
URM Plant Scientist Highlights - Thelma Madzima (she/her)
BlogDr. Thelma Madzima (she/her) is one of very few Black faculty in the USA who are plant molecular biologists. Originally from Zimbabwe, Thelma immigrated to the US at the age of 17 to attend college. She received her B.S. in Plant Science and Plant Biotechnology from Fort Valley State University, a historically…
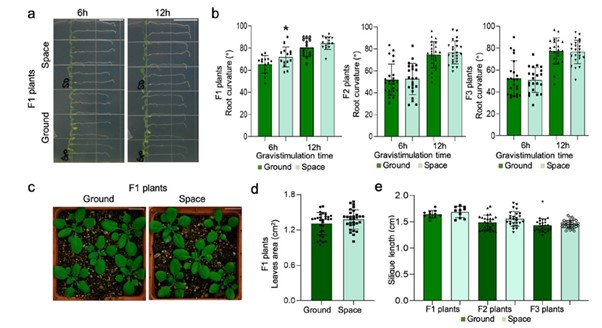
Potential evidence for transgenerational epigenetic memory in Arabidopsis thaliana following spaceflight (Commun. Biol.)
Plant Science Research WeeklyTransgenerational memory can occur through epigenetic regulation of gene expression (for example through DNA methylation) when plants have been exposed to abiotic stresses. Transferring a specific biochemical adaption to the next generation of plants can help the plant counter stress. Here Xu et al.…
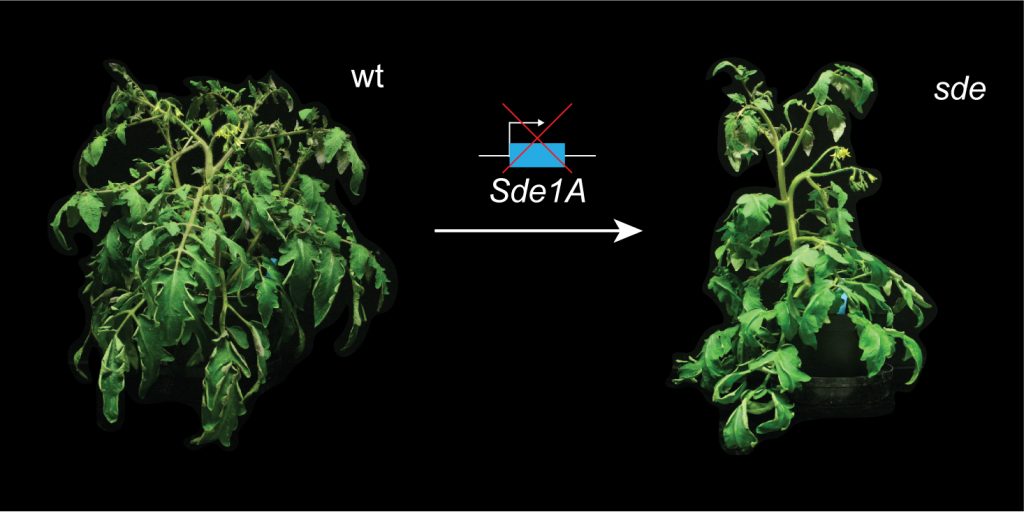
Sde1A enables axillary meristem formation at the leaf axil boundary
The Plant Cell: In a NutshellBy Hernán López and Klaus Theres, Max Planck institute for Plant Breeding Research.
López and colleagues identify the gene mutated in the tomato super determinant (sde) mutant, which affects vegetative shoot branching, but not seed set.
