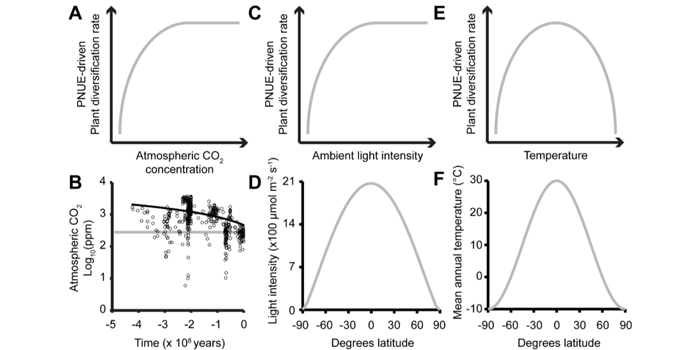
The amount of nitrogen used for photosynthesis modulates molecular evolution in plants (Mol Biol Evol)
Blog, Plant Science Research Weekly, Research, Research BlogPlant growth is often limited by the availability of nitrogen (N), which is required to synthesise monomers and macromolecules, and is especially important in the synthesis of the carbon assimilating enzymes of the Calvin-Benson-Bassham (CBB) cycle. In this article, Kelly has demonstrated that photosynthetic…
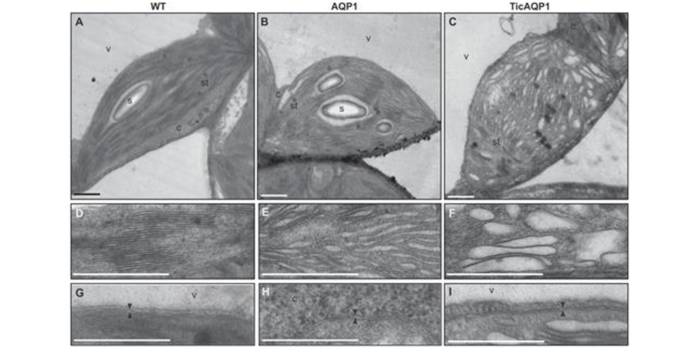
Physiological performance of transplastomic tobacco plants overexpressing aquaporin AQP1 in chloroplast membranes (JXB)
Blog, Plant Science Research Weekly, Research, Research BlogA major factor in determining photosynthetic rate is the availability of CO2 at the site of fixation in the chloroplast stroma. Classically, this has been thought to be mainly limited by stomatal conductance (diffusion from the air, through stomata, to sub-stomatal cavities). However, more recently…
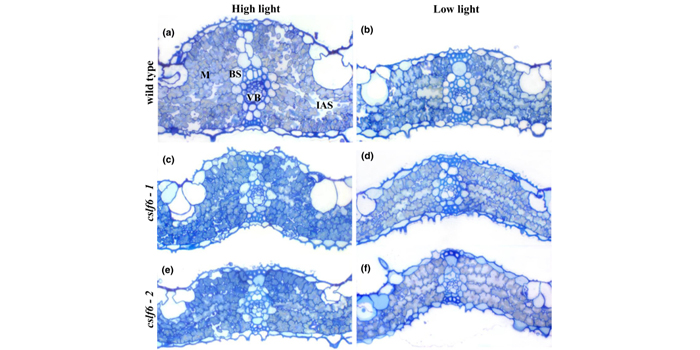
Cell wall properties in Oryza sativa influence mesophyll carbon dioxide conductance (New Phytol) $
Blog, Plant Science Research Weekly, Research, Research BlogMesophyll CO2 conductance (gm) is an important factor in determining the concentration of CO2 at the site of fixation in the chloroplast stroma, and as such is crucial for determining photosynthetic capacity. The mesophyll cell wall provides a major site of resistance to CO2 diffusion into the stroma…
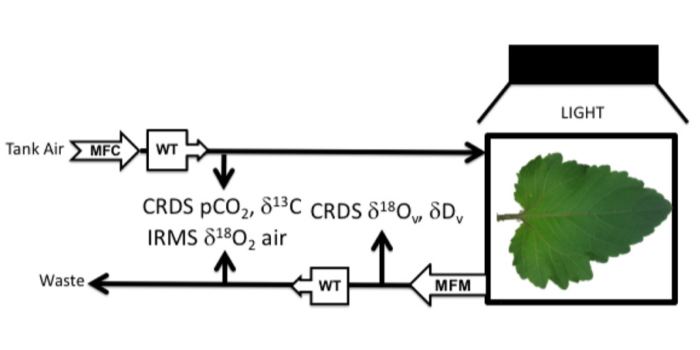
Measurement of gross photosynthesis, respiration in the light, and mesophyll conductance using H218O labeling (Plant Physiol)
Blog, Plant Science Research Weekly, Research, Research BlogIt is relatively simple to determine net O2 flux in leaves. However, this data provides no information on the underlying processes responsible for this flux, namely gross oxygen production (GOP, water splitting), mitochondrial respiration in light, Rubisco oxygenation, and photorespiration. In this…
Phosphorous Deficiency and Photosynthesis
Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: On The Inside, ResearchPhosphorus (P) is an essential macronutrient, and P deficiency limits plant productivity. P influences many aspects of photosynthesis P-deficient plants typically remain green and do not develop leaf chlorosis and yet P starvation immediately affects CO2 assimilation. Specifically, P deficiency is believed…

Review: Rubisco is not really so bad ($) (Plant Cell Environ)
Plant Science Research WeeklyThe carbon-fixing enzyme Rubisco (Ribulose‐1,5‐bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase) is much-maligned and has been described as “sluggish” and with “confused specificity”. In this new Review, Bathellier et al. argue that it is “not really so bad”. Their reasoning is that when Rubisco’s…

Red algal Rubisco fails to accumulate in tobacco expressing Griffithsia monilis RbcL and RbcS genes (Plant Direct)
Plant Science Research WeeklyFollowing up on earlier studies in which they introduced cyanobacterial Rubisco into tobacco, Lin and Hanson endeavoured to introduce into tobacco Rubisco genes from a red alga, which has an unusually high CO2/O2 specificity. Although they were able to demonstrate the presence of the genes and their…

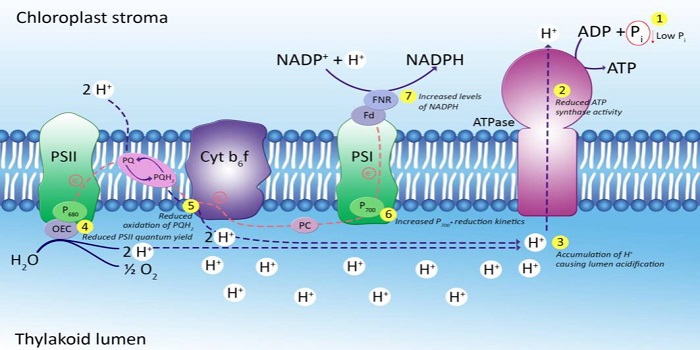
The impacts of phosphorus deficiency on the photosynthetic electron transport chain (Plant Physiol)
Plant Science Research WeeklyPhosphorus deficiency is widespread and can severely limit plant growth. Carstensen et al. investigated how P deficiency affects photosynthesis in barley. They compared chlorophyll a fluorescence transients (OJIP transients) between P-deficient, sufficient and resupplied plants. They observed depletion…
Saving Algae from Environmental Stresses
Research, The Plant Cell, The Plant Cell: In a NutshellDu et al. investigate an important protein that regulates photosynthesis under stress. Plant Cell. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.17.00446.
Background:…

