
Plant Cell Wall Composition: Does Ploidy Matter?
Blog, Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: News and ViewsMost of the carbon dioxide sequestered by plants during photosynthesis is converted into sugars and stored into polysaccharide-enriched cells walls that constitute the majority of the plant biomass. While plants have long been considered a valuable resource of biomaterials for the chemical and textile…
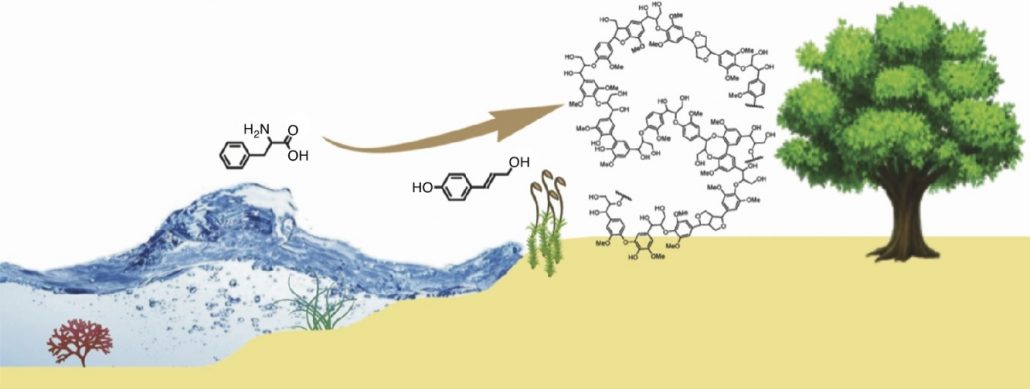
Special Issue - Plant Biotechnology, focus on lignin (Curr Opin Biotechnol) ($)
Plant Science Research WeeklyA forthcoming issue of Current Opinion in Biotechnology features a set of reviews on the topic of lignin, particularly its chemistry and applications. Lignin is a complex set of polymers that provide structural support to vascular plants (See Renault et al. for insights into lignin's evolutionary origins).…
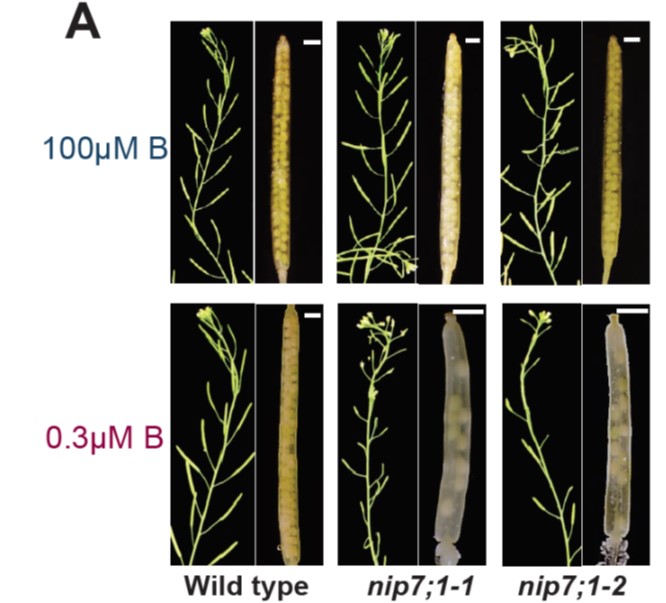

A Tapetal Boric Acid Channel Involved in Pollen Cell Wall Formation
Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: On The InsideBoron (B) is an essential plant micronutrient that plays a major role in cell wall structure and function by providing cross-linking of the rhamnogalacturonan II (RG-II) pectin component of the cell wall. Under normal pH conditions, B is found principally as boric acid. Although boric acid permeates…

