When pollinators are also herbivores ($)
Plant Science Research Weekly, Research0 Comments
/
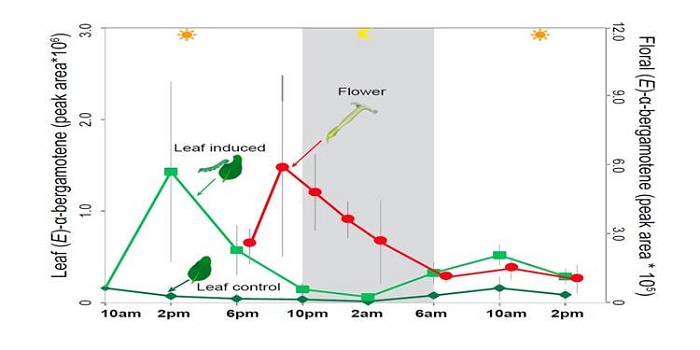
The interaction between wild tobacco (Nicotiana attenuata) and the moth Manduca sexta, which is both a pollinator and a herbivore, is a model for plant/ arthropod interactions and has revealed insights into chemical signals and defenses. Zhou et al. show that a single compound, the sesquiterpene (E)-α-bergamotene,…
Discovery of nitrate–CPK–NLP signalling in central nutrient–growth networks ($)
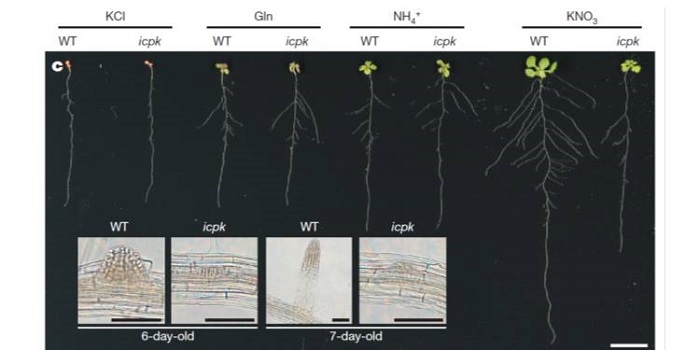
Plant Science Research Weekly, ResearchNitrate acts as a potent signal as well as a source of nutritional nitrogen, but key players in the nitrate response have been missing from our understanding. Liu et al. identified a unique calcium signal stimulated by nitrate in mesophyll cells. They then found that in vitro kinase activity of Ca2+-sensor…

Folate, DNA Methylation and Flowering Time
Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: On The Inside, ResearchTetrahydrofolate (THF) and its derivatives, collectively termed folates, are a group of essential B-complex vitamins that have long been recognized as necessary nutrients to support normal cell differentiation and growth. Folates function as co-enzymes in one-carbon transfer reactions and play a central…
Suppression of plant hypoxia responses by cysteine oxidases and arginyl transferases that initiate transcription factor turnover by N-end rule pathway
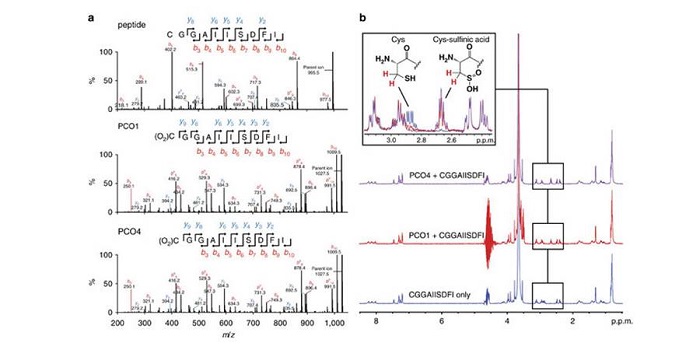
Plant Science Research Weekly, ResearchFlooding “drowns” plants by depriving them of oxygen, leading to hypoxia and ultimately death. Ethylene-responsive transcription factors (ERFs) have been identified that induce expression of genes to support anaerobic metabolism and are critical for hypoxia survival. ERFs are selectively destabilized…
The emergence, evolution, and diversification of the miR390-TAS3-ARF pathway in land plants ($)
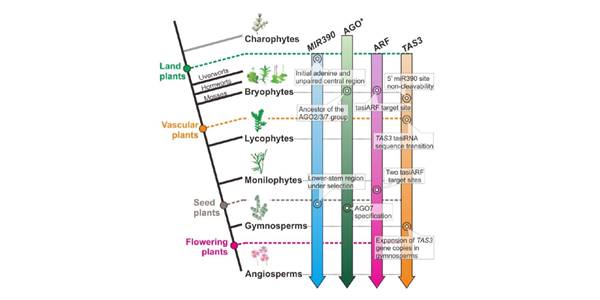