Background:
The degree of shoot branching is an important…
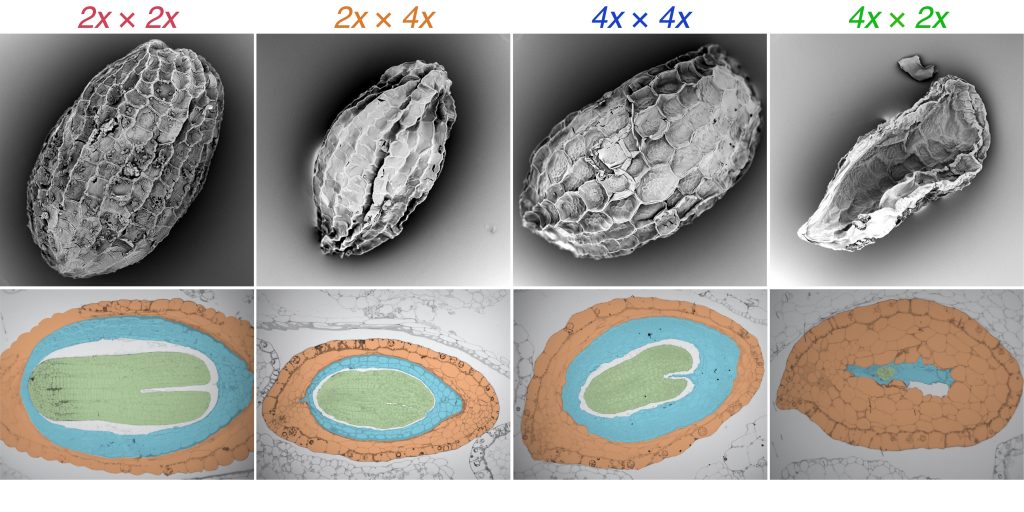
We’re just not compatible…. Plant species with different parenting strategies can’t quite coordinate in rearing hybrid babies
The Plant Cell: In a NutshellKinser and colleagues explore the transcriptomic, genomic and epigenomic consequences of mixing two genomes with the same number or twice as many chromosomes in monkeyflower.
By Taliesin Kinser (University of Florida) and Joshua Puzey (College of William and Mary)
Background: Flowering plants…
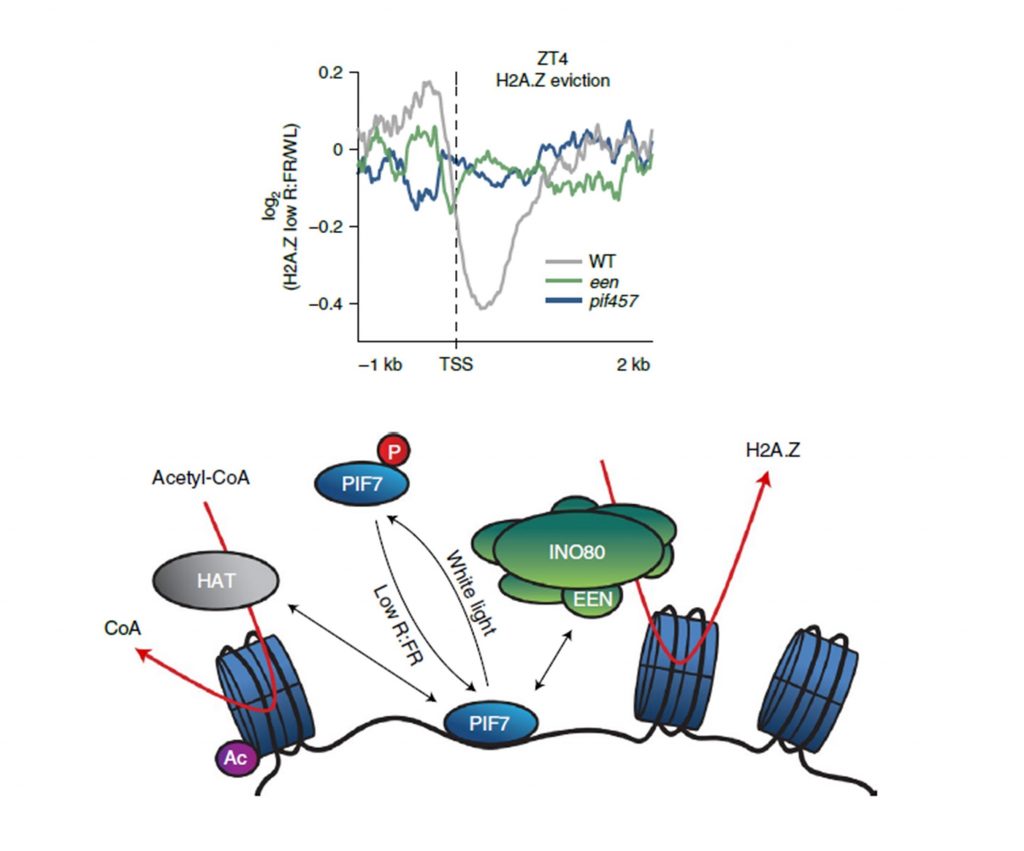
PIFs link environmental changes with chromatin dynamics (Nature Genetics)
