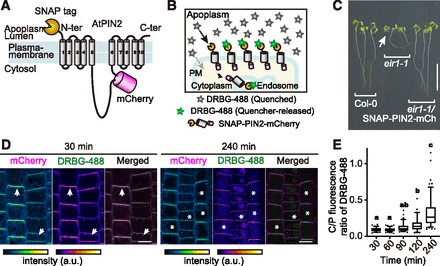
SNAP ‘n’ Track: Protein localization using fluorescent dyes (Plant Cell)
Plant Science Research WeeklyProteins’ sub-cellular localizations provide a wealth of information regarding their functional attributes. Protein localization in plant cells is usually done through genetically combining fluorescent proteins to the protein-of-interest. Now, Iwatate and colleagues report the successful localization…
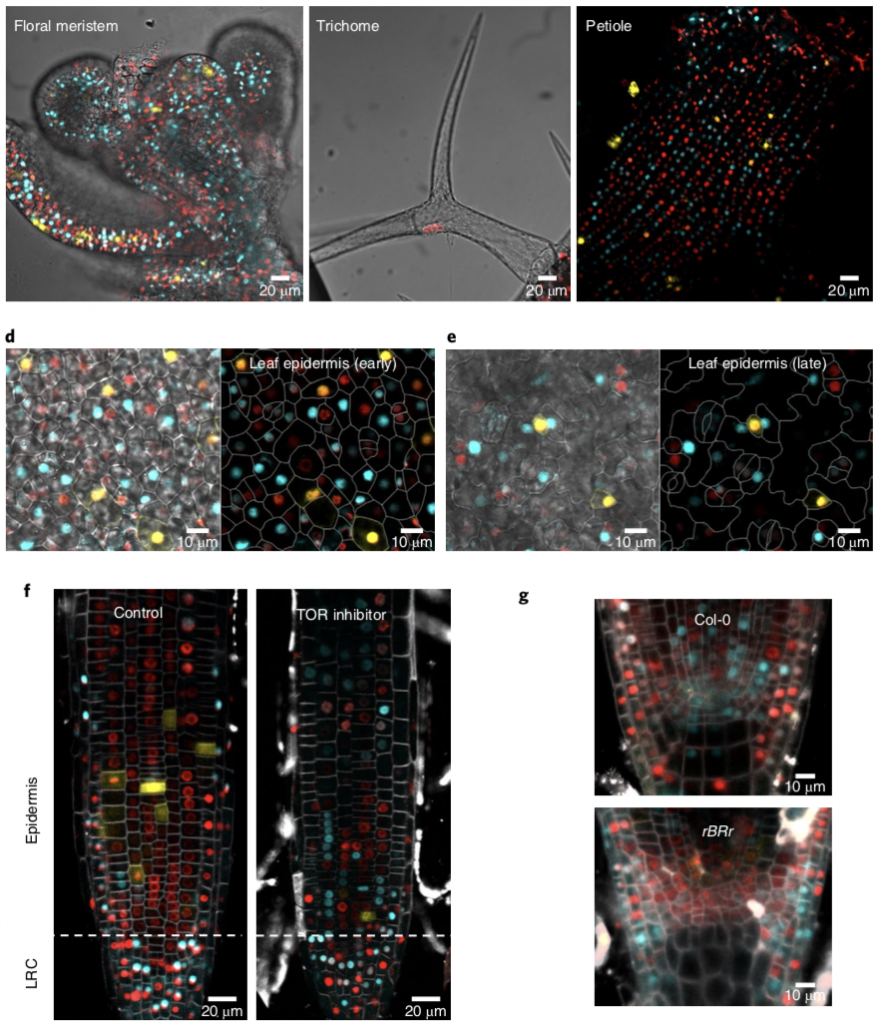
PlaCCI (Plant cell cycle indicator); fluorescent sensor for spatiotemporal cell cycle analysis (Nature Plants)
Plant Science Research WeeklyThe cell cycle requires a series of transitions from G1 to S, S to G2, G2 to M and M to G1 phases. Determining the cell cycle phase is critical for understanding the molecular events specific to a given stage of cell cycle. However, markers for identifying these cell cycle transitions in plants are not…
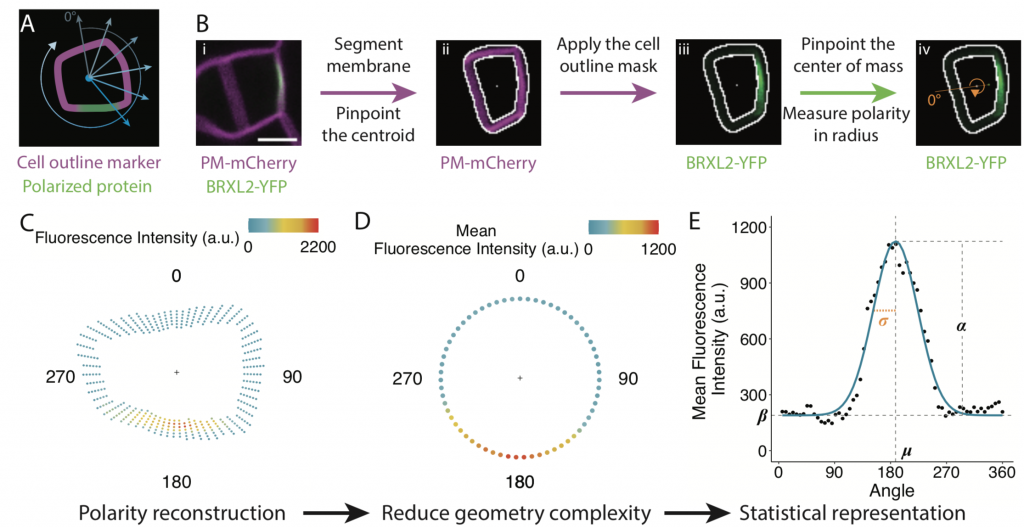
POME: Quantitative and dynamic cell polarity tracking pipeline (bioRxiv)