Plant Science Research Weekly, ResearchTrans-acting small interfering RNAs (tasiRNAs) are unique to plants. They are the products of TAS genes, but they function to regulate other genes (thus the name “trans-acting”). The production of tasiRNAs requires miRNAs, which bind to and ultimately lead to cleavage of the primary TAS transcript.…

H2A monoubiquitination in Arabidopsis is generally independent of LHP1 and PRC2 activity
Plant Science Research Weekly, ResearchGene silencing by chromatin marks occurs in plants and animals, but there are often some differences in the details. Polycomb repressive complex 1 (PRC1) and PRC2 were first characterized in animals and shown to repress gene expression in part through histone modification; PRC1 has histone H2A E3 ubiquitin…
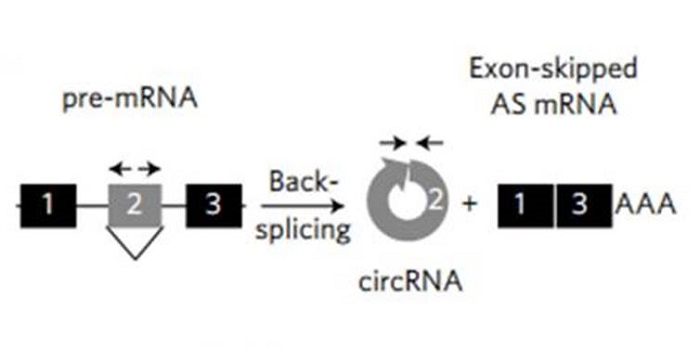
A circRNA from SEPALLATA3 regulates splicing of its cognate mRNA through R-loop formation ($)
Plant Science Research Weekly, ResearchCircular RNAs (circRNAs) are a recently discovered form of stable, covalently-closed RNA found in all domains of eukaryotic life. The origins and functions of circRNAs have been under intensive investigation. Often, circRNAs consist of one or more exons, often corresponding to skipped exons from genes…
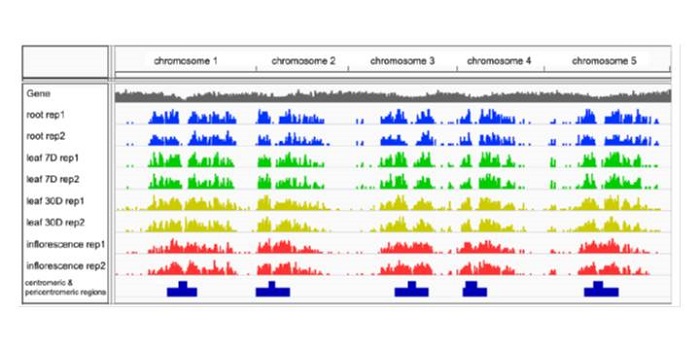
Non-random domain organization of the Arabidopsis genome at the nuclear periphery
Plant Science Research Weekly, ResearchChromatin in the nucleus is not randomly arranged. In animal cells, studies have identified an enrichment for non-genic or silenced DNA near the nuclear envelope, as demonstrated by its association with the nuclear lamin proteins. Plants don’t have proteins like animal lamins, but a few envelope-associated…
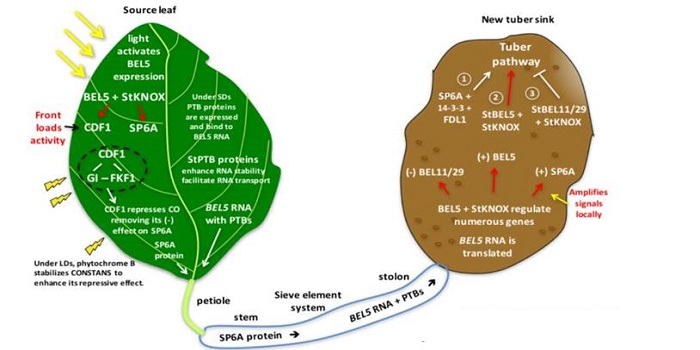
Update: The multiple signals that control tuber formation
Plant Physiology: Updates, Plant Science Research Weekly, ResearchPotato is an important food crop, but unlike most of the other major foods, it is a tuber, not a seed. Classic studies showed that there is a mobile, photoperiod-induced signal that moves from the shoot to the stolen tip (an underground, stem-like structure) to initiate tuberization. Experimental studies…

