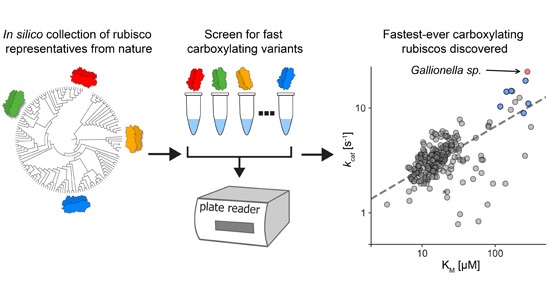
Highly active rubiscos discovered by systematic interrogation of natural sequence diversity (EMBO J)
Plant Science Research WeeklyThis is a fascinating and very well-written paper that investigates the diversity of rubisco's kinetic properties. Rubisco’s relationship with its substrate CO2 is complicated by its relationship with O2, and it has often been suggested that for this reason rubisco is locked into a slow rate of catalysis.…
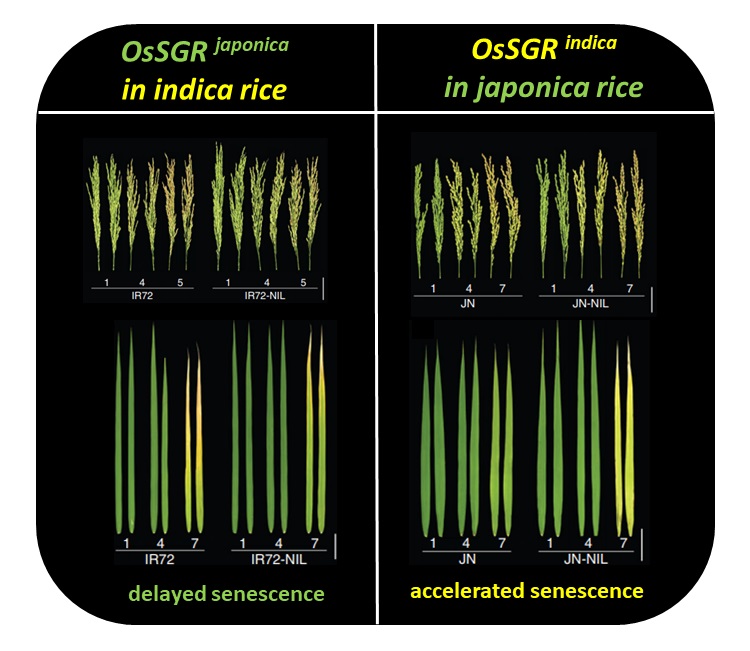
Natural variations at the Stay-Green gene promoter control lifespan and yield in rice cultivars (Nature Comms)
Plant Science Research WeeklyCrop production is greatly influenced by the duration of the last stage of plant life cycle, senescence, through degradation of resources in leaves and remobilization of nutrients to developing seeds. Indeed, higher grain yield of important cereals such as maize and sorghum can be achieved by using stay-green…

Role of two phosphatases in state transition of Chlamydomonas (Plant Physiol.)
Plant Science Research WeeklyPlants and green algae can rapidly adapt to changing light conditions. Depending on light availability or other metabolic needs, Light Harvesting Complexes (LHC) II can be reallocated to photosystem I (PSI) from photosystem II (PSII) and vice versa. This is known as state transition and is mediated by…
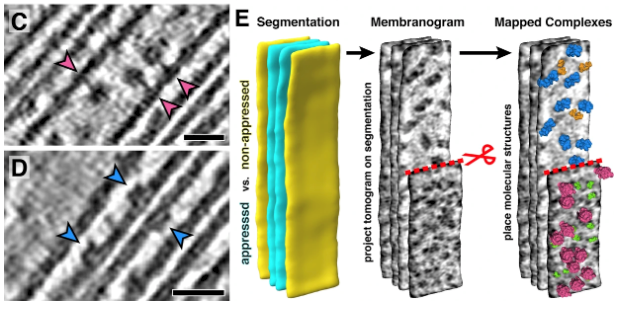
A close-up view of the thylakoids (eLIFE)
Plant Science Research WeeklyThe thylakoid membranes inside the chloroplasts house the major protein complexes required for photosynthesis, including photosystems I and II (PSI/II), the b6f complex and ATP synthase. To optimize photosynthetic efficiency, the distribution and abundance of these complexes are dynamically regulated…
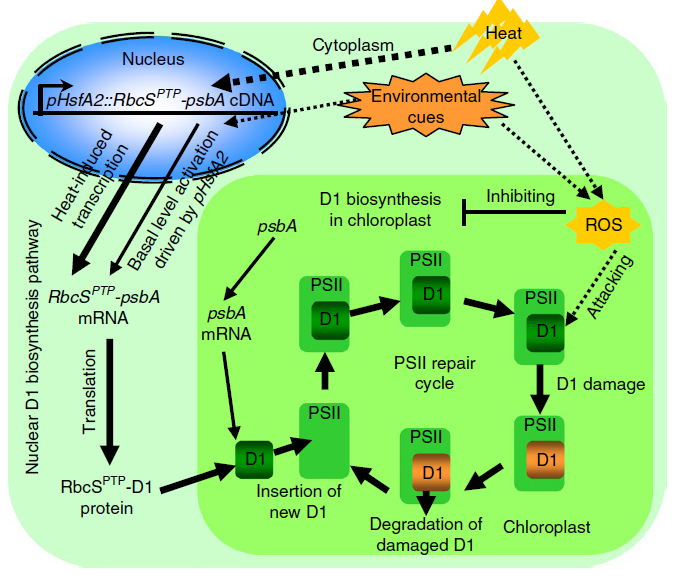
Nuclear-encoded synthesis of the D1 subunit of photosystem II increases photosynthetic efficiency and crop yield (Nature Plants)
Plant Science Research WeeklyPhotosystem II (PSII) is a protein complex located in the thylakoid membrane of chloroplasts that is involved in executing the initial reaction of photosynthesis in plants. When plants are exposed to extreme temperature conditions, PSII gets damaged. To repair the damage, one of the core proteins of…