Plant Science Research WeeklyMany proteins polarize in the cell creating a subcellular niche for various functions. Asymmetric distribution of proteins is a general mechanism for localized growth, directional long-range signaling, cell migration, and asymmetric cell divisions. Well-known examples of polarity proteins include PIN-FORMED1…

Mini foxtail millet as a new C4 model species (Nat. Plants) ($)
Plant Science Research Weekly
The three most widely adopted plant models all use C3 photosynthesis, but discoveries made in these plants are not always applicable to C4 plants. Foxtail millet (Setaria italica) has been emerging as a potential C4 model species, but its use for genomics research is challenging due to long generation…
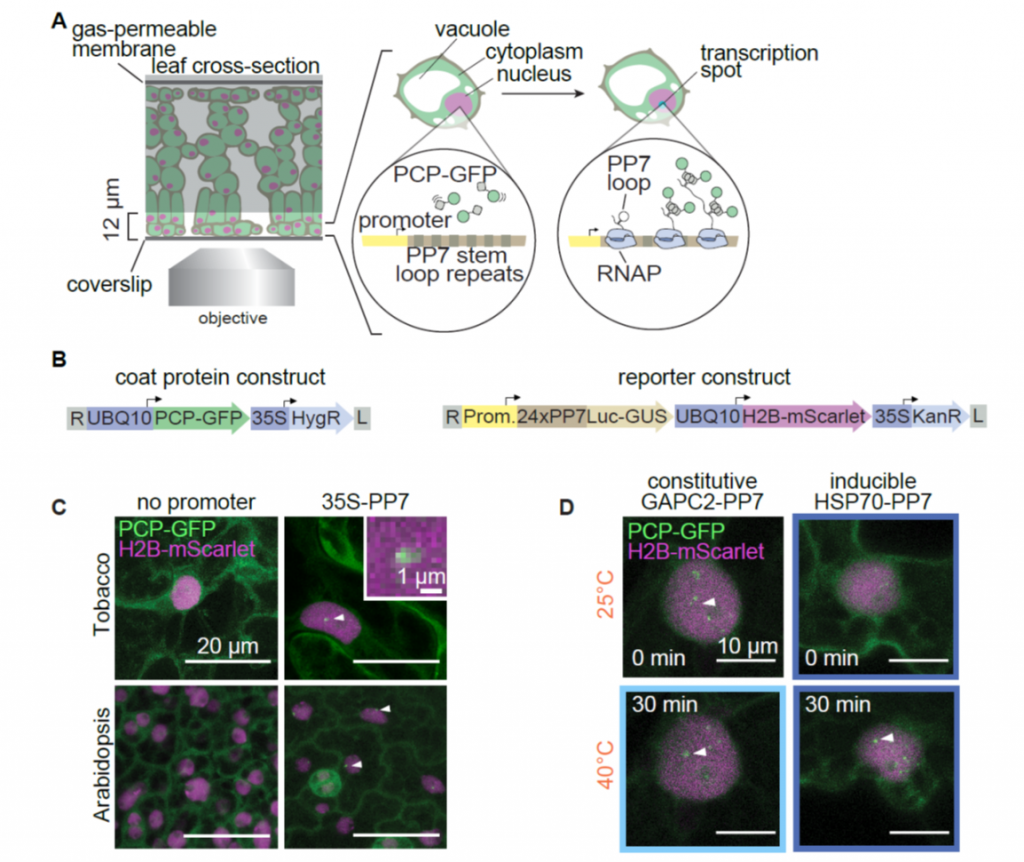
Real time quantitative imaging of transcriptional activity at the single cell level (bioRxiv)
Plant Science Research WeeklyHow plants transcriptionally operate developmental programs and responses to stress in time and space has been an important question in plant biology. Fluorescent protein reporters are commonly used to address this question, but their performance is limited at short timescales (<30 min) before the…

Review. Imaging flowers: a guide to current microscopy and tomography techniques to study flower development (J. Exp. Bot.)
