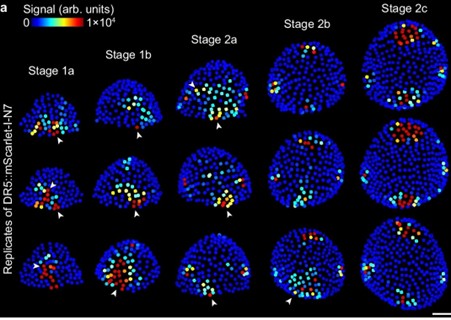
Stochastic gene expression, an ordinary part of multicellular life
Plant Science Research WeeklyStochasticity is an important feature of genes, allowing for variability in their abundance and activity prior to ‘fine-tuning’ at later periods of development. Kong et al. describe this feature in auxin responsive genes, attributing their ‘stochastic’- or inherently random expression – as…
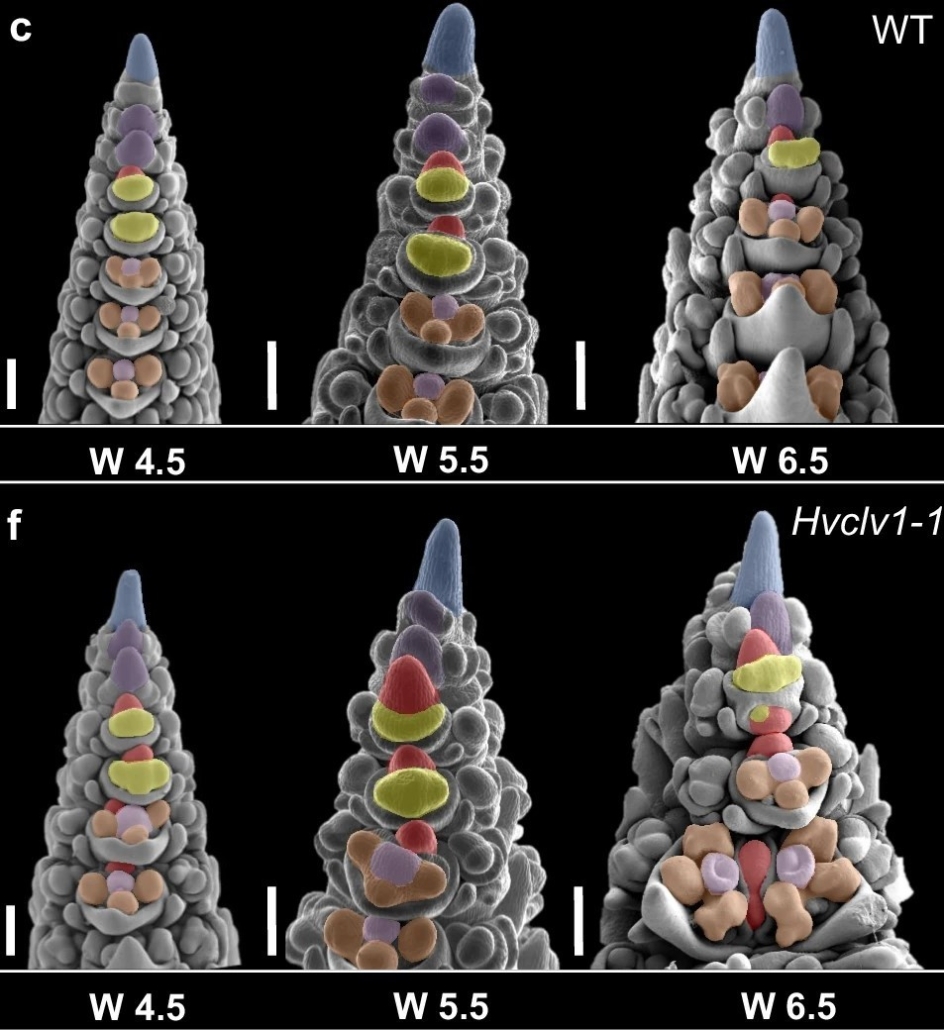
When CLV walked in fields of gold
Plant Science Research WeeklyA recent study by Vardanega et al. focuses on the development of the unique barley inflorescence architecture and unveils key molecular controls underlying meristematic determinacy. The CLAVATA3/EMBRYO SURROUNDING REGION-related (CLE) – CLAVATA1 (CLV1) interaction has been tied to meristem size and…
