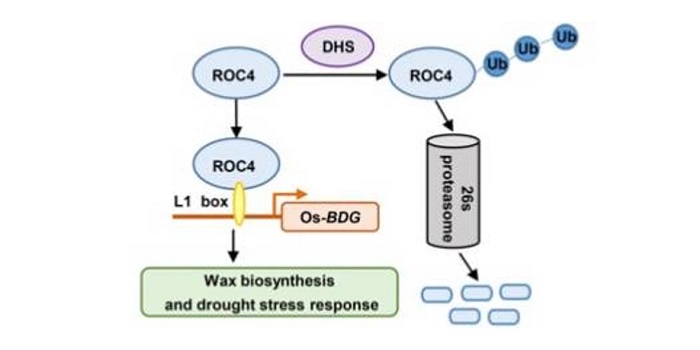
DROUGHT HYPERSENSITIVE negatively regulates cuticular wax biosynthesis by promoting the degradation of transcription factor ROC4 in rice
Blog, Plant Science Research Weekly, Research, Research BlogWax covering the outer surface of the shoot (epicuticular wax) is crucial in the ability of the plant to conserve water. Wang et al. identified a drought hypersensitive plant that overexpresses an E3 ubiquitin ligase which they named DROUGHT HYPERSENSITIVE. In these overexpression plants, there was a…

Mediator complex subunits in the regulation of phenylpropanoid biosynthesis ($)
Blog, Plant Science Research Weekly, Research, Research BlogThe Mediator complex is a transcriptional co-regulator that is conserved across kingdoms. Several subunits have been identified through genetic approaches in Arabidopsis. Recessive loss-of-function mutants of MED5 subunits cause phenylpropanoid overaccumulation, but ef4-3, a semi-dominant mutation of…
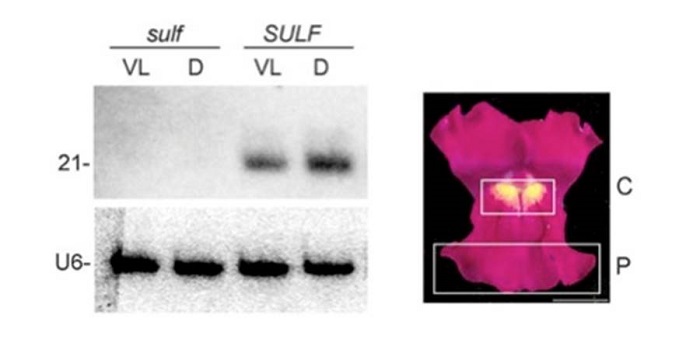
Regulatory small RNAs responsible for natural variation in snapdragon flower color patterning ($)
Blog, Plant Science Research Weekly, Research, Research BlogFlower color pattern is a major trait influencing pollinator attraction, but underlying regulatory mechanisms are still poorly understood. Using co-existing Snapdragon subspecies displaying different flower pigmentation motifs, Bradley et al. investigated the molecular basis of flower color patterning.…
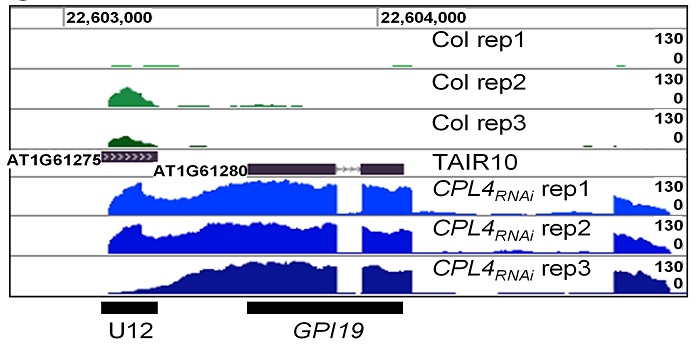
Granting an Extension: mRNAs Produced by Read-through from Small Nuclear RNAs
Blog, Research, Research Blog, The Plant Cell, The Plant Cell: In BriefThe C-terminal domain (CTD) of RNA polymerase II (Pol II) extends from the catalytic core and consists of repeats of a seven-amino acid motif. The CTD functions in the regulation of Pol II function and is subject to just about every protein modification you can think of, including methylation, acetylation,…
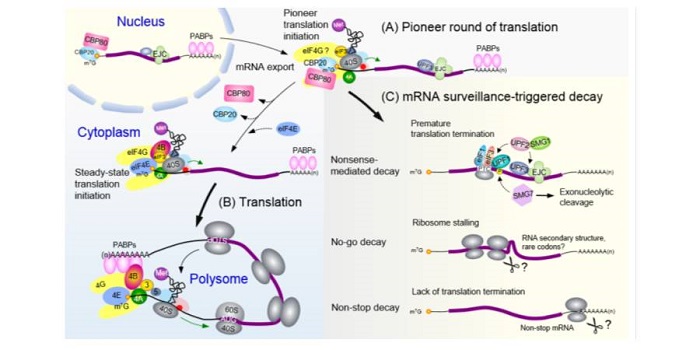
Update: Cytoplasmic mRNA dynamics
Blog, Plant Physiology: Updates, Research, Research BlogBy Thanin Chantarachot and Julia Bailey-Serres
The export of an mRNA from the nucleus to the cytoplasm begins an odyssey of dynamic regulation that determines the location, longevity and use of the transcript in the production of polypeptides by ribosomes in plant cells. Recent leveraging of mutants,…

