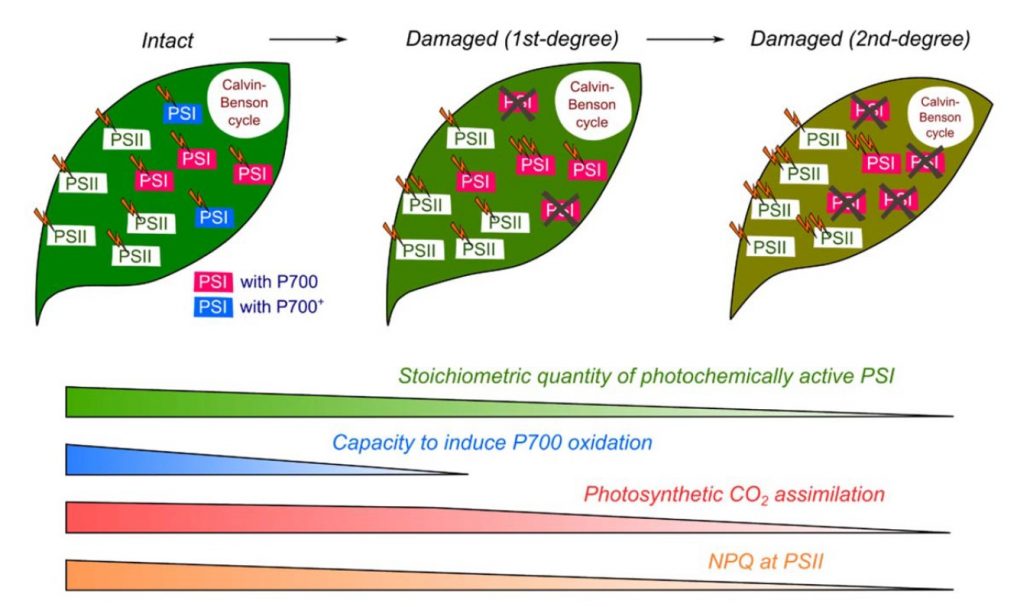
What quantity of photosystem I is optimum for safe photosynthesis? ($) (Plant Physiol)
Plant Science Research WeeklyPhotosynthesis is one of the most vital and complex processes carried out by plants. During photosynthesis, Photosystem I and II (PSI and PSII) undergo photo-excitation. Excessive photo-excitation can damage and deactivate the PSI by generating reactive oxygen species (ROS). This kind of photoinhibition…

Rubisco condensate formation by CcmM in β-carboxysome biogenesis (Nature) ($)
Plant Science Research WeeklyCyanobacterial carbon-dioxide concentrating mechanisms elevate intracellular inorganic carbon as bicarbonate, and then concentrate it as carbon-dioxide around the enzyme Rubisco in specialized protein micro-compartments called carboxysomes. The formation of B-carboxysomes involves an aggregation between…

Synthetic glycolate metabolism pathways stimulate crop growth and productivity in the field ($) (Science)
