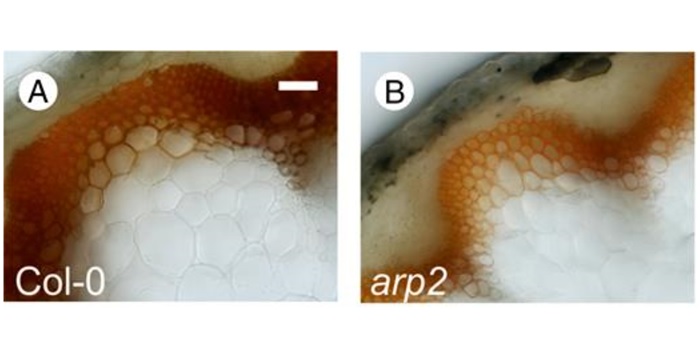
Arabidopsis thaliana plants lacking the ARP2/3 complex show defects in cell wall assembly and auxin distribution
Blog, Plant Science Research Weekly, Research, Research BlogThe plant cytoskeleton determines cell shape and integrity by delivering cellulose microfibrils and other cell wall components to the plasma membrane and cell wall. Auxin is involved in establishing the polarity of cell expansion and auxin distribution is partly regulated by actin. Sahi et al. examine…
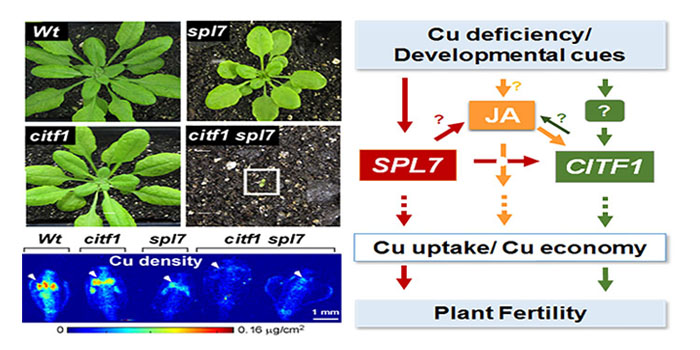
Anthers Crave Copper
Research, The Plant Cell, The Plant Cell: In a NutshellYan et al. searched for proteins that regulate the delivery of the micronutrient copper to flowers to ensure successful reproduction https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.17.00363
By Jiapei Yan, Ju-Chen Chia, and Olena Vatamaniuk
Background: Global food security and the demand for high-yielding grain crops…
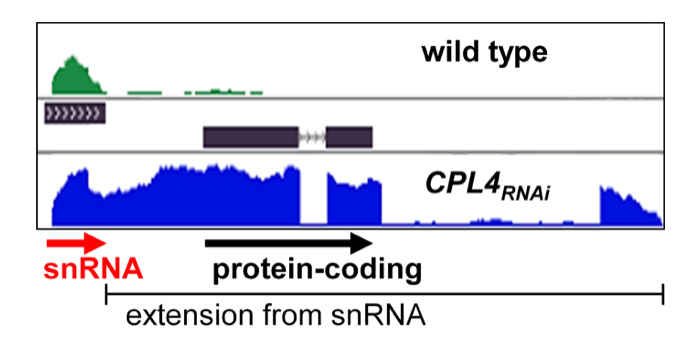
Transcriptional Switching Makes New Messages
Research, The Plant Cell, The Plant Cell: In a NutshellFukudome et al. explore the significance of Pol II C-terminal phosphorylation https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.17.00331
By Akihito Fukudome and Hisashi Koiwa
Background: In animals and plants, gene expression begins with an enzyme called RNA polymerase II (Pol II), which produces ribonucleic acid (RNA)…