Resistance to Wheat Stripe Rust
Blog, Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: On The Inside, ResearchWheat (Triticum aestivum) yields can be severely reduced by the obligate biotrophic pathogen Puccinia striiformis f. sp. tritici (Pst). Currently, approaches to manage this disease rely on cultivar resistance coupled with fungicide application. However, driven by a greater need for wheat production,…

Chromatin accessibility changes between Arabidopsis stem cells and mesophyll cells illuminate cell type-specific
Blog, Plant Science Research Weekly, Research, Research BlogWhat gives stem cells their plasticity and why are differentiated cells so specialized? Sijacic et al. approach this question by analyzing transcription factor (TF) accessibility to chromatin. Nuclei were isolated from shoot apical meristem (SAM) pluripotent stem cells and fully-differentiated mesophyll…
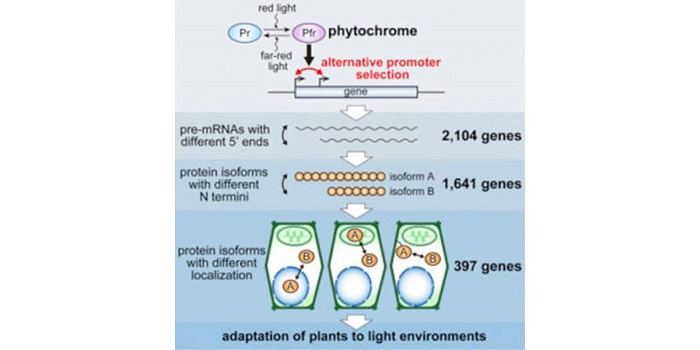
Light controls protein localization through phytochrome-mediated alternative promoter selection ($)
Blog, Plant Science Research Weekly, Research, Research BlogPrevious studies have shown that some genes use multiple promoters, but the extent to which this occurs has not been fully resolved. Ushijima et al. showed widespread phytochrome-mediated differential promoter use in response to light. They identified more than 2000 genes with light-dependent alternative…

Duplication of an upstream silencer of FZP increases grain yield in rice
Blog, Plant Science Research Weekly, Research, Research BlogThe trade-off between grain size and number has been traditionally hard to break. Bai et al established that differences in panicle architecture between two rice cultivars resulted from duplication of a long-distance silencer of the FRIZZY PANICLE (FZP) gene in one cultivar (Chuan 7). Increased silencing…