Plant Science Research WeeklyRubisco uses CO2 from the air to carboxylate its substrate RuBP, resulting in an increase in fixed carbon. However, rubisco can also oxygenate RuBP and this leads to the production of glycolate. Plants must invest energy in recycling this toxic by-product in a process called photorespiration, resulting…

New Insights into Carboxysomes
Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: On The InsideDespite its essential role in photosynthetic carbon fixation, ribulose 1,5 bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase (Rubisco) is a relatively inefficient enzyme, due in part to its inability to discriminate between CO2 and O2 as substrates. To suppress the oxygenase reaction and enhance the carboxylase activity…
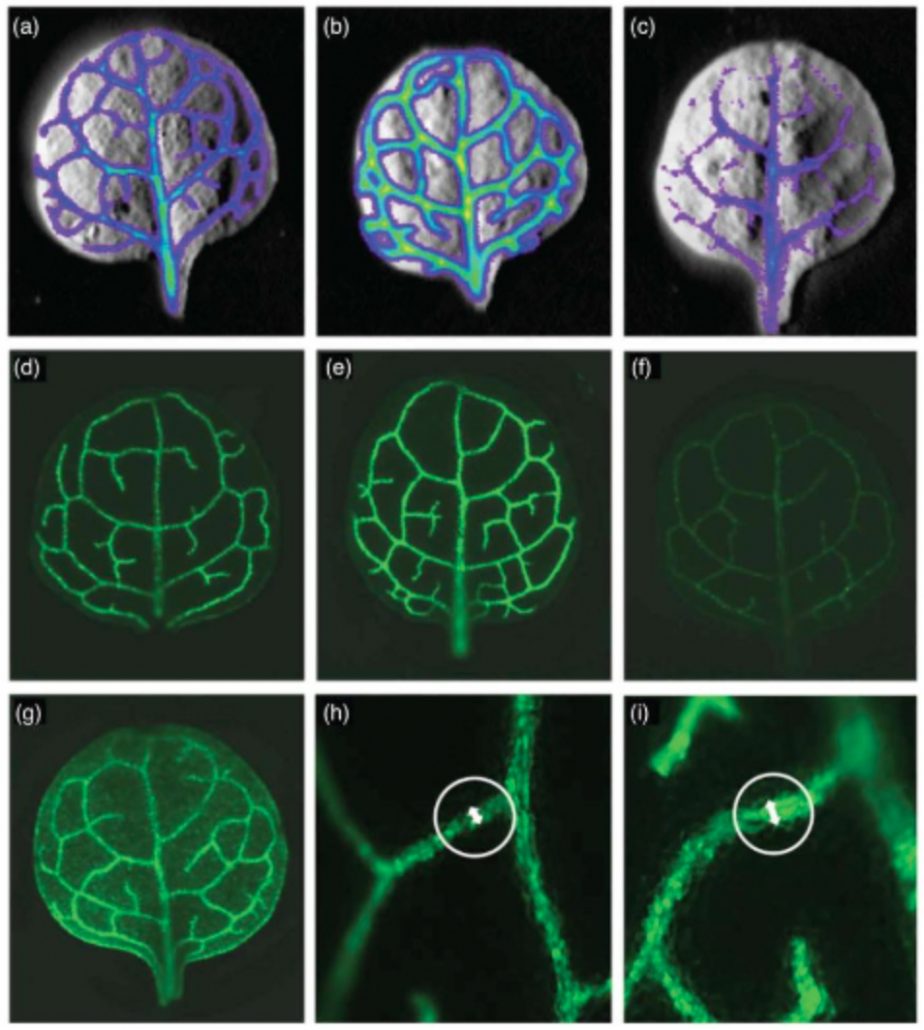
Reporter‐based screen to identify bundle sheath anatomy mutants ($) (Plant J)
Plant Science Research WeeklyInstallation of C4 photosynthesis into C3 crops appears a realistic way to boost crop yields. A key aspect of C4 photosynthesis is an enlarged bundle sheath volume and an increase in bundle sheath chloroplast number. To identify the regulators of this phenotype, Döring et al. subjected Arabidopsis…