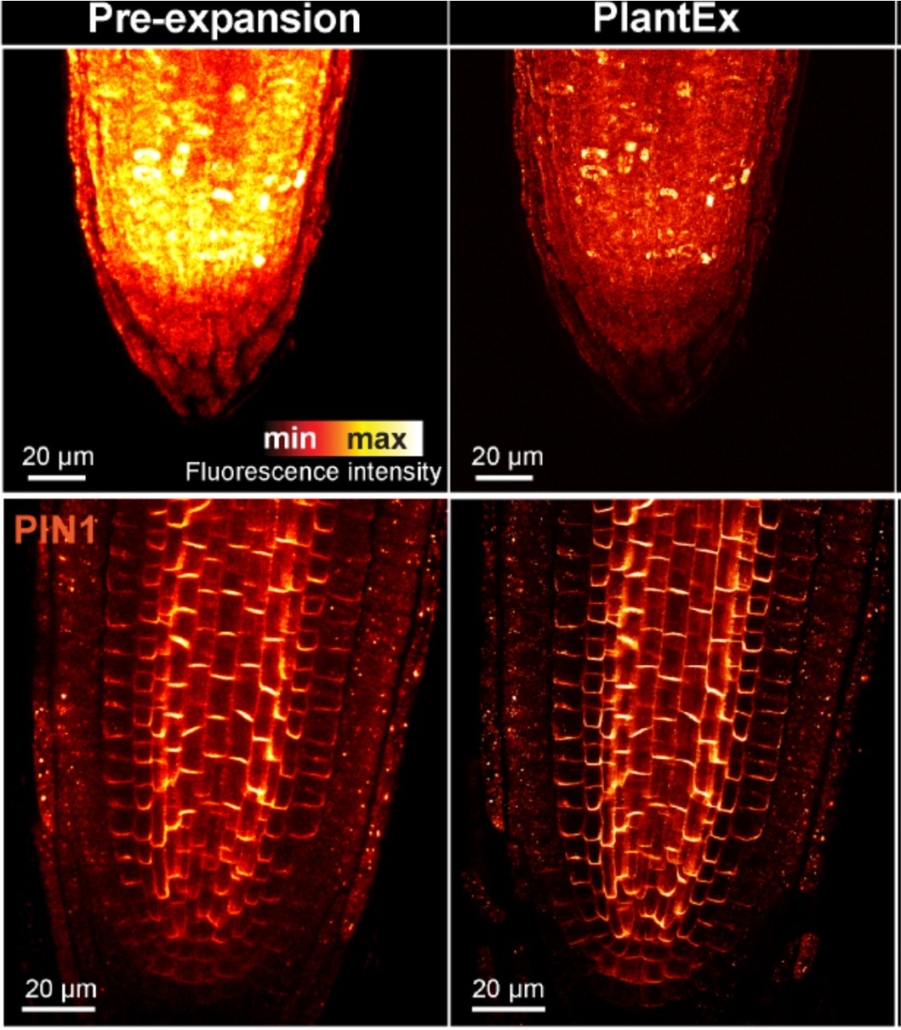

Expanding the resolution limits of conventional microscopy in whole plant tissues
Plant Science Research WeeklyHow can we precisely image plant tissues in super-resolution when approaching the optical limits of conventional microscopes? One solution lies in expansion microscopy, a technique that embeds tissue samples in an expandable hydrogel that proportionally increases the distances between structures, allowing…
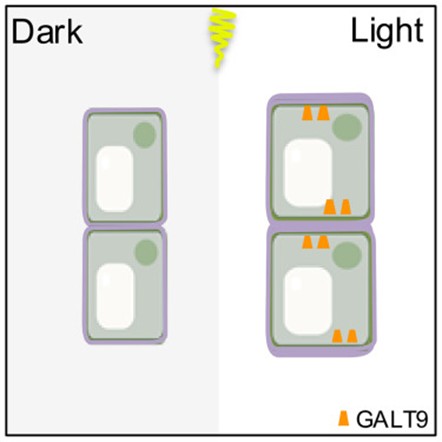
Lights, camera, pectin: Bringing hypocotyl elongation out of the dark
Plant Science Research WeeklyLight is a powerful signal, shaping plant development and growth. However, the cellular mechanisms that translate light signals into precise developmental