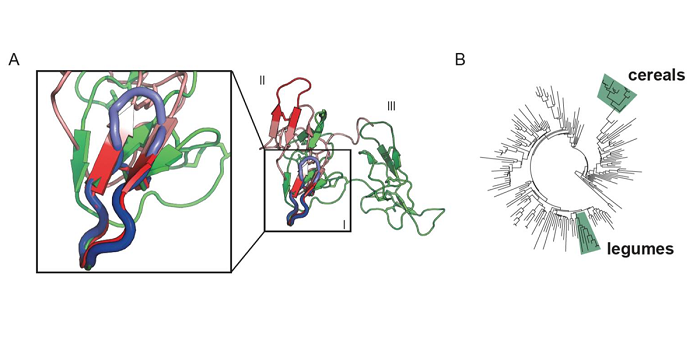
Evidence for Ancient Origins of Bowman-Birk Inhibitors from Selaginella moellendorffii
Plant Science Research Weekly, Research0 Comments
/
Many seeds produce protease inhibitors that are thought to help protect them from pathogens and predation. One class are the Bowman-Birk Inhibitors (BBIs), which form folded loops that specifically bind to and inhibit trypsin and/or chymotrypsin proteases. Originally characterized from legumes, BBIs…
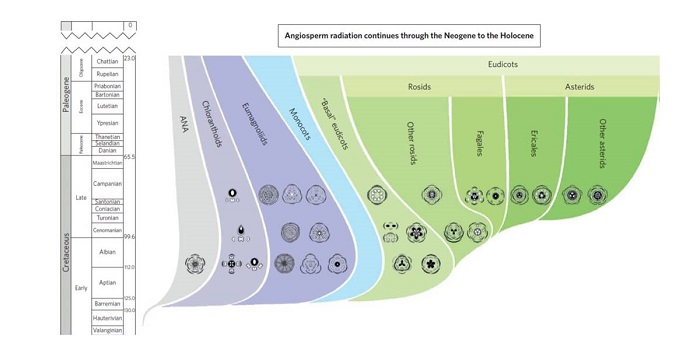
Review: Palaeobotanical redux: revisiting the age of the angiosperms
Plant Science Research Weekly, ResearchAlthough angiosperms are the dominant autotrophs in most parts of the world, their evolutionary origins remain somewhat mysterious. Herendeen et al. review the earliest evidence for angiosperms from the Early Cretaceous, and discuss fossil remains from earlier periods (Jurassic, Triassic) that have some…

A phenol-enriched cuticle is ancestral to lignin evolution in land plants
Plant Science Research Weekly, ResearchMoss are non-vascular plants and do not produce the phenolic polymer lignin, but they do have some enzymes associated with the lignin pathway, raising the question of the evolutionary origins of lignin. In angiosperms, the cytochrome P450 enzyme encoded by CYP98 catalyzes the first irreversible step…