Sweet and Juicy: Identification and Origins of the Dry Alleles in Sorghum
The Plant Cell, The Plant Cell: In BriefSorghum (Sorghum bicolor) is the fifth most important cereal crop globally and is considered to be the “camel among crops” due to its ability to flourish in low-nutrient soils and to withstand prolonged drought. Cultivated varieties are phenotypically and morphological diverse. Consequently, sorghum…
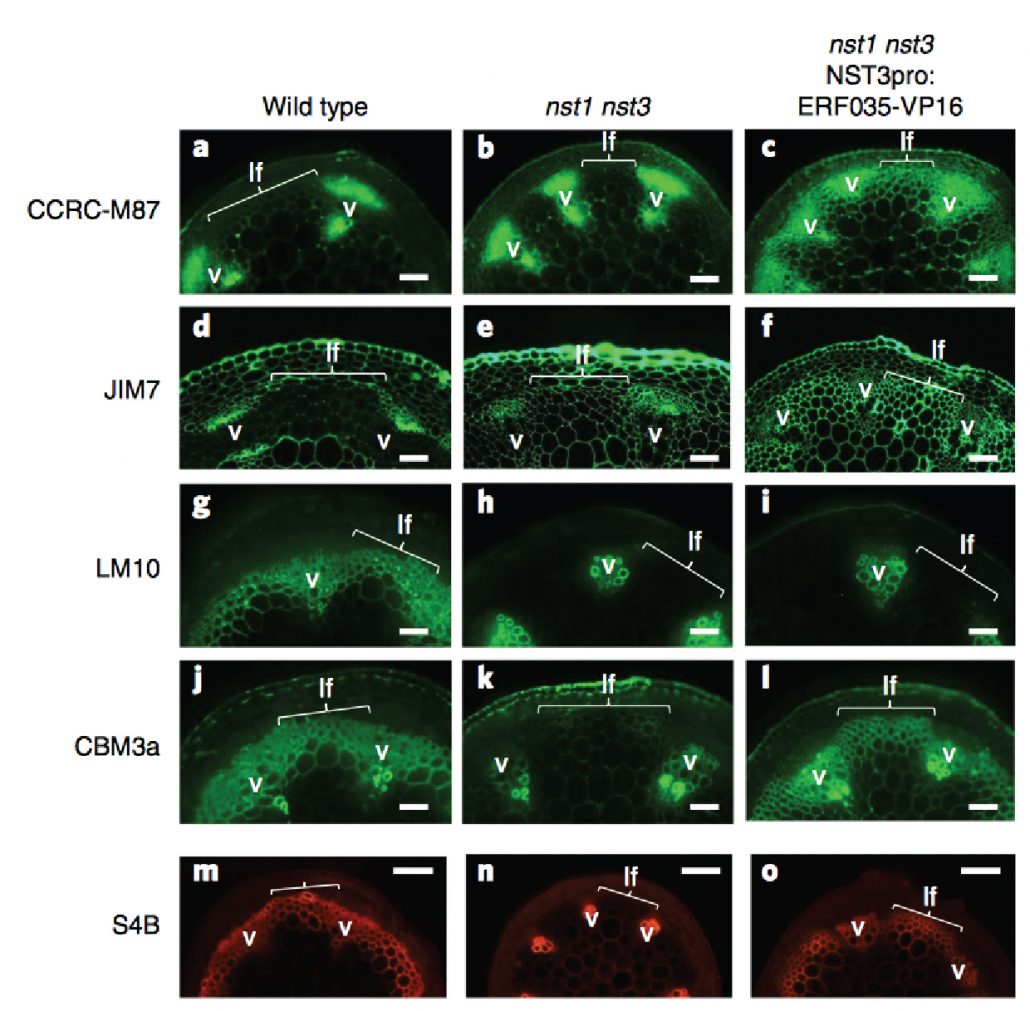
Complete substitution of a secondary cell wall with primary cell wall in Arabidopsis (Nature Plants - $)
Plant Science Research WeeklyPlant cell walls are important for terrestrial lifestyle, providing support and directing the plant growth. The primary and secondary cell walls differ in their chemical composition and flexibility. Secondary cell walls are less perceptive to industrial degradation processes and therefore pose problems…

Cellulose Synthase Stoichiometry Varies among Species and Tissues
Blog, Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: News and ViewsCellulose, the most abundant biopolymer on earth, is an important structural component of the primary and secondary cell wall of plant cells. It is also found in animals (tunicates), oomycetes, and bacteria (Kumar and Turner, 2015). Besides providing support and rigidity in living organisms, cellulose…
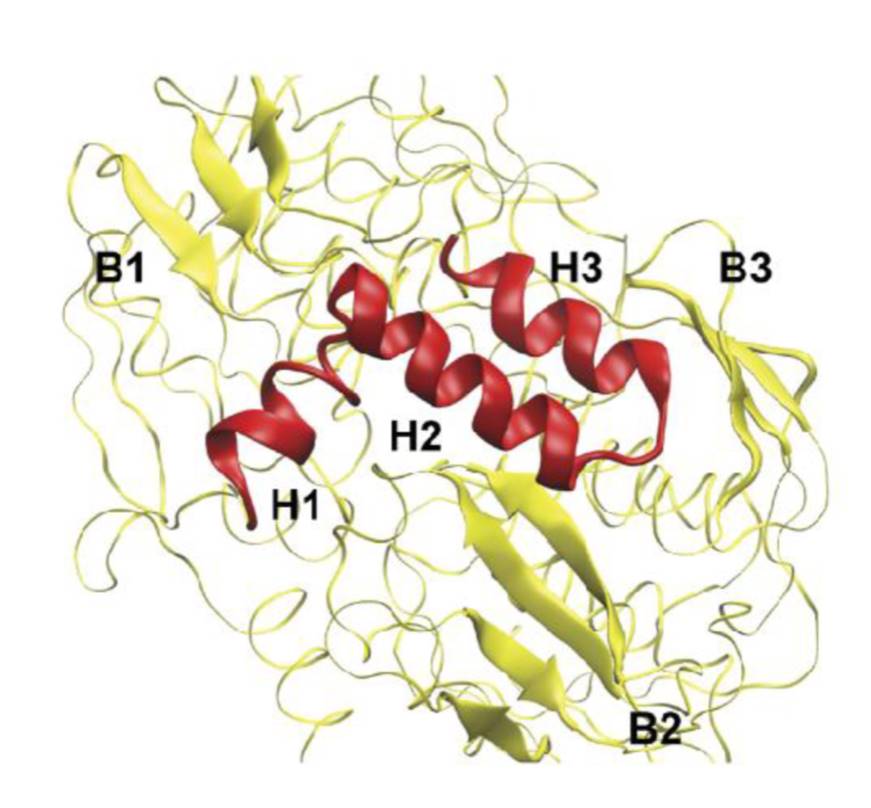
