
Review: The genomic basis of adaptation in plants ($)
Plant Science Research Weekly, Research0 Comments
/
Evolution starts with molecular variation and phenotypic diversity, upon which selection acts. Flood and Hancock review the approaches used to detect adaptive evolution. The top down approach starts with the phenotype and works to identify its genomic basis; examples are quantitative trait locus (QTL)…
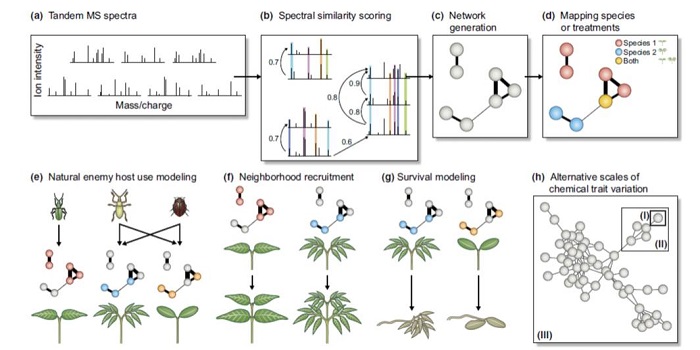
Review: The cryptic chemical traits that mediate plant community composition
Plant Science Research Weekly, Research, Research BlogPlants produce a huge variety of specialized metabolites, many with roles in defense. Metabolic profiles rarely follow phylogenetic lines; in fact, closely related species often produce dramatically different suites of metabolites. When it comes to defense chemistry, it is advantageous to be different…
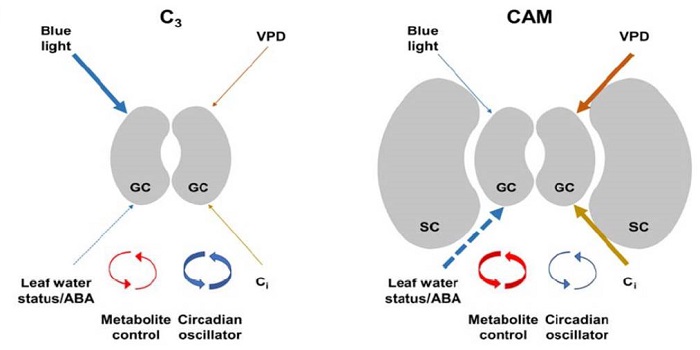
Update: Stomatal biology of CAM plants
Plant Physiology: Updates, Plant Science Research Weekly, Research BlogCrassulacean acid metabolism (CAM) plants open their stomata at night, decreasing water loss and increasing water-use efficiency as well as drought tolerance. Males and Griffiths review the stomatal biology of CAM plants as compared to C3 plants. For example, CAM stomata are relatively insensitive to…
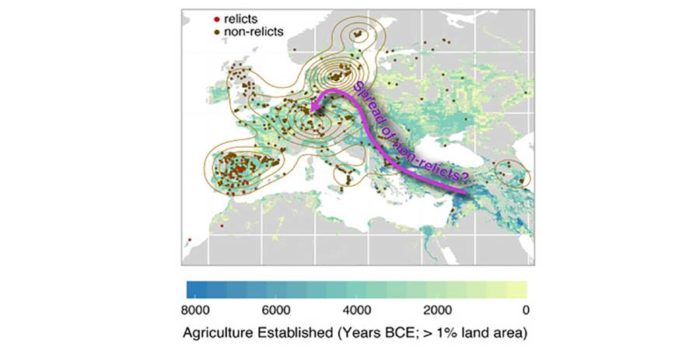
1135 Arabidopsis genomes reveal global pattern of polymorphism
Plant Science Research Weekly, ResearchThere are many accessions of Arabidopsis thaliana beyond the ecotypes predominantly used in research laboratories. In this article, The 1001 Genomes Consortium describe a resource based on whole-genome sequencing of 1,135 A. thaliana genomes from Europe, North Africa, and North America. This data…
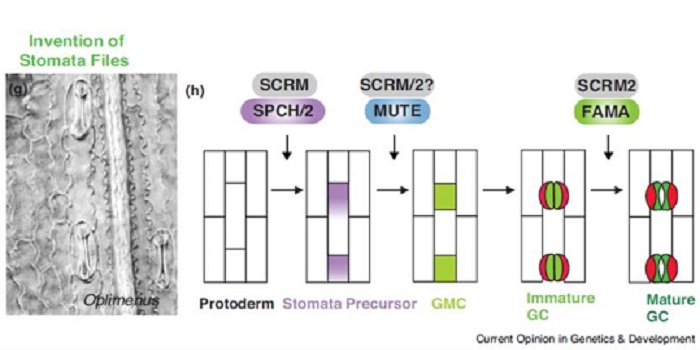
Review: Stomatal development in time: the past and the future ($)
