
A DNA Methylation Reader with an Affinity for Salt Stress
Blog, Research, The Plant Cell, The Plant Cell: In BriefHigh levels of soil salinity lead to toxic accumulation of sodium (Na+) and chloride (Cl-) ions in plants, which adversely affect plant growth and yield. Plants use several strategies to cope with salt stress. These include removal and compartmentalization of toxic ions, and maintenance of growth and…
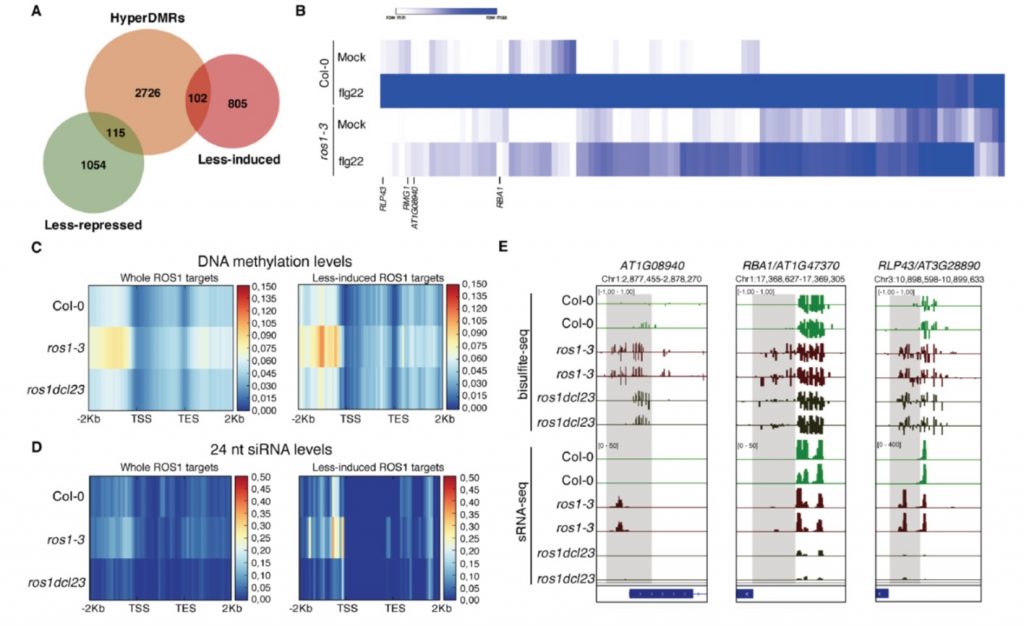
Active DNA demethylation controls defense gene regulation and antibacterial resistance (bioRxiv)
Plant Science Research Weekly
Epigenetic reprogramming, such as DNA methylation changes, has emerged as a crucial regulator of plant defense responses. Homeostasis of DNA methylation is controlled by a balance between methylation and demethylation. ROS1 (Repressor Of Silencing 1) is an Arabidopsis demethylases that is known to…
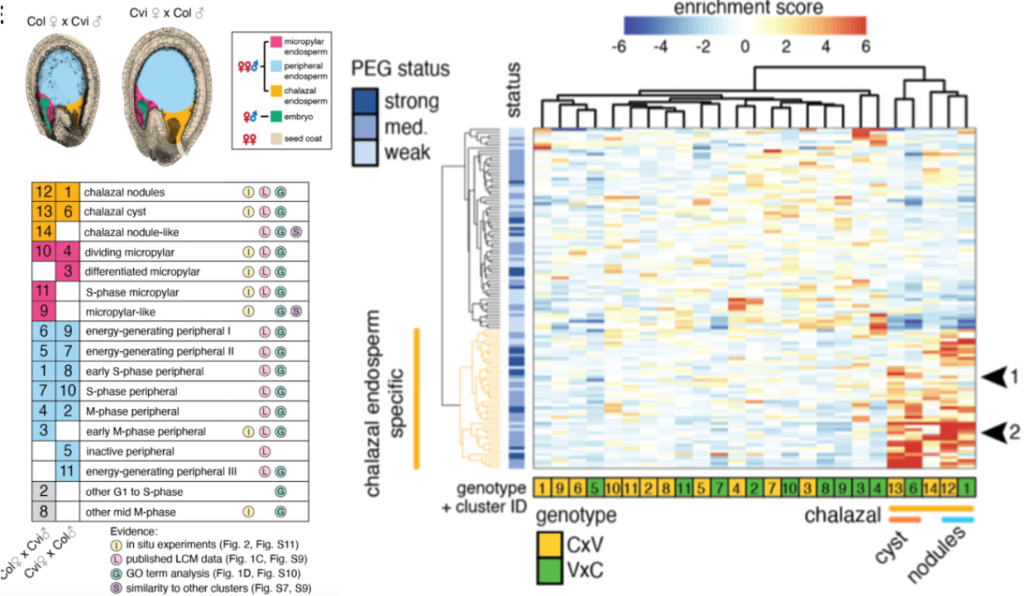
Single nucleus analysis of Arabidopsis seeds reveals new cell types and imprinting dynamics (bioRxiv)
Plant Science Research WeeklyArabidopsis seeds consist of various tissue like seed coat, embryo, and endosperm. The endosperm provides the nutrient supplies to the growing embryo and has three domains namely, micropylar (surrounding embryo), chalazal (opposite end of the seed), and peripheral (in between micropylar and chalazal)…