responses are still being unravelled. The Arabidopsis hypocotyl (the embryonic stem, situated underneath the cotyledons in seedlings) rapidly restricts…
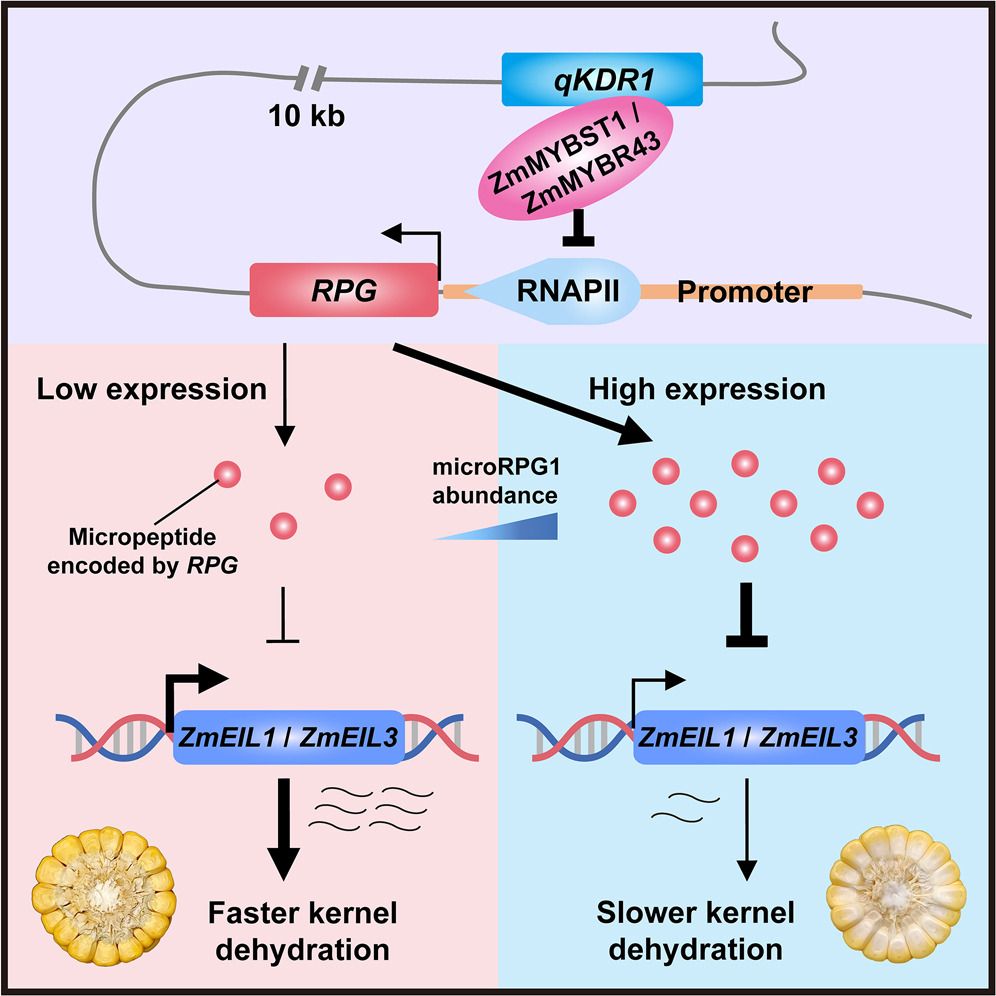
A novel micropeptide regulates kernel dehydration in maize through ethylene signaling
Plant Science Research WeeklyKernel dehydration rate (KDR) is a critical factor affecting mechanized maize harvesting and kernel quality. Despite its agricultural importance, the molecular mechanisms regulating KDR remain unclear. Previous studies have identified several QTLs controlling KDR, but their functional characterization…
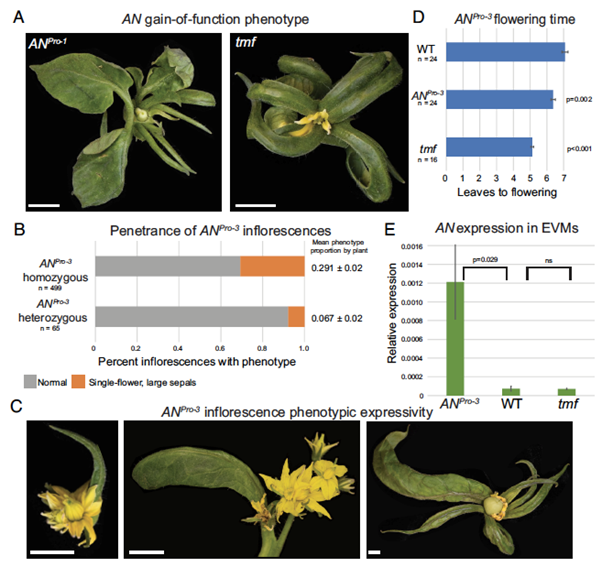
Developmental robustness from antagonizing cis-elements