Plant Science Research Weekly, ResearchStomata, epidermal pores for gas exchange, first appeared about 400 million years ago. Since then, there has been functional and structural diversification. Qu et al. synthesize the developmental genetics underpinning diverse stomata, spanning from bryophytes through monocots and the astomatous (without…
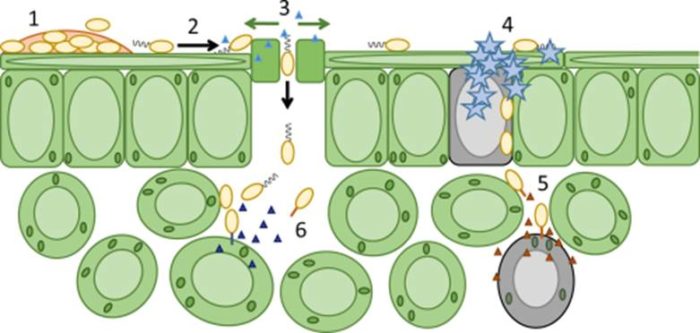
Reviews: Challenges in bacterial molecular plant pathology
Plant Science Research Weekly, ResearchMolecular Plant Pathology has released a new series of free reviews on “Challenges in Bacterial Molecular Plant Pathology.” Topics so far:
Morris et al. Frontiers for research on the ecology of plant-pathogenic bacteria: fundamentals for sustainability 1111/mpp.12508
Pfeilmeier et al. Bacterial…
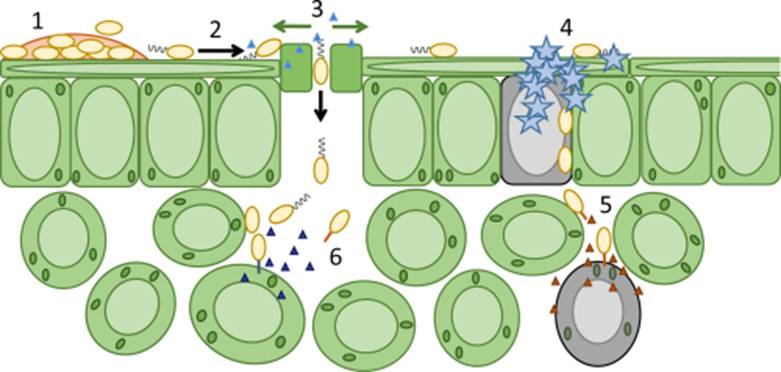
Reviews: Challenges in bacterial molecular plant pathology
Plant Science Research Weekly, ResearchMolecular Plant Pathology has released a new series of free reviews on “Challenges in Bacterial Molecular Plant Pathology.” Topics so far:
Morris et al. Frontiers for research on the ecology of plant-pathogenic bacteria: fundamentals for sustainability 1111/mpp.12508
Pfeilmeier et al. Bacterial…
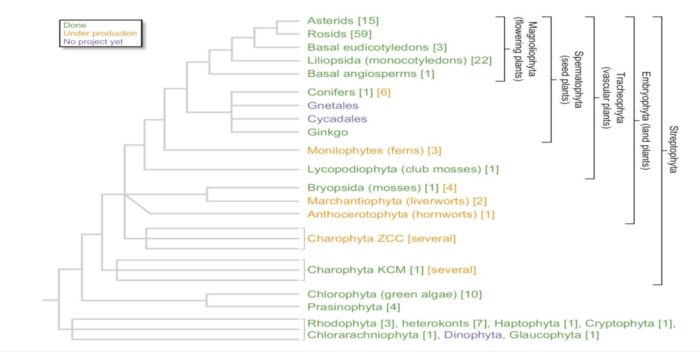
Insight: Why we need more non-seed plant models
Plant Science Research Weekly, ResearchThere is much to be learned from comparing plant genomes, but as Rensing writes, currently available genomic data are skewed heavily towards angiosperms. He argues that a richer understanding of plant evolution depends upon gaining insights into the non-seed plants, including ferns, mosses and liverworts,…
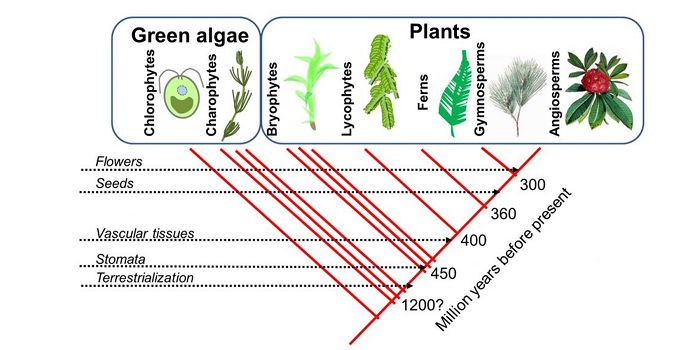
From LUCA to Lily: 12 perspectives for teaching about plants
Blog, Education, Resources, Resources, Undergraduate
The other day I was talking to a friend about the need to demystify plants, so that teachers feel as confident in their teaching of plant biology as they do about animal biology. I wonder if sometimes we teach plants too much in isolation, so it’s not always clear how plants relate to other organisms…