In the Transcripts: Long-read Transcriptomics Enables a Novel Type of Transposable Element Annotation in Plants
Blog, Research, The Plant Cell, The Plant Cell: In BriefTransposable Elements (TEs) are mobile genetic elements and major constituents of eukaryotic chromosomes. TEs promote genetic and epigenetic variation within genomes and are a major source of evolutionary novelty and adaptation (Lisch, 2013). In plants, TEs represent from 20% of the genomic content in…

The 3′ processing of antisense RNAs physically links to chromatin-based transcriptional control (PNAS)
Plant Science Research WeeklyIn Arabidopsis, multiple genetic pathways control the floral transition in response to external and internal stimuli. Among these, components of the autonomous pathway promote flowering by negatively regulating the central floral repressor FLOWERING LOCUS C (FLC). Despite the wealth of information on…
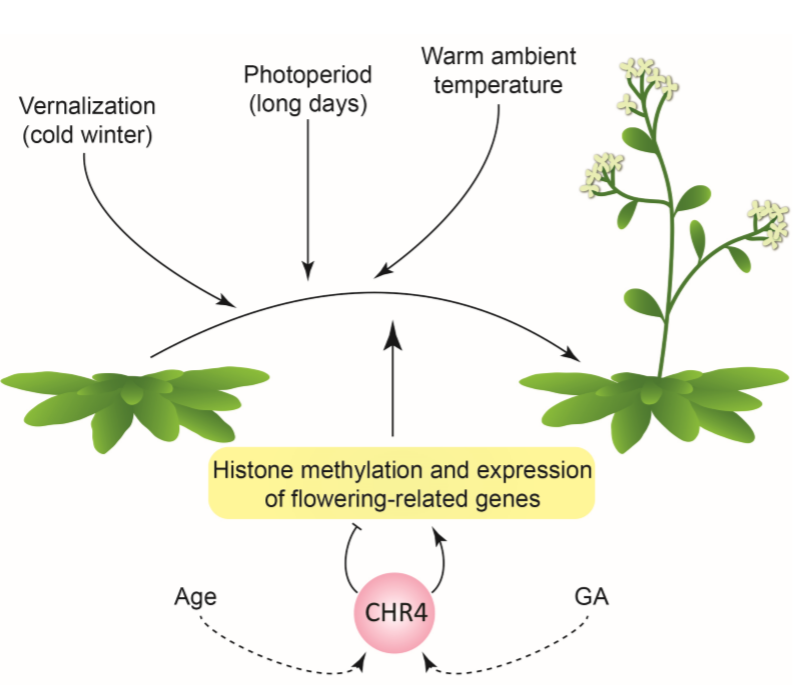
Roles for CHROMATIN REMODELING 4 in Arabidopsis floral transition (Plant Cell)
Plant Science Research WeeklyThe time at which flowers appear is critical for plant reproductive success. As such, the vegetative to reproductive growth transition is governed by several cues: environmental (photoperiod, temperature) and endogenous (gibberellins, age). Here, Sang et al. used an elegant forward-genetics approach…