Plant Science Research WeeklyDevelopmental transitions in plants are tightly regulated by transcriptional networks that require fine-tuned temporal and spatial control, with noncoding sequences in gene promoters playing a key role. The conserved transcriptional regulator UNUSUAL FLORAL ORGANS (UFO) is essential for floral development.…
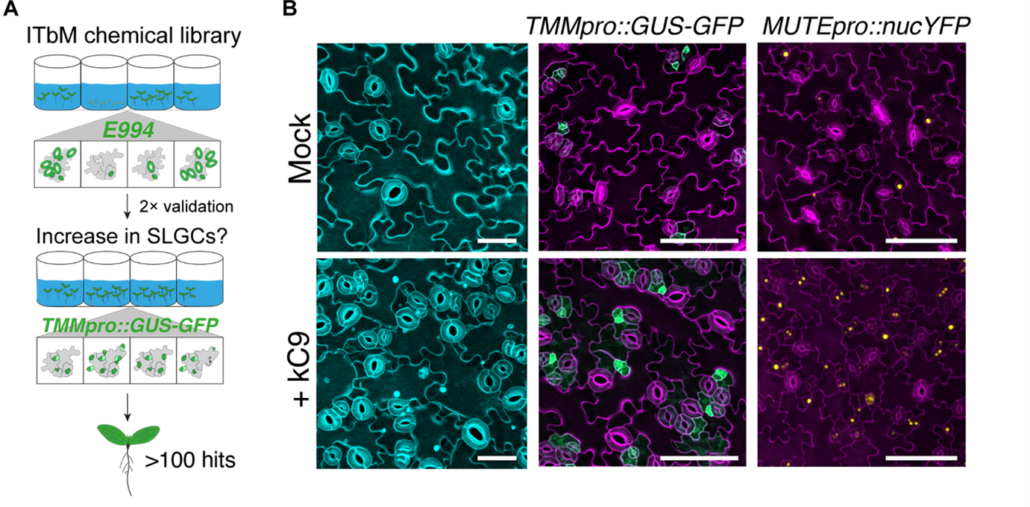
Finding balance: How plants achieve signal specificity in stomatal development and defense
Plant Science Research WeeklyPlants need to develop and grow within their environment whilst defending themselves against potential external threats. There are limited resources for these energy-intensive processes and so cross-talk is common between the signalling pathways to find balance between growth and defence. Hermann et…
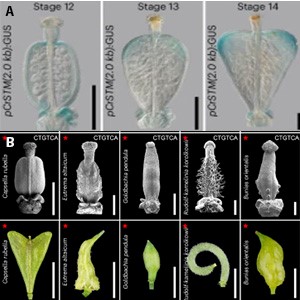
Capsella rubella: My Fruity Valentine
