VASCULATURE COMPLEXITY AND CONNECTIVITY required for bilateral symmetry but not for dorsoventrality in Arabidopsis leaves
The formation of the lobes at the Arabidopsis leaf margin are due to differences in local auxin accumulation, coordinated by auxin efflux carrier (PIN1) and transcriptional regulator (CUC2), but the molecular mechanisms acting upstream are not yet understood. Among viable leaf shape mutants, Wilson-Sanchez…

Update: Seedling establishment: a dimmer switch-regulated process between dark and light signaling
By Charlotte M.M. Gommers and Elena Monte
Abstract
By being exquisitely sensitive to their light surroundings, plants are able to continuously adjust their growth to optimize fitness. Darkness is an important cue for plants and a time when they actively grow and develop through regulation of the…

Engineering Increased Stomatal Density in Rice
The coordinated differentiation of cell types during the metamorphosis of an organ is crucial for ensuring that the final form of the organ is appropriate for itsfunction. A case in point is the photosynthetic function of plant leaves that requires chloroplast-containing cells in the middle leaf layers…

VERNALIZATION1 modulates root system architecture in wheat and barley
Root angle determines the rooting depth and was recently associated with the VERNALIZATION1 locus. Using hexaploid wheat, Voss-Fels et al. mapped the root angle to the locus encoding the MADS-box transcription factor, which was previously associated with flowering time. The group found that the lines…

Increasing leaf vein density in rice results in an enhanced rate of photosynthesis
Increased leaf vein density is considered to be a key early step in the evolution of C4 photosynthesis. Feldman et al. analyzed five mutants with high vein densities in the C3 crop rice to determine if photosynthetic assimilation was improved. The mutants all had higher photosynthetic rates under…
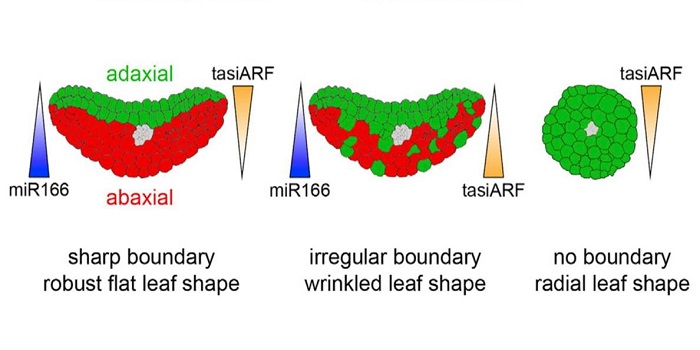
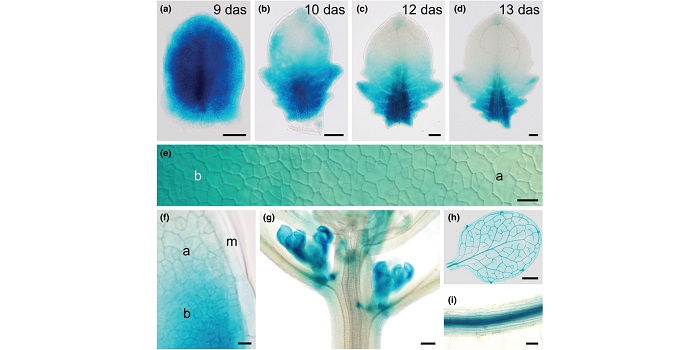
Boundary formation through direct threshold-based readout of mobile small RNA gradients
How does a flat leaf form? Previous studies have indicated that the formation of a flattened blade depends upon a boundary layer between the upper and lower cell layers, and that mobile small RNAs contribute to this boundary, but how this occurs is not fully resolved. For example, although the small…

J. Exp. Bot. Special Issue. The plant cuticle: old challenges, new perspectives ($)
The cuticle is a cell-wall polymer that protects against desiccation, pathogens and UV light. Domínguez et al. provide an open-access editorial that describes this fine collection of articles covering all aspects of the plant cuticle, from its evolutionary origins to its ecological significance. Within…

Chromatin accessibility changes between Arabidopsis stem cells and mesophyll cells illuminate cell type-specific
What gives stem cells their plasticity and why are differentiated cells so specialized? Sijacic et al. approach this question by analyzing transcription factor (TF) accessibility to chromatin. Nuclei were isolated from shoot apical meristem (SAM) pluripotent stem cells and fully-differentiated mesophyll…
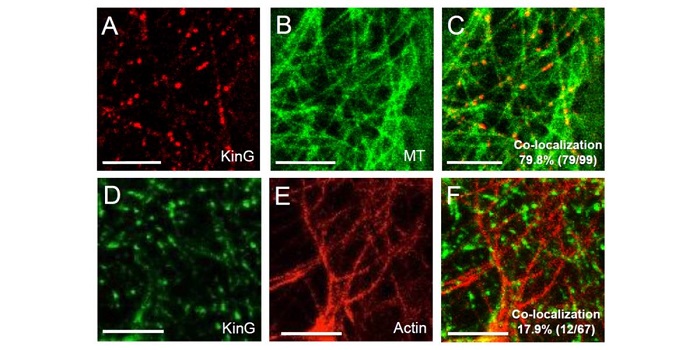
A plant-specific kinesin KinG regulates intra- and intercellular movement of SHORT-ROOT
SHORT-ROOT (SRT) is a transcription factor that has previously been shown to move between cells and so contribute to developmental patterning. Spiegelman et al. investigated the cellular machinery that contributes to SRT’s movement. Previous work showed that the movement of SRT depends on the endosome…

