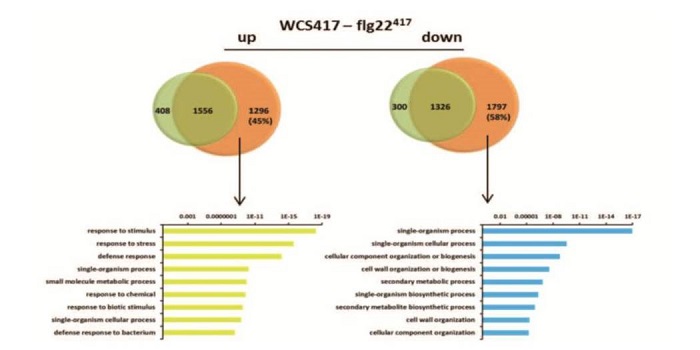
Signatures of adaptation to mutualists revealed by root transcriptional dynamics
Blog, Plant Science Research Weekly, Research, Research BlogA plant's rhizosphere consists of a huge array of pathogenic microbes many of which can trigger defense responses, leading to decreased growth. On the other hand, beneficial microbes such as rhizobacteria promote growth and can induce systemic resistance while suppressing local immune responses. A recent…
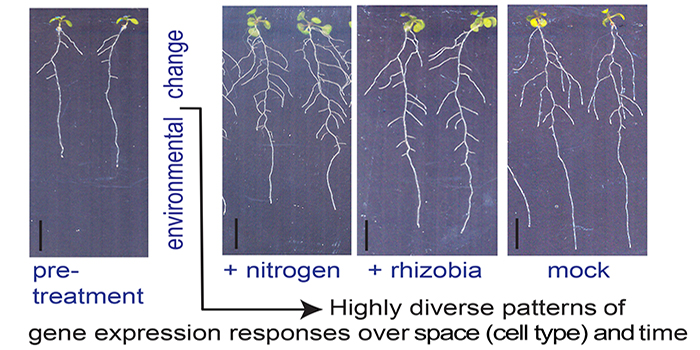
Space-Time Continuum of Gene Expression in Lateral Root Development
Research, The Plant Cell, The Plant Cell: In a NutshellWalker et al. explore how the environment shapes root architecture. The Plant Cell 2017. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.16.00961
By Liam Walker
Background: To acquire nutrients and anchor themselves, plant roots spread both vertically and horizontally in soil. Plants typically have a primary root…
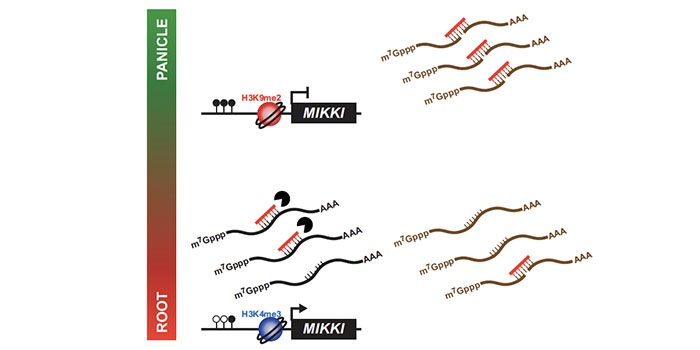
Regulation of rice root development by a retrotransposon acting as a microRNA sponge
Blog, Plant Science Research Weekly, Research, Research BlogTransposable elements are known to affect their neighboring genes, but they were so far unknown to affect the function of distant genes. Cho and Paszkowski observed a high level of transposon transcription expressed in rice. A transposon with root specific expression, MIKKI, was found to contain an imperfect…
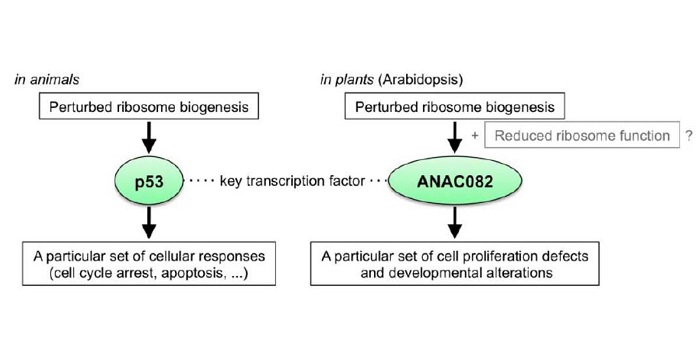
Proliferate at Your Own Risk: Ribosomal Stress and Regeneration
Blog, Research, Research Blog, The Plant Cell, The Plant Cell: In BriefPlant growth and development are extremely adaptable to changes in the external environment, including nutrient status, light quality and intensity, and temperature. Thanks to their developmental plasticity, plants can also initiate new organs from differentiated tissue following wounding, to the benefit…

Thrown for a Loop: How RNase H1 and DNA Gyrases Limit R-loops and Maintain Genome Stability in Chloroplasts
