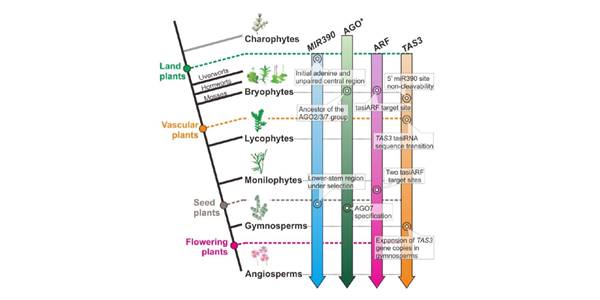
The emergence, evolution, and diversification of the miR390-TAS3-ARF pathway in land plants ($)
Plant Science Research Weekly, Research0 Comments
/
Trans-acting small interfering RNAs (tasiRNAs) are unique to plants. They are the products of TAS genes, but they function to regulate other genes (thus the name “trans-acting”). The production of tasiRNAs requires miRNAs, which bind to and ultimately lead to cleavage of the primary TAS transcript.…
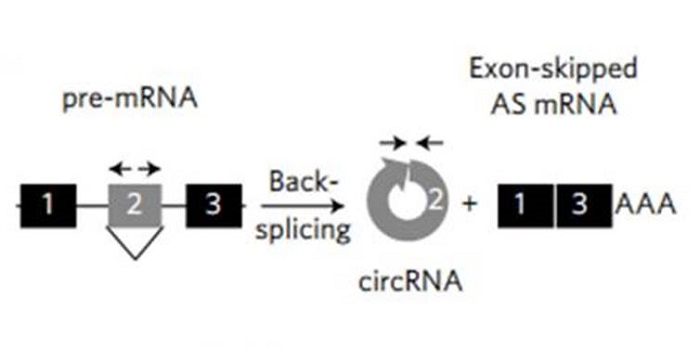
A circRNA from SEPALLATA3 regulates splicing of its cognate mRNA through R-loop formation ($)
Plant Science Research Weekly, ResearchCircular RNAs (circRNAs) are a recently discovered form of stable, covalently-closed RNA found in all domains of eukaryotic life. The origins and functions of circRNAs have been under intensive investigation. Often, circRNAs consist of one or more exons, often corresponding to skipped exons from genes…
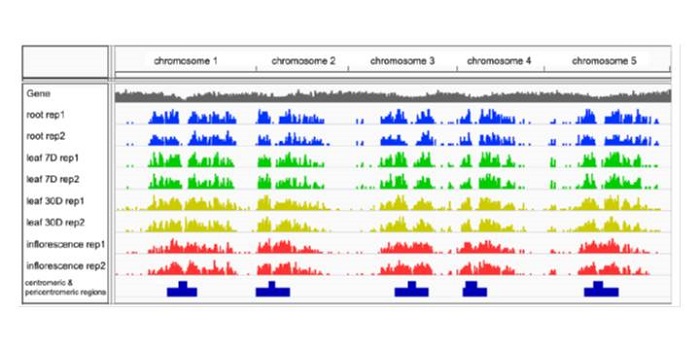
Non-random domain organization of the Arabidopsis genome at the nuclear periphery
Plant Science Research Weekly, ResearchChromatin in the nucleus is not randomly arranged. In animal cells, studies have identified an enrichment for non-genic or silenced DNA near the nuclear envelope, as demonstrated by its association with the nuclear lamin proteins. Plants don’t have proteins like animal lamins, but a few envelope-associated…
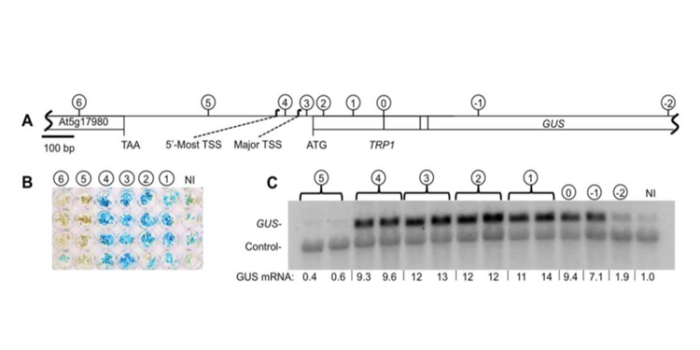
Intron DNA sequences can be more important than the proximal promoter in determining the site of transcript initiation
Plant Science Research Weekly, ResearchThe site at which transcription begins is traditionally thought to be determined in the proximal promoter by assembly of the pre-initiation complex just upstream of the transcription start site (TSS). New results from Gallegos and Rose challenge this assumption. Prior studies have shown that the presence…

Special issue: Flowering of jasmonate research
