
Intracellular distribution of manganese by NRAMP2 critical for photosynthesis and redox homeostasis
Manganese is a micronutrient essential for the function of several proteins including manganese superoxide dismutase (localized in the peroxisome and mitochondria) and the photosystem II reaction center (localized in the chloroplast). Mn is transported via NRAMP (Natural Resistance-Associated Macrophage…

Fe sparing in Arabidopsis rosettes
All cells need iron (Fe), which is frequently limiting for life. Plants (like other organisms) have complex strategies for uptake of Fe from their environment. Studies in the green alga Chlamodomonas have demonstrated that these organisms are able to prioritize certain pathways when Fe is limiting, a…
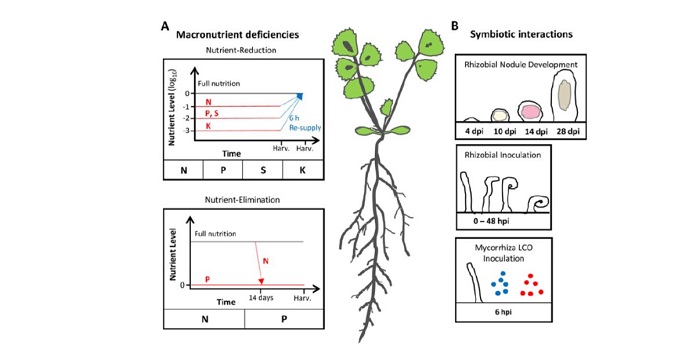
The Small Secreted Peptides of Legumes
Small secreted peptides (SSPs) are peptides of 5 to 50 amino acid residues that are secreted into the apoplast. SSPs are critical regulators of a diverse array of growth and developmental processes in plants, including root growth, nutrient homeostasis, meristem maintenance, stress acclimation, pathogen…
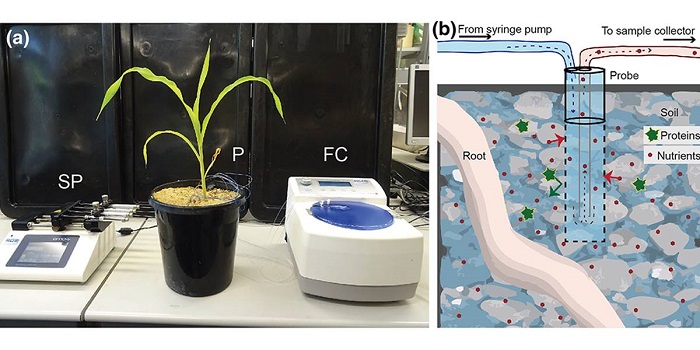
Roots-eye view: Using microdialysis and microCT to non-destructively map root nutrient depletion and accumulation zones
Plant roots constantly engage in nutrient and water uptake for crop productivity. Increasing the nutrient uptake efficiency of roots will promote sustainable agriculture by decreasing the need for fertilizer applications. To achieve this task, we need to understand the physiology of intact roots in their…
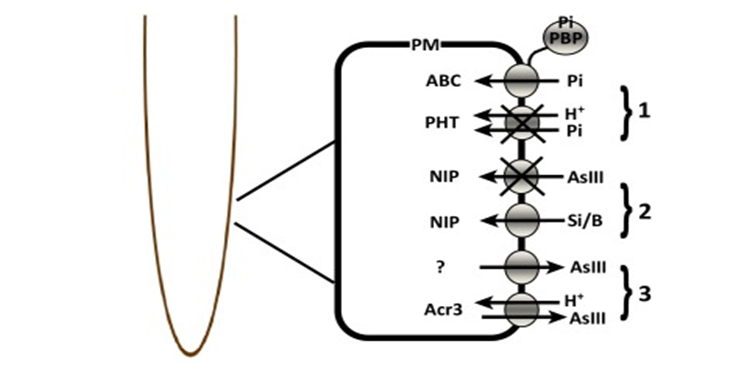
Review: New molecular mechanisms to reduce arsenic in crops ($)
“Over 200 million humans are at risk of arsenic poisoning,” due to arsenic in groundwater and its uptake into crops. Our understanding of the transporters through which arsenic enters the plant, moves through the plant, and enters the seed has increased substantially in recent years, opening the…
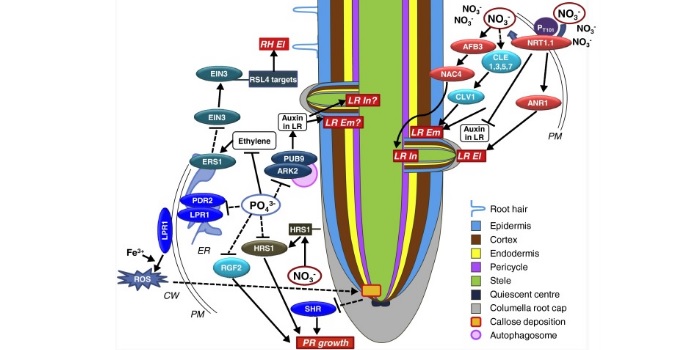
Review: The responses of root system architecture to nutrients
The arrangement of a plant’s root system in the soil (root system architecture, RSA) changes in response to nutrients through different signaling pathways. It is assumed that RSA adapts to optimize the uptake of nutrients from the environment, but strong evidence is still lacking. This review by Shahzad…

Strategy for enhancement of iron and zinc in biofortified rice
Polished white rice is a major food source for much of the world but is not a good source of the essential micronutrients iron and zinc. Like microbes, plants enhance their uptake of iron from the environment by synthesizing small “iron carrying” molecules called respectively siderophores or phytosiderophores…
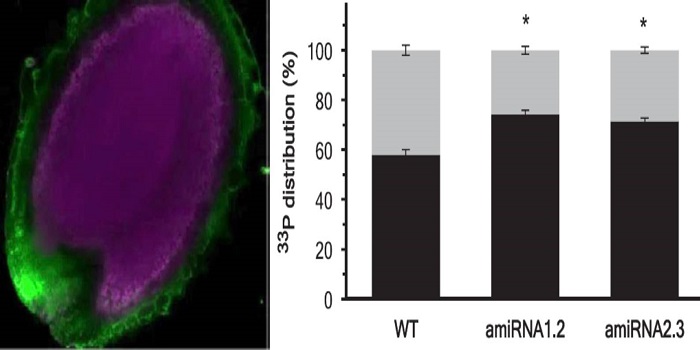
Phosphate transfer from maternal tissue to embryo
Many nutrients move through the plant body via the phloem. The developing embryo, which depends on the maternal plant for its nutrients, is not directly (symplastically) connected to maternal tissues, so nutrients must be exported across membranes to reach the embryo. PHO1 was identified previously as…

A root hair-seeking endophytic microbe from an unusual volcanic swamp corn enhances phosphate uptake
In plants the location of microbes to specific cell types, including endophytes, is still scarcely described in contrast with the situation in the animal kingdom. Shehata et al. describe a bacterial endophyte (Strain 3F11, possibly Enterobacter asburiae) from Zea nicaraguensis, a wild corn growing at…