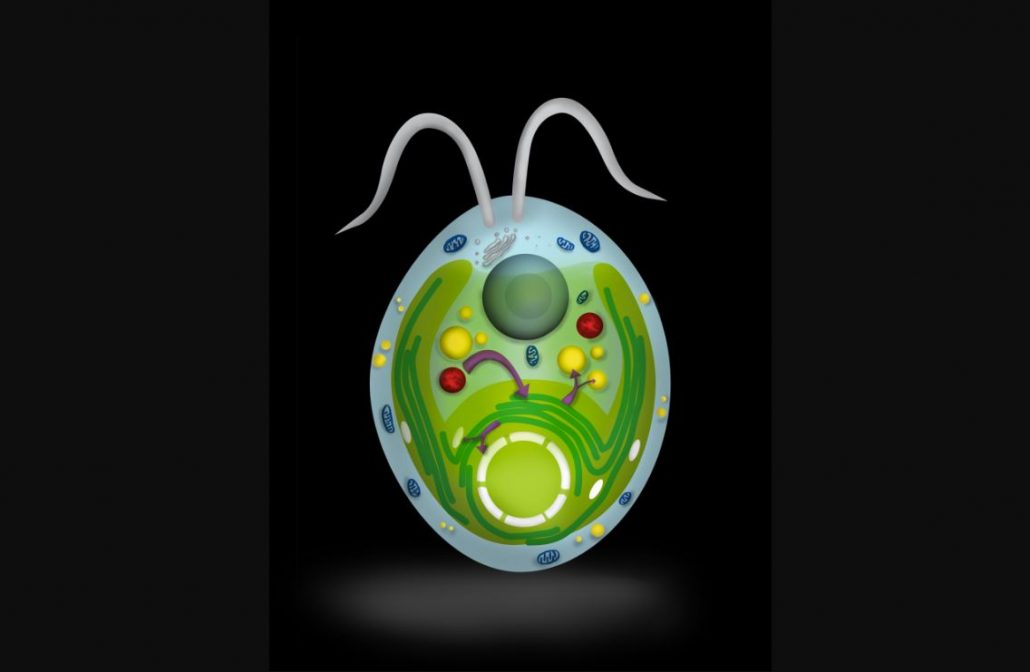
How Peroxisomes Modulate Chloroplast Activity in a Microalga
Research, The Plant Cell, The Plant Cell: In a NutshellBackground: Chloroplasts are the major powerhouse of plant and algal cells, where photosynthesis—the conversion of carbon dioxide into organic compounds using sunlight energy—occurs. Chloroplasts are also where important cell components (such as membrane lipids and pigments) and energy-rich compounds…
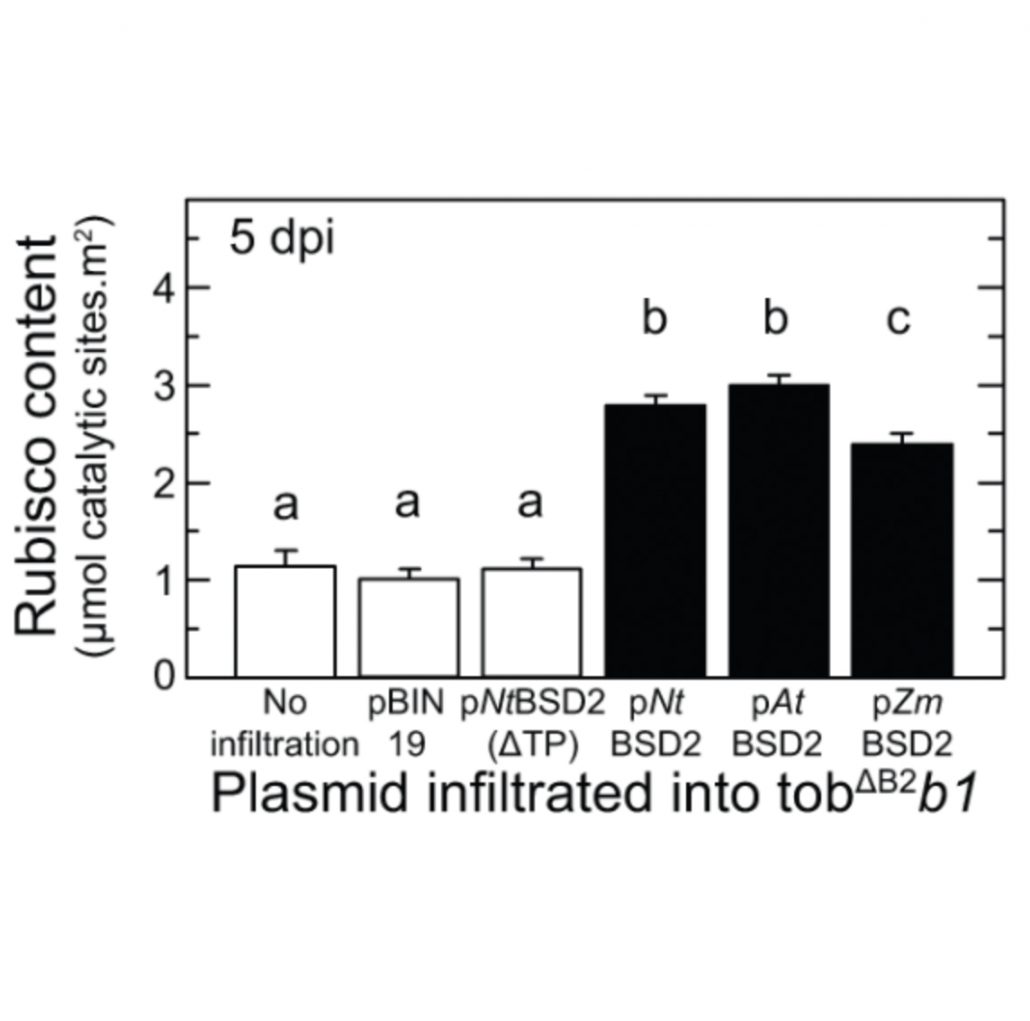
BSD2 is a Rubisco specific assembly chaperone, forms intermediary hetero‐oligomeric complexes and is non‐limiting to growth in tobacco (Plant Cell Environ)
Plant Science Research WeeklyThe rubisco holoenzyme is comprised of eight large subunits and eight small subunits (L8S8). Several auxiliary proteins are required to correctly assemble the functional protein. In this manuscript, Conlan et al investigate the chaperone function of one of these proteins, BSD2, in tobacco. The authors…