Plant Science Research WeeklyPHYTOCHROME INTERACTING FACTORS (PIFs) play a pivotal role in mediating the responses of plants to various environmental stimuli. Although the importance of PIFs in shade avoidance response is well known, the relative contributions of different PIFs have not been discretely determined. In a recent study,…
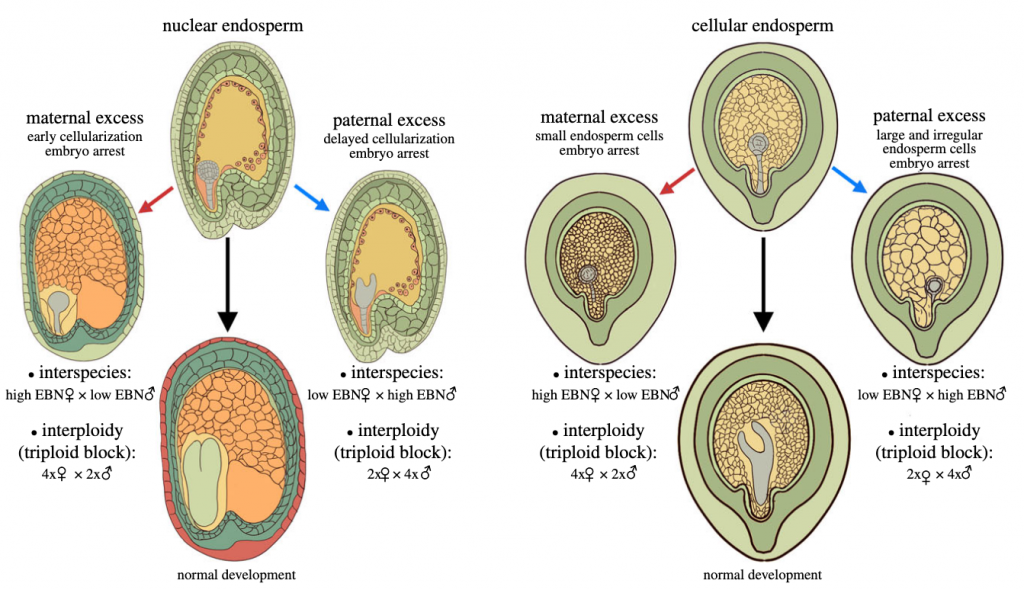
Review: Postzygotic reproductive isolation established in the endosperm: mechanisms, drivers and relevance ($) (Phil. Trans. R. Soc. B)
Plant Science Research WeeklyIn this fascinating review, Köhler and colleagues show us that the seed endosperm is not only a nutritive tissue that supports embryo growth, it also nourishes the course of plant evolution. When closely related species or species with different ploidy levels hybridize, endosperm development deviates…