Plant Science Research Weekly, ResearchJasmonates are a family of compounds including jasmonic acid and its derivatives that regulate many plant processes from germination to defense. The Journal of Experimental Botany has a special issue on jasmonate research, which commemorates the advances in this field in the ten years since the JAZ proteins…
Nematode Cysts and DNA Methylation
Plant Physiology: On The Inside, ResearchPlant-parasitic cyst nematodes (Heterodera species) are among the most devastating pathogens of plant roots. These obligate parasites initiate a long period of biotic interactions with their host plants where formation of an operative feeding structure, the syncytium, is vital for nematode survival and…

Drought-Responsive Novel MicroRNAs in Grapevine
Blog, Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: On The Inside, Research, Research BlogEuropean grapevines (Vitis vinifera) are routinely grafted on interspecific hybrid rootstocks mainly to control infestation by phylloxera (Daktulosphaira vitifoliae). Research has shown, however, that these rootstocks can also affect scion growth vigor and resistance to abiotic stresses such as drought.…
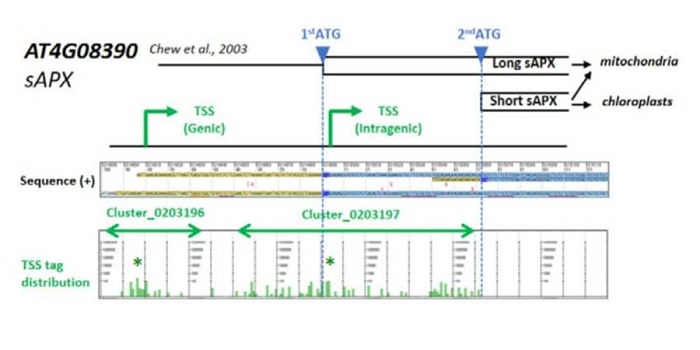
Identification of Arabidopsis genic and non-genic promoters
Plant Science Research Weekly, ResearchA promoter is a region that “determines the position, direction, frequency, and timing of transcription”. A cell can decode the sequence of the promoter to ensure appropriate transcription, but we still can’t. Tokizawa et al. performed a large-scale survey of promoters by sequencing regions upstream…
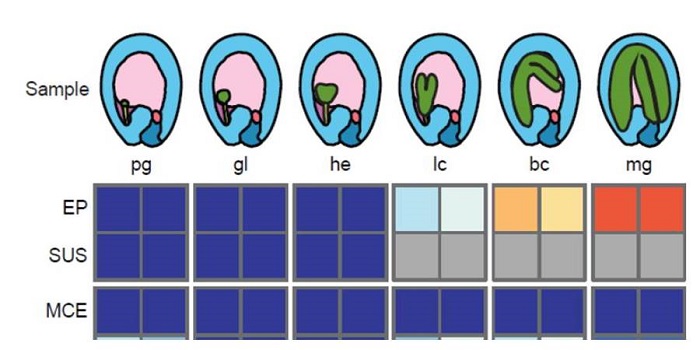
Commentary: Widespread contamination of Arabidopsis embryo and endosperm transcriptome datasets
Plant Science Research Weekly, ResearchKnowing where a gene is expressed provides valuable information about its function, but that information is compromised if the RNA source is contaminated by other tissues. Schon and Nodine investigated the extent to which Arabidopsis embryo and endosperm transcriptome datasets are affected by tissue…