How to transfer lipids from one membrane to another during thylakoid biogenesis (PNAS)
Plant Science Research WeeklyThe thylakoid membranes are located in the stroma of chloroplasts and house the machinery for the photosynthetic light reactions. They emerge largely de novo during the transition from pro-plastids into mature, photosynthesizing chloroplasts. Generating new thylakoid membranes requires a supply of lipids,…
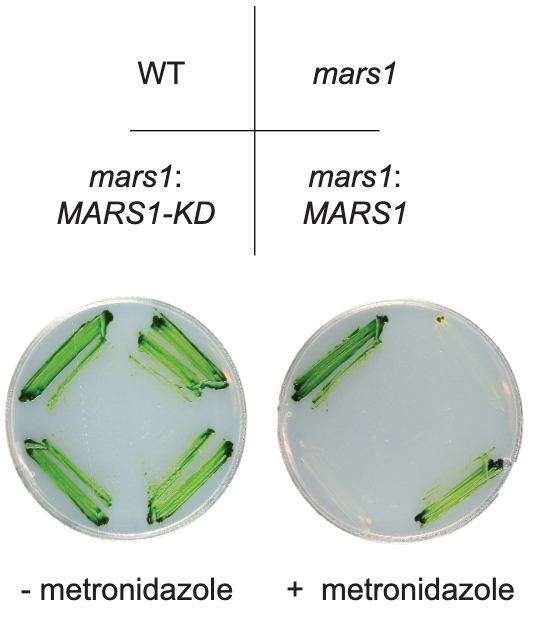
Mars1 kinase signaling in the chloroplast unfolded protein response (eLIFE)
Plant Science Research WeeklyIn stressful situations, such as high light and nutrient scarcity, the chloroplast may experience increased proteotoxicity due to a surge in damaging reactive oxygen species. In response, a signal is sent to the nucleus to increase production of many proteins, including proteases and chaperones to help…

Breaking Water-wise Photosynthesis
Research, The Plant Cell, The Plant Cell: In a NutshellBoxall et al. explore the effects of silencing phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase in a Crassulacean acid metabolism species. Plant Cell https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.19.00481
By Susie Boxall and James Hartwell
Background: Severe droughts and high temperatures are becoming more frequent due to climate…
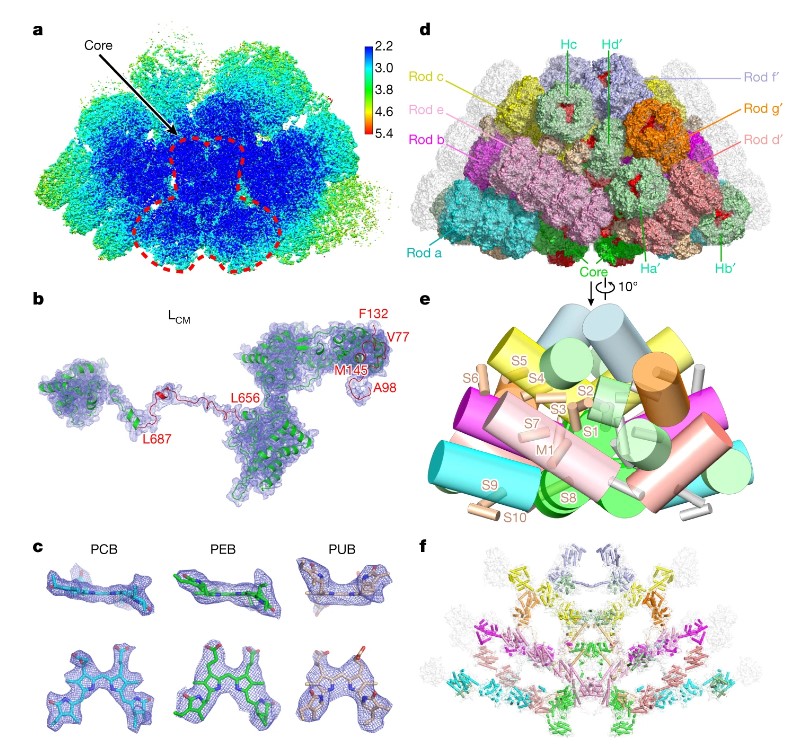
Structural basis of unidirectional energy transfer in Porphyridium purpureum phycobilisome (Nature)
Plant Science Research WeeklyCyanobacteria and red algae employ phycobilisomes (PBSs) as light-harvesting systems to adapt to fluctuating environments. PBSs are composed of phycobiliproteins, linker proteins and chromophores. Ma et al. used cryo-EM to determine the 2.82 Å structure of the very large (14.7-megadalton, 706 protein…