Plant Science Research WeeklyFlowers bear the reproductive organs and determine the reproductive success of plants by producing fruits and seeds. Flowers usually include four whorls of organs: sepals, petals, stamen and carpel. In this review, Prunet and Duncan discuss various microscopic and tomographic techniques to image flower…
Multiple QTL mapping in autopolyploids: A random-effect model approach with application in a hexaploid sweetpotato full-sib population (Genetics)
Plant Science Research WeeklyGene mapping and QTL identification for the improvement of important traits have not been fully explored in an autopolyploid species like sweetpotatoes (2n=6x=90) due to its genetic complexity. Most sweet potato QTL mapping efforts have relied on models used for diploid species, leading to low density…
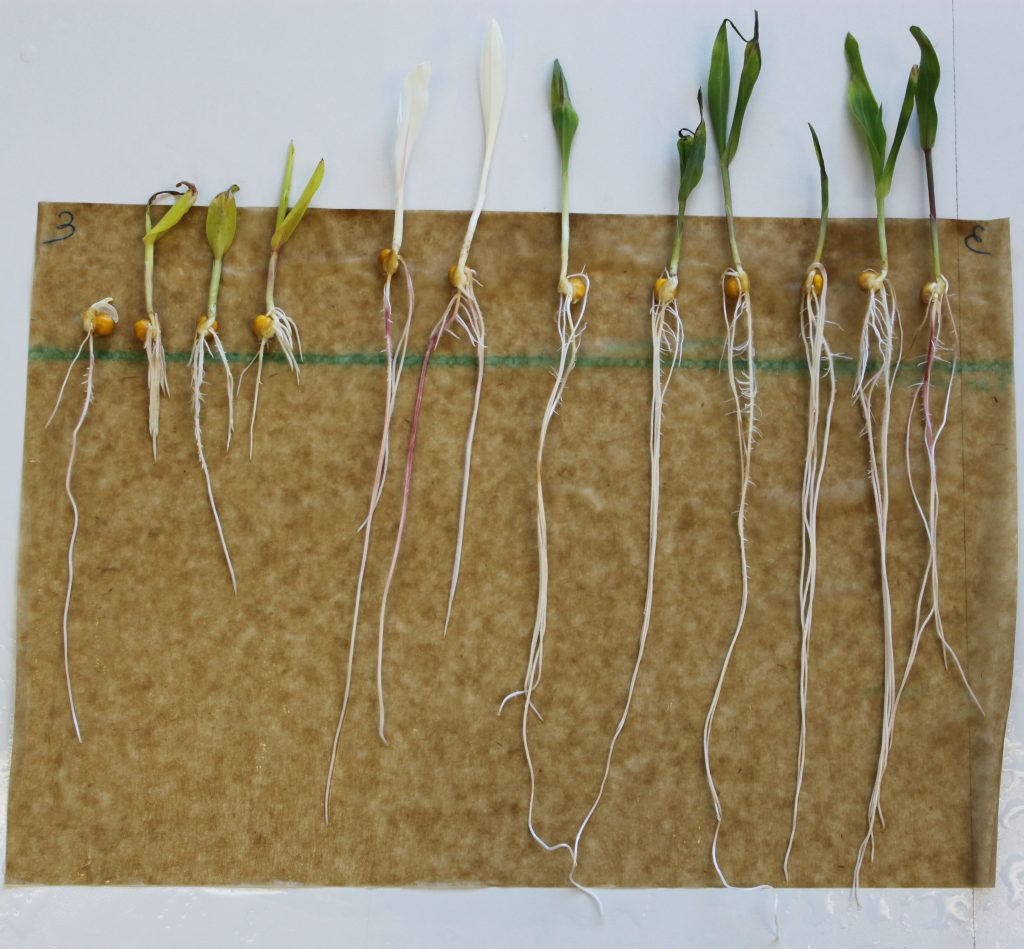

BonnMu: a sequence-indexed resource of transposon-induced maize mutations for functional genomics studies (Plant Physiol.)
Plant Science Research WeeklyLoss-of-function mutants have been invaluable tools in the geneticist’s toolbox for more than a century. More recently, libraries have been developed of knockout insertion mutants at known sites. Here, a new Mu-transposon insertion sequence-indexed maize resource is described. This new collection,…

Complete microviscosity maps of living plant cells and tissues with a toolbox of targeting mechanoprobes (PNAS)
Plant Science Research WeeklyBiological processes are ruled by physical as well as chemical forces and properties, but the former are much less well understood and studied. Here, Michels et al. describe a collection of fluorescent probes that provide a quantitative visual readout of microviscocity, reflecting the physical properties…

