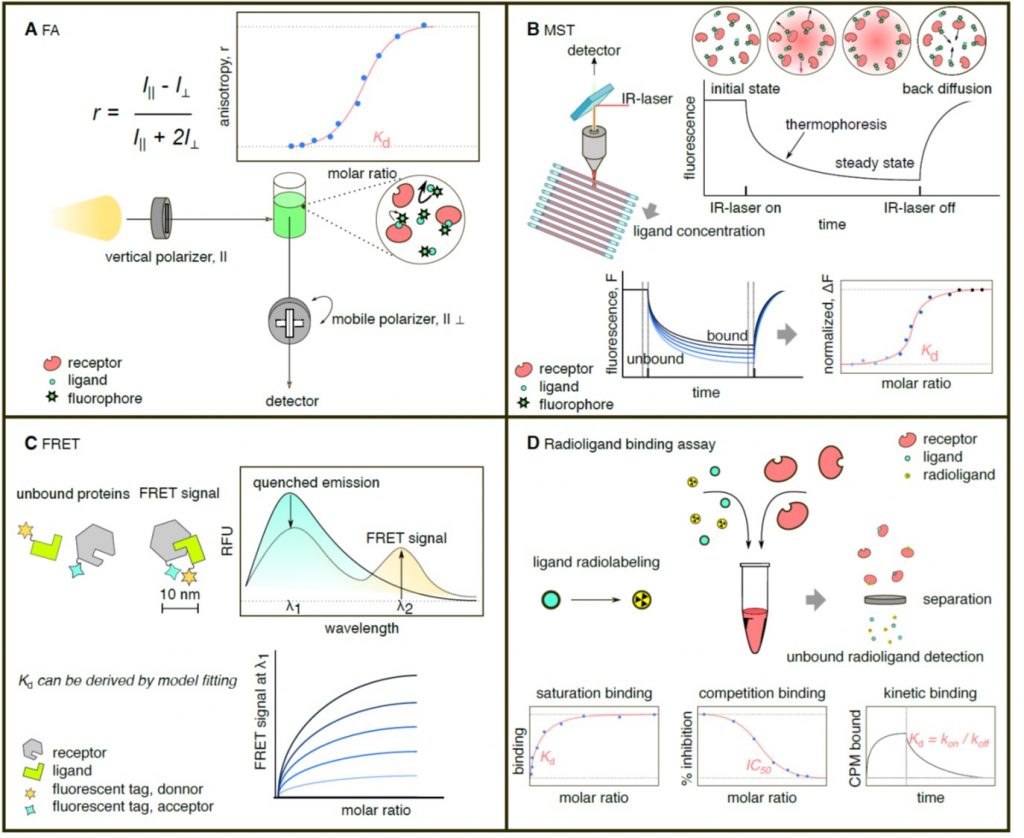
Review: In vitro analytical approaches to study plant ligand-receptor interactions (Plant Physiol)
Plant Science Research WeeklyIt seems every other paper shows a nice diagram of a signaling cascade that includes a receptor interacting with its ligand. However, sometimes these diagrams are little more than speculation or guesswork. It’s not always easy to figure out if this interaction is real. Here, Sandoval and Santiago review…
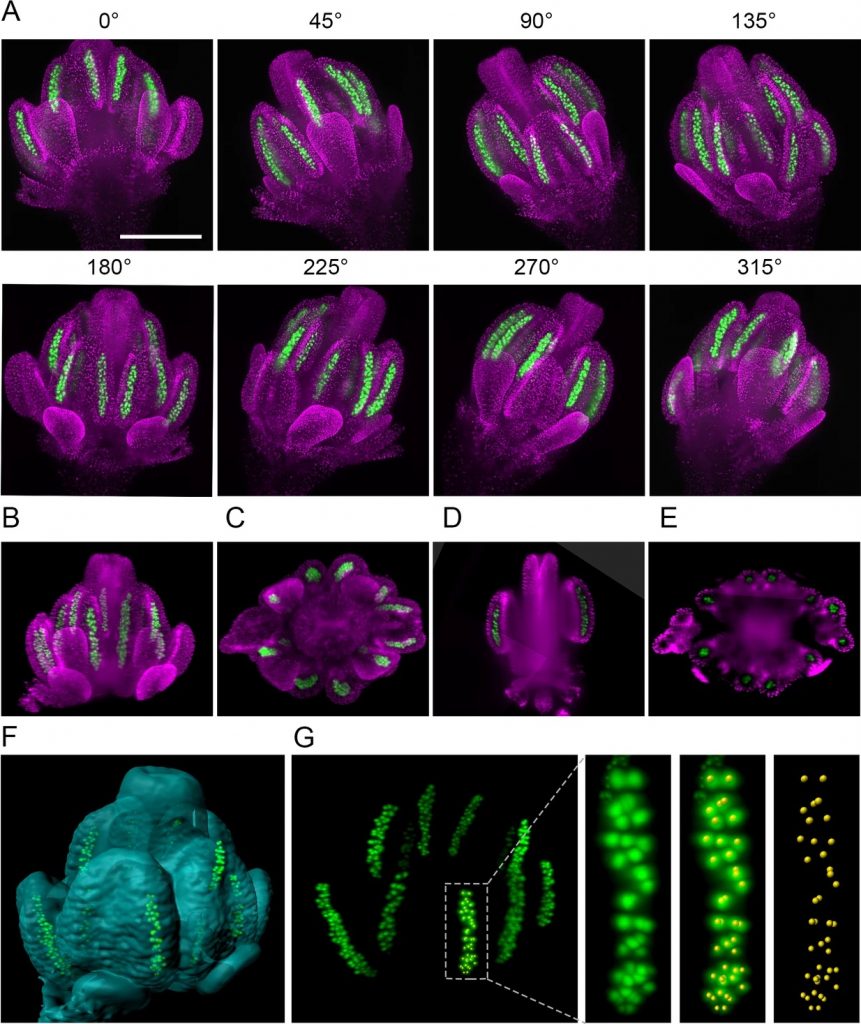
Imaging plant germline differentiation within Arabidopsis flowers by light sheet microscopy (eLIFE)
Plant Science Research WeeklyAdvances in microscopy have greatly informed our understanding of fundamental plant processes, but the germline cells in flowers have been hard to image as they are tiny and embedded within other tissues. Valuchova et al. present a method using light sheet fluorescence microscopy that allows live cell…

Review: Methods to visualize elements in plants (Plant Physiol)
Plant Science Research Weekly
Plant Science Research Weekly: February 14
February 14, 2020/in Blog, WWR Full Post /by Mary Williams
Review: Deep learning for plant genomics and crop improvement
One of the goals of plant science is to use the molecular phenotype (genome, transcriptome, proteome) to predict the…