Enzyme helps as a transcription factor in lignin production
Blog, The Plant Cell, The Plant Cell: NewsArjen Dijkgraaf | Wednesday, July 4, 2018 (Originally published in C2W Boeken. Translation by Google Translate)
In poplars a protein appears to have a bizarre double function: it makes building blocks for amino acids but also regulates the production of lignin. It could be a new way to create…
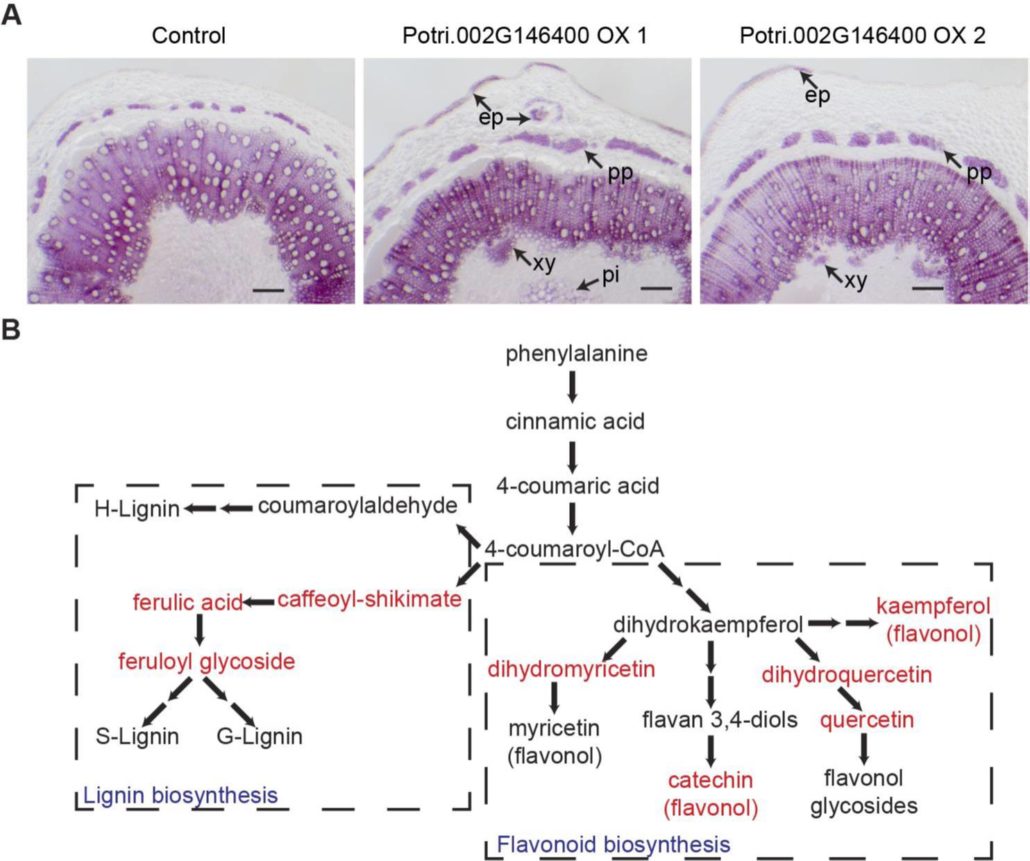
A 5-enolpyruvylshikimate 3-phosphate synthase functions as a transcriptional repressor in Populus
Plant Science Research WeeklyHere’s a fascinating story; starting with an association study, Xie et al. found that a protein previously identified as an enzyme involved in phenylpropanoid metabolism (specifically, 5-enolpyruvylshikimate 3-phosphate synthase, EPSP) also acts as a transcriptional regulator of this pathway, not only…
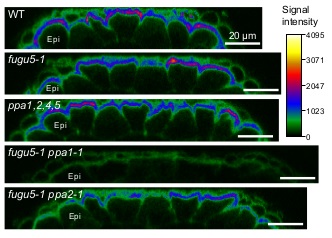
Life of PPi: Soluble PPases and H+-PPase act cooperatively to keep pyrophosphate levels in check
Blog, Research, The Plant Cell, The Plant Cell: In BriefInorganic phosphate (PPi) is a byproduct of many metabolic reactions, including those involved in sucrose, sugar nucleotide, and cellulose biosynthesis. Although PPi is an important phosphate donor and source of cellular energy, high levels of cytosolic PPi are toxic, disrupting the metabolic reactions…