Blog, Research, Research Blog, The Plant Cell, The Plant Cell: In BriefWe all know that DNA is the stable nucleic acid, in comparison to its flighty, unstable cousin RNA, right? Well, unusual things happen when metabolic processes require DNA to unwind from its stable, redundant double-helical form. For example, during transcription, the RNA that exits RNA polymerase can…
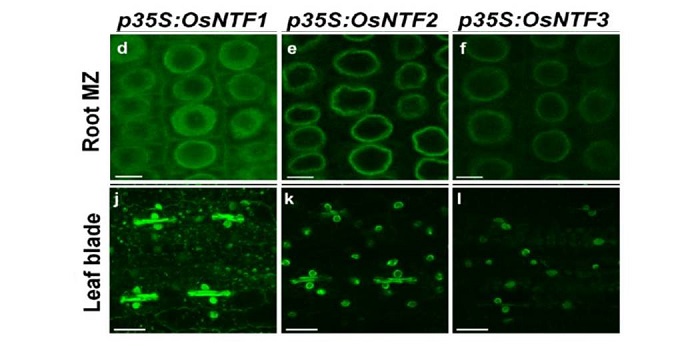
Nuclear transcriptomes at high resolution using retooled INTACT
Blog, Plant Science Research Weekly, Research, Research BlogReynoso et al. describe the Isolation of Nuclei from TAgged specific Cell Types (INTACT) in rice. In this method, modified from one described previously in Arabidopsis and tomato, nuclei are labeled with a biotinylated nuclear-envelope anchored protein. Best results were obtained when a rice WIP (WPP-Interacting…

BLADE-ON-PETIOLE proteins act in an E3 ubiquitin ligase complex to regulate PHYTOCHROME INTERACTING FACTOR 4 abundance
Blog, Plant Science Research Weekly, Research, Research BlogPlants need light not only for photosynthesis but also for light dependent development (called photomorphogensis). PHYTOCHROME INTERACTING FACTOR (PIF) proteins accumulate in dark to negatively regulate photomorphogensis. PIFs get degraded via 26S proteasome pathway in response to light e.g., PIF4 is…
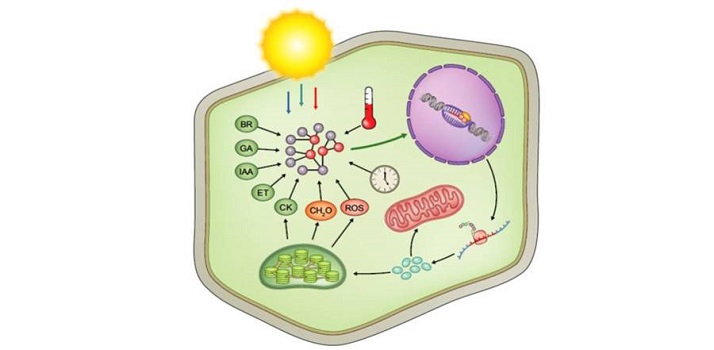
Review: Transcriptional control of photosynthetic capacity - conservation and divergence from Arabidopsis to rice
Blog, Plant Science Research Weekly, Research, Research BlogAbout 3000 genes are required for a plant to carry out photosynthesis. Wang et al. review the transcriptional control of these photosynthetic genes, drawing on transcriptomic and evolutionary studies to make comparisons between Arabidopsis and grasses. Photosynthesis of course starts with light, and…
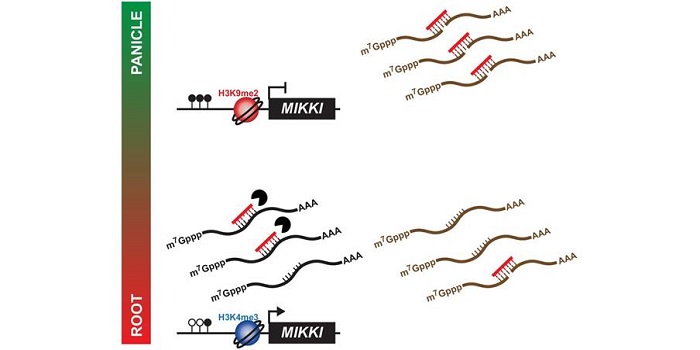
Regulation of rice root development by a retrotransposon acting as a microRNA sponge
Blog, Plant Science Research Weekly, Research, Research BlogTransposable elements (TEs) compose a considerable portion of most plant genomes, and mounting evidence shows various roles of TEs in the regulation of gene expression. Some TE transcripts have been hypothesized to work as “sponges” to help fine-tune the levels of miRNAs through complementary binding.…