Multiple Mediator Subunits Impact Metabolism
Research, The Plant Cell, The Plant Cell: In a NutshellDolan et al. examine how a complex that regulates gene expression alters the production of phenylpropanoids https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.17.00282
By Whitney Dolan and Clint Chapple
Background: Plants produce a vast array of compounds known as phenylpropanoids from the amino acid phenylalanine.…
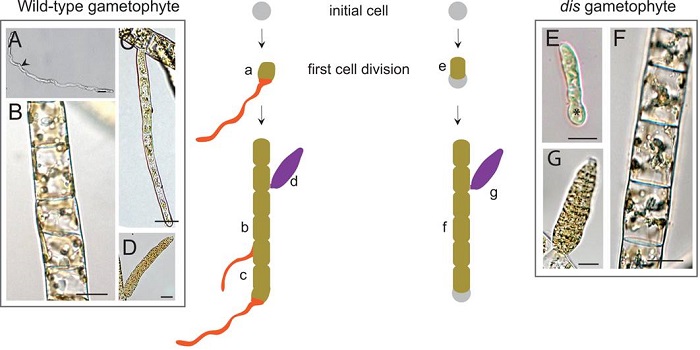
Axis of Algae: Disruption of Basal Cell Fates in the Brown Alga Ectocarpus
Blog, Research, The Plant Cell, The Plant Cell: In BriefPolarization may be bad for civil discourse, but sometimes polarization can be good—for example, if you’re a multicellular organism setting its body axes. In many organisms, polarity within the zygote sets the stage for an asymmetric cell division that defines the apical-basal polarity of the developing…
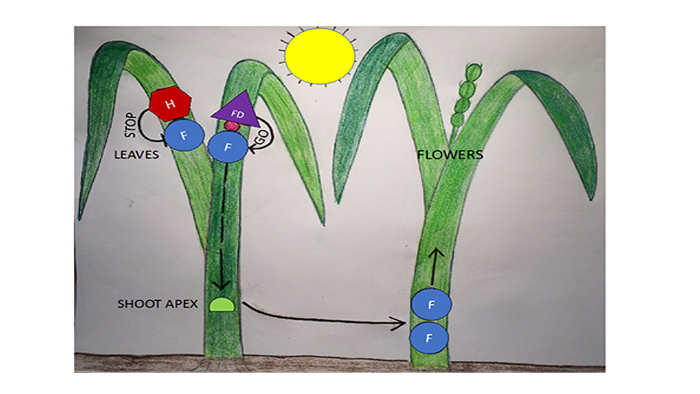
How Signals in Plant Leaves Influence Flowering
Research, The Plant Cell, The Plant Cell: In a NutshellBrambilla et al. describe antagonistic signals in rice leaves that control flowering https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.17.00645
By Vittoria Brambilla
Background: A plant’s lifecycle is marked by a major switch occurring when the plant stops producing leaves and starts to make flowers. This switch is…
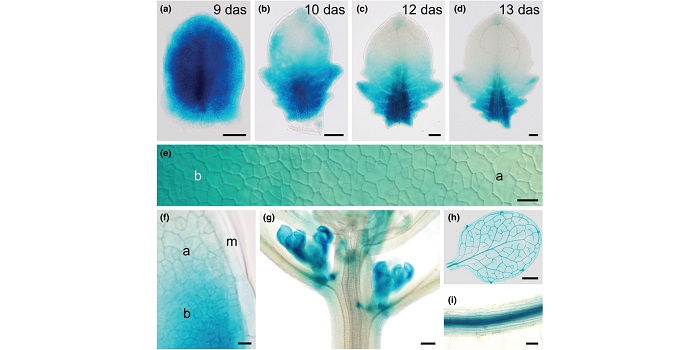
VASCULATURE COMPLEXITY AND CONNECTIVITY required for bilateral symmetry but not for dorsoventrality in Arabidopsis leaves
Blog, Plant Science Research Weekly, Research, Research BlogThe formation of the lobes at the Arabidopsis leaf margin are due to differences in local auxin accumulation, coordinated by auxin efflux carrier (PIN1) and transcriptional regulator (CUC2), but the molecular mechanisms acting upstream are not yet understood. Among viable leaf shape mutants, Wilson-Sanchez…

Update: Seedling establishment: a dimmer switch-regulated process between dark and light signaling
Blog, Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: Updates, Research, Research BlogBy Charlotte M.M. Gommers and Elena Monte
Abstract
By being exquisitely sensitive to their light surroundings, plants are able to continuously adjust their growth to optimize fitness. Darkness is an important cue for plants and a time when they actively grow and develop through regulation of the…

Engineering Increased Stomatal Density in Rice
Blog, Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: On The Inside, Research, Research BlogThe coordinated differentiation of cell types during the metamorphosis of an organ is crucial for ensuring that the final form of the organ is appropriate for itsfunction. A case in point is the photosynthetic function of plant leaves that requires chloroplast-containing cells in the middle leaf layers…