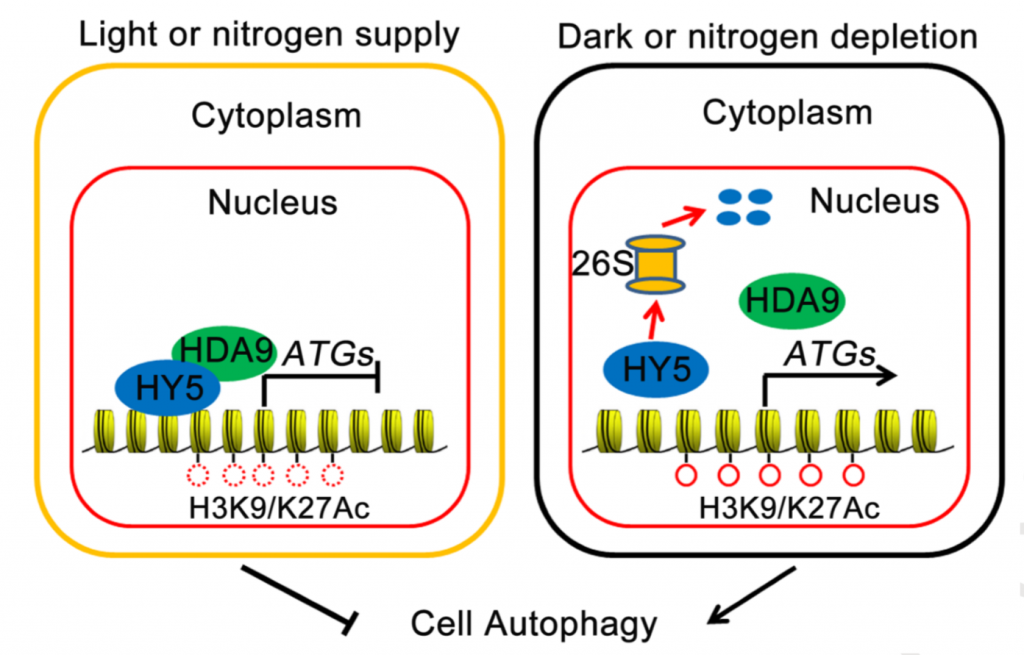
HY5 interacts with and recruits HDA9 to negatively regulate autophagy (Mol. Plant)
Plant Science Research WeeklyPlants activate autophagy, a cellular recycling process, to recycle useful nutrients or remove harmful items, helping them to withstand harsh conditions. Recently, Yang et al. found that HY5 is a hub connecting the light signaling and autophagy pathways. Under replete conditions (e.g., light and nitrogen-sufficient),…

Enhanced sustainable green revolution yield via nitrogen-responsive chromatin modulation in rice ($) (Science)
Plant Science Research WeeklyThe well-known success of the green-revolution was accomplished through the development of semi-dwarf grasses (rice and wheat), which led to decreased losses to lodging and higher yields; however, the benefits of these improved varieties depends on the application of nitrogen-rich fertilizer. As N-rich…
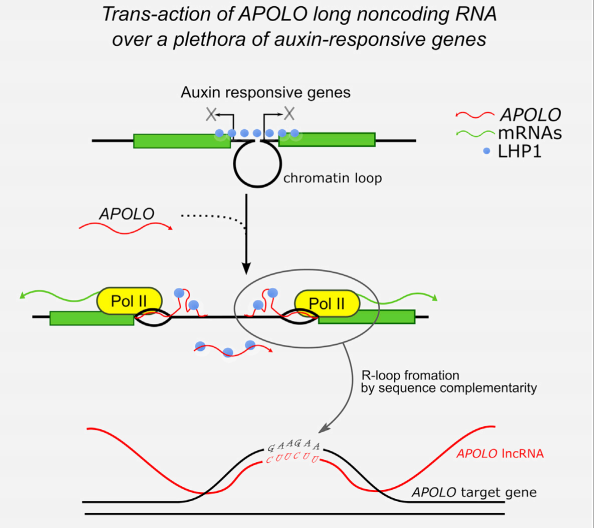
R-Loop Mediated trans Action of the APOLO Long Noncoding RNA
Plant Science Research Weekly
It was shown that the Arabidopsis intergenic long noncoding RNA (LncRNA) APOLO (AUXIN-REGULATED PROMOTER LOOP) modulates in cis its neighbor gene PID forming a chromatin loop. However, it remained unknown whether it can act also in trans modulating the expression of other genes. Now, Ariel et…