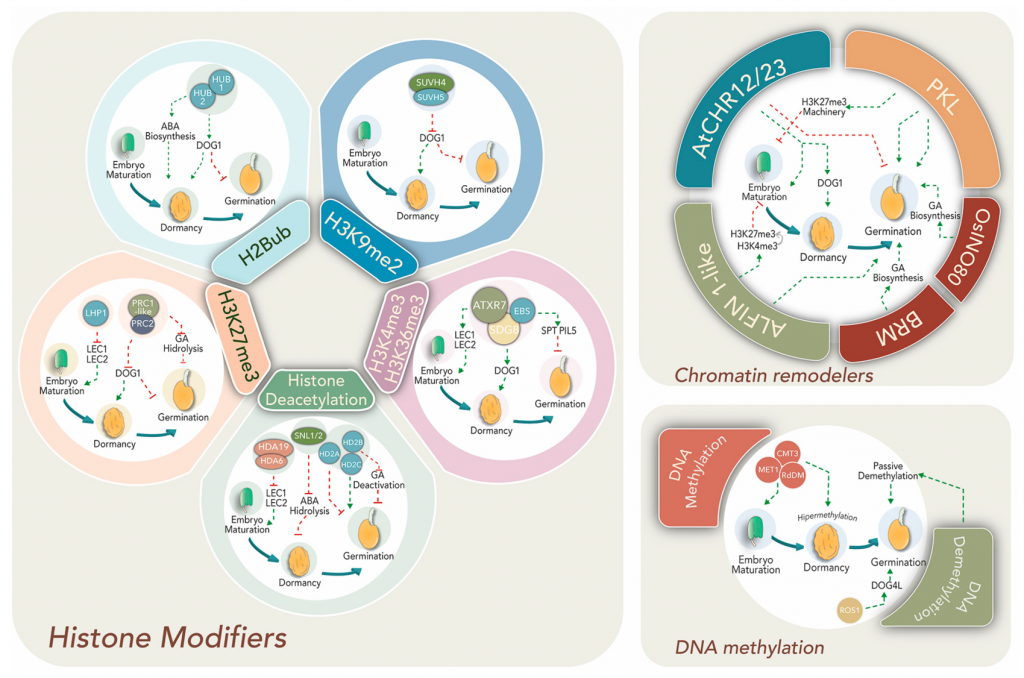
Review: Time to wake up: Epigenetic and small-RNA-mediated regulation during seed germination (Plants)
Plant Science Research WeeklySeed germination is a crucial step in plants' life cycle and has critical implications in ecological and agronomic contexts. Therefore, there has been an increasing interest in understanding the mechanisms that prevent or trigger this process. Here, Luján-Soto and Dinkova provide a thorough review of…
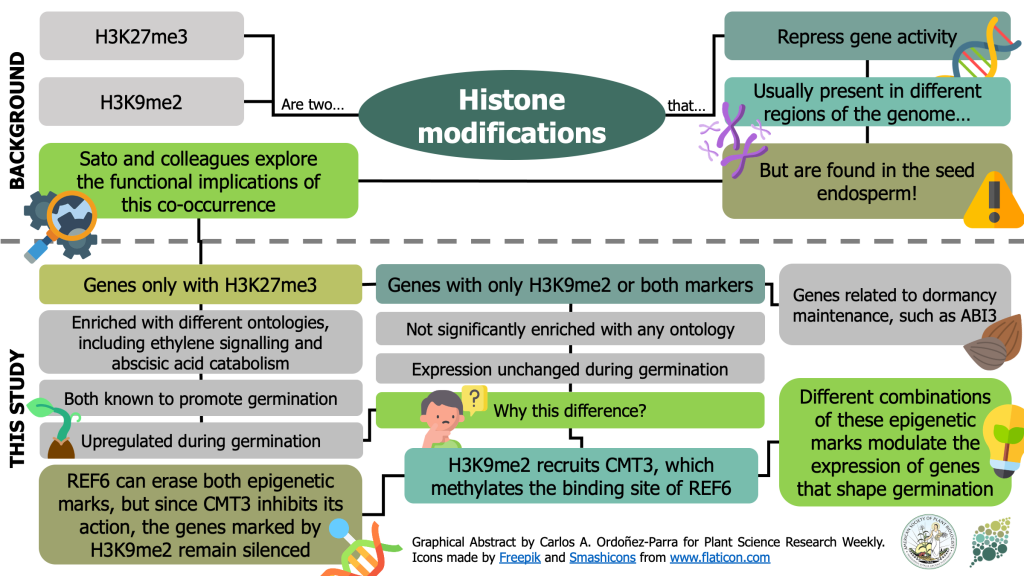
Combinations of maternal-specific repressive epigenetic marks in the endosperm control seed dormancy (bioRxiv.)