The rice paradox: Multiple origins but single domestication in Asian rice
Plant Science Research Weekly, ResearchRice is the world’s most important food crop and its domestication was a key event in human history. Centuries of propagation across large geographical areas have resulted in five domesticated subpopulations: aus, indica, temperate japonica, tropical japonica, and aromatic rice. Choi et al. analyzed…
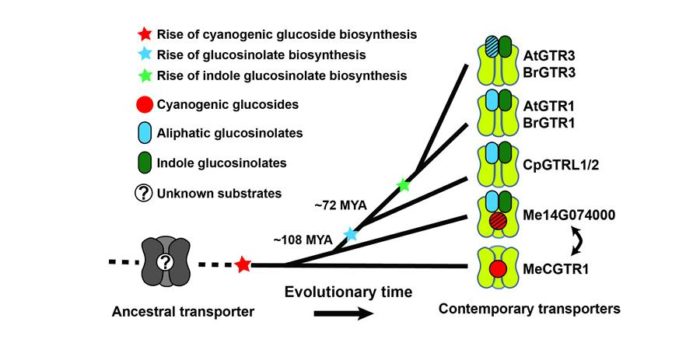
Origin and evolution of transporter substrate specificity within the NPF family
Plant Science Research Weekly, ResearchWhich arose first during evolution- a metabolite molecule or a transporter that could move it across a membrane? Jørgensen et al. studied transporters for glucosinolate defense molecules in Brassicales species. Glucosinolates are derived from the broad class of cyanogenic glucosides, and glucosinolates…
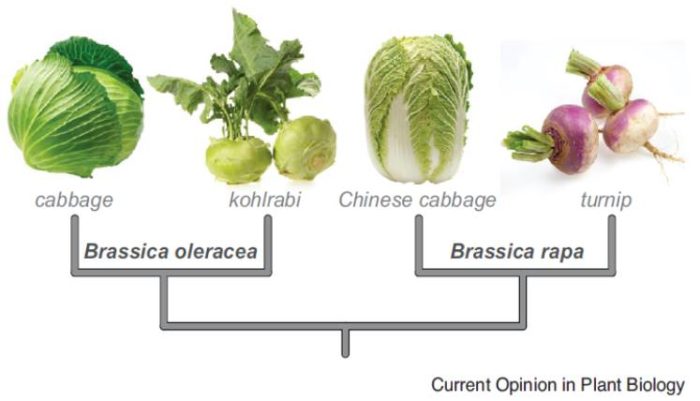
Review: Using mustard genomes to explore the genetic basis of evolutionary change ($)
Plant Science Research Weekly, ResearchBrassicaceae is one of the largest angiosperm families and provides many opportunities for studies of evolution. Of course, its most famous species, Arabidopsis thaliana is an important resource, but Brassicaceae also includes the very interesting Brassica crops (cabbage, turnip) that demonstrate the…
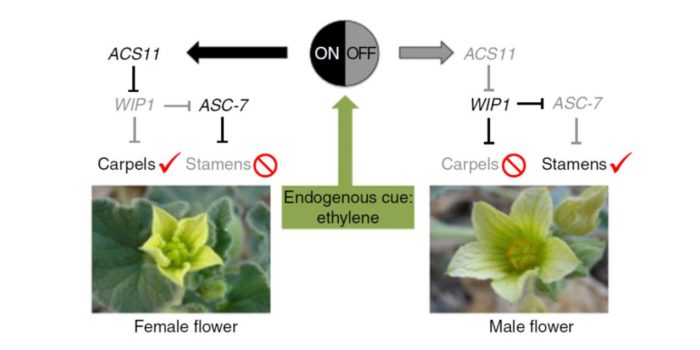
Review: Plant sex determination
Plant Science Research Weekly, ResearchMost angiosperms are hermaphrodites and produce flowers that have both male (stamens / sperm) and female (carpels / egg) parts. Pannell reviews the developmental and genetic programs that lead to these “perfect” flowers, as well as those that underlie reproductive structure development in dioecious…

Protein doppelgangers are long-lost cousins
Research, Research BlogWednesday, 15 March 2017 Source: University of Western Australia
A 60-year-old mystery has been solved by biochemists at The University of Western Australia investigating the origin of a type of digestion-inhibiting proteins thought only to exist in two plant families that contain the important…
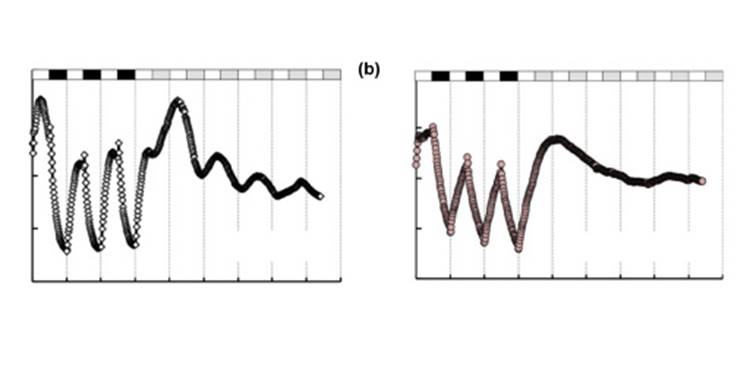
Early evolution of the land plant circadian clock
Plant Science Research Weekly, ResearchClocks in green algae have been described as simple two-gene loops, while clocks in angiosperms have evolved to complex interlocked loops. This striking jump in complexity led Linde et al. to investigate the clocks in bryophytes and charophytes to shed light on this transition. First, through the sequence…