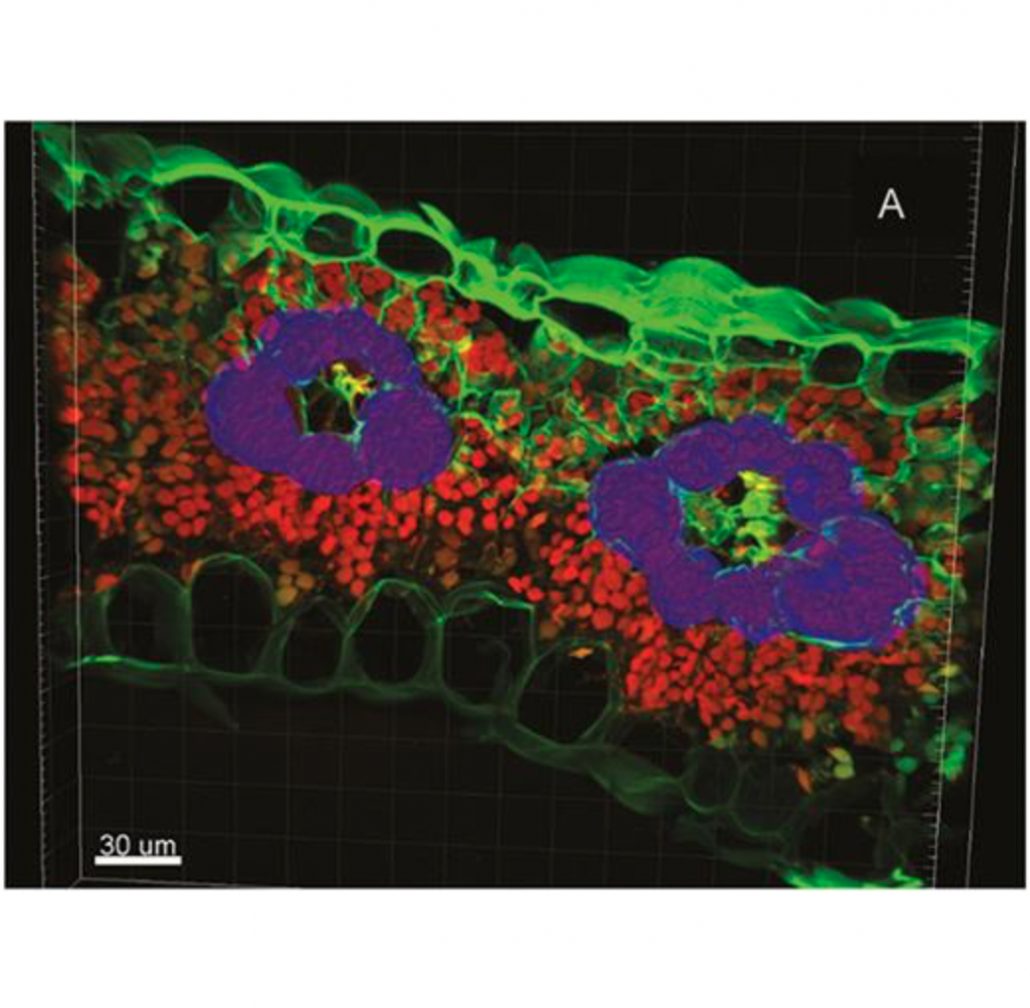
Bundle sheath chloroplast volume can house sufficient Rubisco to avoid limiting C4 photosynthesis during chilling (J Exp Bot)
Plant Science Research WeeklyIt has long been thought that C4 species generally perform less well than C3 species in cold environments as a consequence of a physical space restriction. C3 species tend to accumulate more rubisco under chilling stress to avoid limiting photosynthesis, but there is less capacity for this in C4 species…
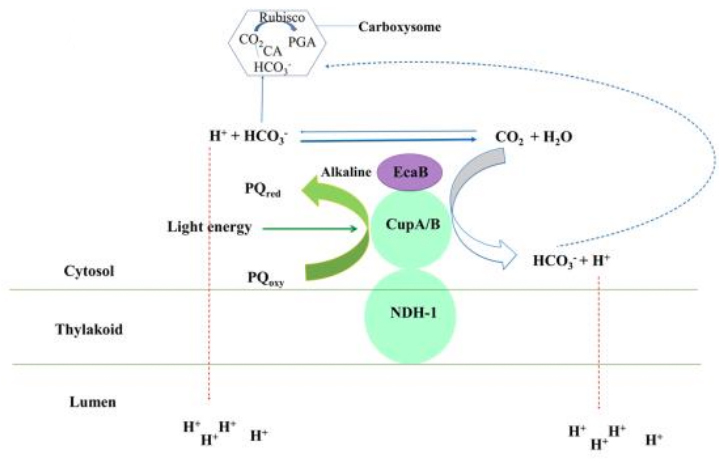
A thylakoid-located carbonic anhydrase regulates CO2 uptake in the cyanobacterium Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803 (New Phytol)
Plant Science Research WeeklyThe cyanobacterial CO2 concentrating mechanism (CCM) is dependent on a continuous supply of inorganic carbon (Ci) to rubisco inside carboxysomes in order to function optimally. CO2 uptake pathways are therefore of great importance for a full understanding of the cyanobacterial CCM. Sun et al demonstrate…