Blog, Plant Science Research WeeklyMost shapes in plant organs are pre-determined at the primordial stage and from this point, growth will establish and maintain this shape. Rarely will re-shaping of an organ occur post-organogenesis. However, Hu et al. describe a notable exception in Capsella rubella, a close relative of Arabidopsis…
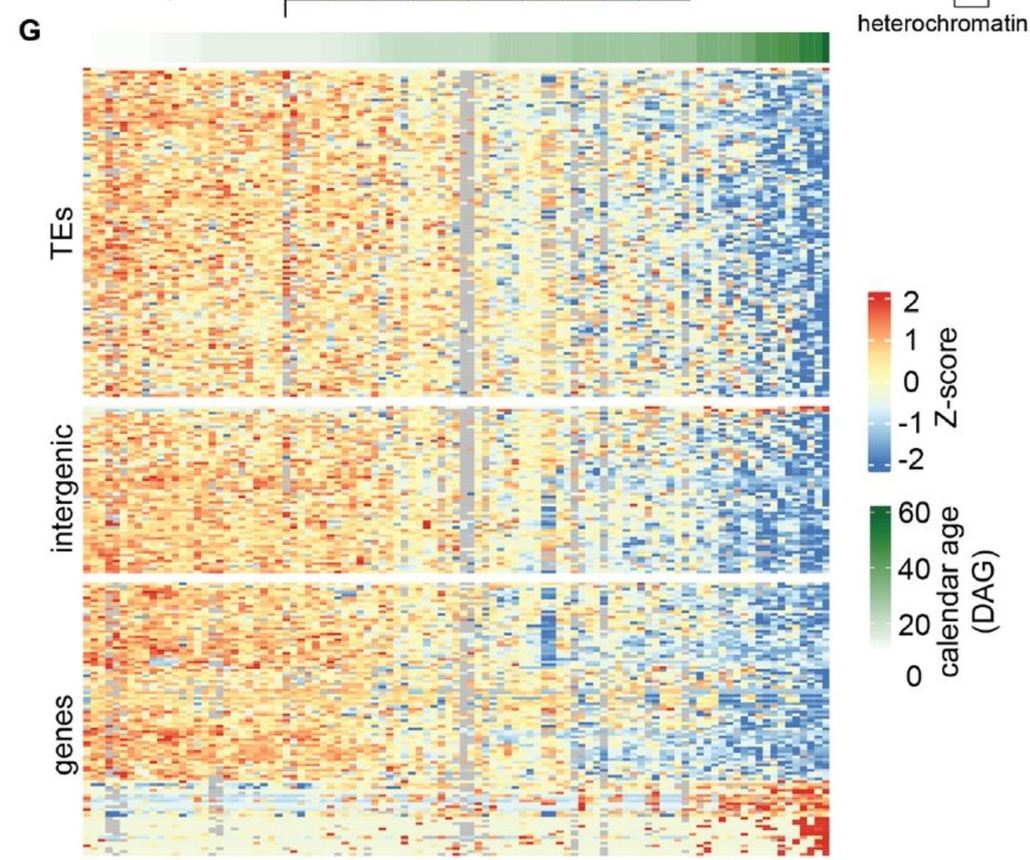
Epigenetic clocks in plants: uncovering DNA methylation decay in aging
Plant Science Research WeeklyWhat if plants could teach us about aging? Understanding how and why living organisms age is a fundamental question in biology and medicine. While most research focuses on humans, the model plant Arabidopsis thaliana offers unique insights into how organisms age. In a recent study, Dai et al. analyzed…

