
Glucose-Induced Trophic Shift in an Endosymbiotic Dinoflagellate
Blog, Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: On The Inside, Research, Research BlogDinoflagellates in the genus Symbiodinium have the ability to enter into endosymbiotic associations with corals, providing the metabolic basis for the highly productive and biologically diverse coral-reef ecosystems, as well as with other cnidarians, including sea anemones and jellyfish. The Symbiodinium-coral…
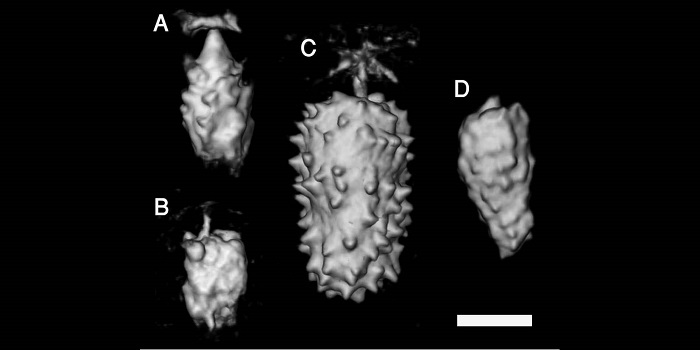
Mineral Deposits in Ficus Leaves
Blog, Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: On The Inside, Research, Research BlogMineral deposits occur in many, but not all plant leaves. In those leaves that do have minerals, the mineral type, morphology and the distributions within the leaves are under strict control. In fact, mineralization in certain leaves is a well-preserved trait throughout evolution, indicating that such…

Phytochrome, metabolism and growth plasticity
Blog, Plant Science Research Weekly, Research, Research BlogPhytochromes are plant photoreceptors that can sense red and far-red light, as-well-as the ratio of these light qualities. This review examines the relationship between phytochrome signalling and carbon metabolism. Krahmer et al. assess the influence of phytochrome signalling on the synthesis of…
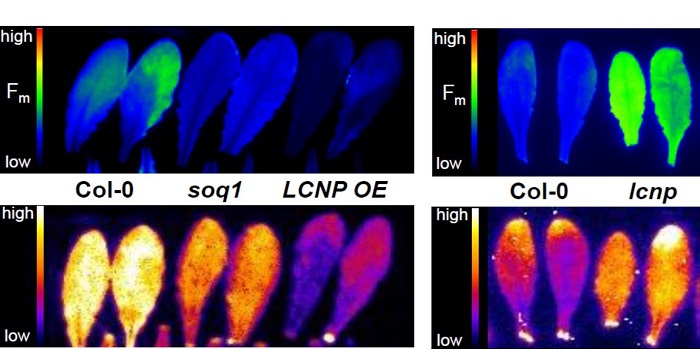
The plastid lipocalin LCNP is required for sustained photoprotective energy dissipation
Blog, Plant Science Research Weekly, Research, Research BlogPlants have several mechanisms to protect themselves from damage from excess light, including a set of reactions collectively described as non-photochemical quenching or NPQ. One of these is a sustained and slowly reversible form of NPQ, which the authors have named qH. How this sustained NPQ functions…

Cell density and airspace patterning in the leaf can be manipulated to increase leaf photosynthetic capacity
Blog, Plant Science Research Weekly, Research, Research BlogIncreasing photosynthetic conversion efficiency is an attractive target for improving crop yields. One way of affecting this is to alter the way CO2 is delivered to Rubisco, the carbon-fixing enzyme of photosynthesis. Lehmeier et al. aimed to change the pattern of air spaces within Arabidopsis leaves…
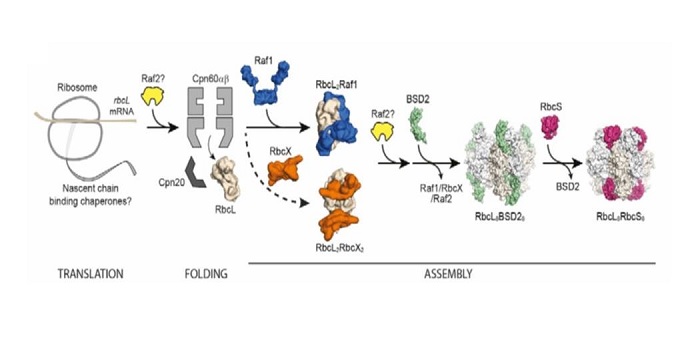
Plant RuBisCo assembly in E. coli with five chloroplast chaperones ($)
Blog, Plant Science Research Weekly, Research, Research BlogIn plants, Ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase (RuBisCo), the enzyme responsible for fixing carbon, is a made up of 8 each of the large and small subunits, making the L8S8 form. Efforts to study this enzyme have been thwarted by the inability to assemble an active L8S8 form in a heterologous…
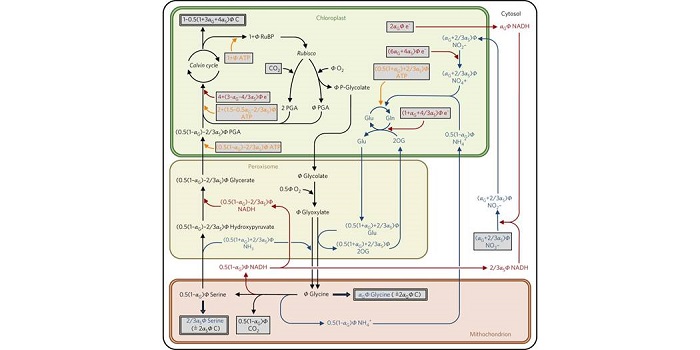
Plants increase CO2 uptake by assimilating nitrogen via the photorespiratory pathway
Blog, Plant Science Research Weekly, Research, Research BlogDuring photosynthesis Rubisco fixes CO2 by carboxylating its substrate RuBP, leading to the de novo production of carbohydrates. Photorespiration has long been considered a wasteful process, initiated by Rubisco-mediated oxygenation of RuBP and resulting in the loss of carbon, nitrogen and energy. …

Engineering Increased Stomatal Density in Rice
Blog, Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: On The Inside, Research, Research BlogThe coordinated differentiation of cell types during the metamorphosis of an organ is crucial for ensuring that the final form of the organ is appropriate for itsfunction. A case in point is the photosynthetic function of plant leaves that requires chloroplast-containing cells in the middle leaf layers…
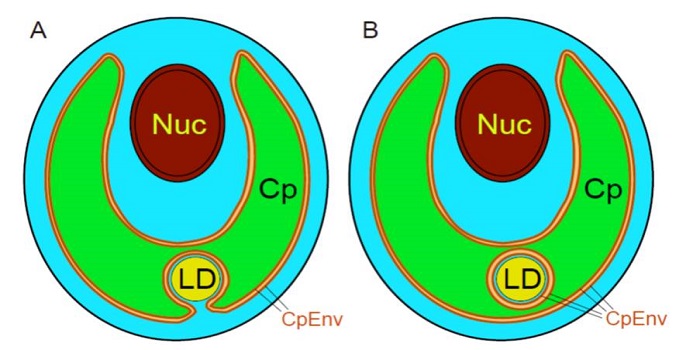
Do Lipid Droplets Exist in the Chloroplast Stroma?
Blog, Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: On The Inside, Research, Research BlogUnderstanding the metabolic pathways underlying oil production and the precise intracellular localization of lipid droplets is crucial for successfully engineering microalgae for biofuel production. The microalga Chlamydomonas reinhardtii accumulates considerable amounts of starch and triacylglycerol…