Plant Science Research Weekly
H3K27me3 [K27 (Lysine 27) trimethylation on histone H3] and H3K9me2 are two epigenetic modifications that repress gene activity in plants. While they are typically present in different genomic regions, both marks are found in the seed endosperm. Here, Sato and colleagues show that this histone modification…
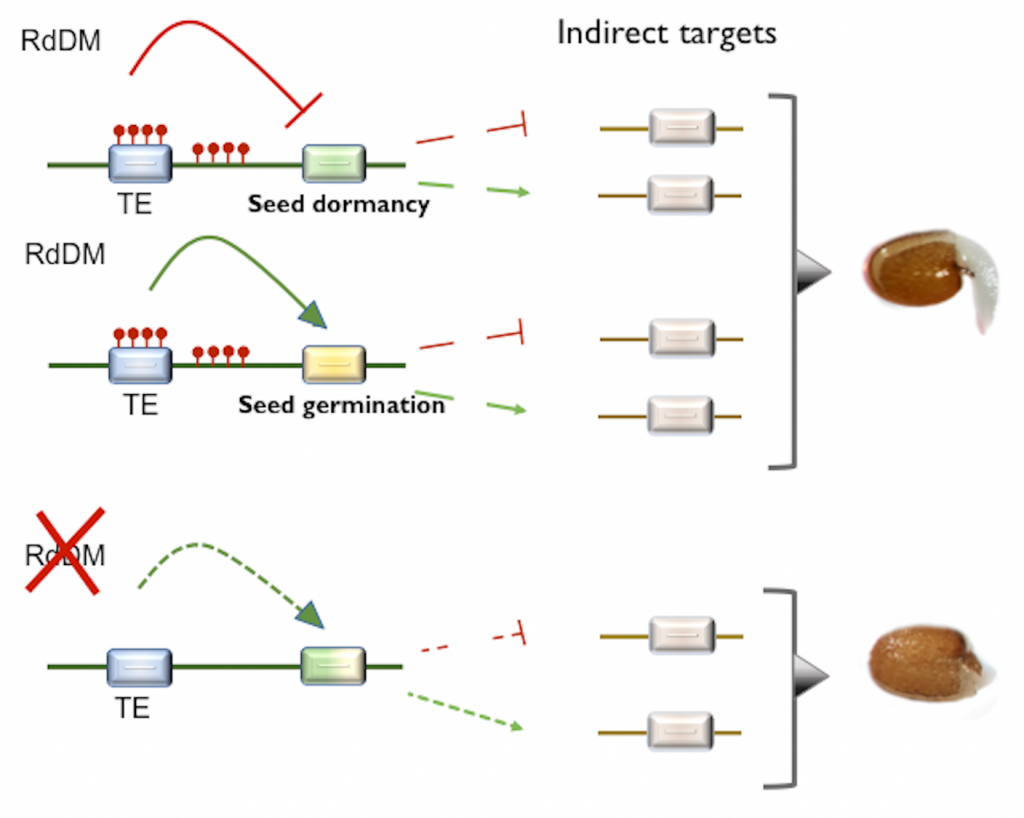
The canonical RdDM pathway mediates the control of seed germination timing under salinity ($) (Plant J.)
Plant Science Research WeeklyThe canonical RdDM pathway mediates the control of seed germination timing under salinity ($)
Epigenetic regulation can ensure that plant developmental programs and stress responses are tightly coordinated so that environmental changes do not compromise plant fitness. One of the mechanisms to achieve…

