
Update on autophagy: Dynamics of autophagosome formation
By Junmarie Soto-Burgos, Xiao-Hong Zhuang, Liwen Jiang, and Diane C. Bassham
Autophagy, literally defined as “self-eating”, functions as a degradation process by recycling cytoplasmic contents under stress conditions or during development. Upon activation of autophagy, a membrane structure known…
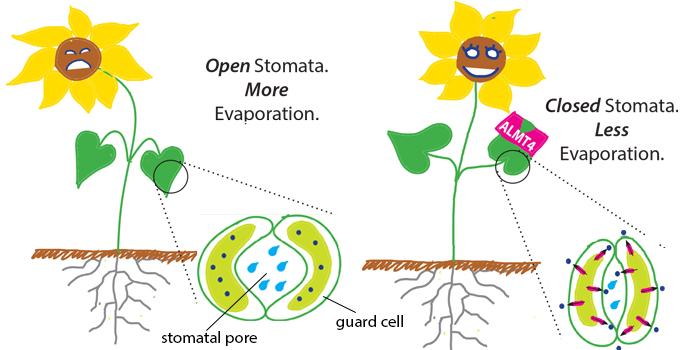
An Ion Channel Active in Plant Drought Response
Eisenach et al. discover A new ion channel of the plant vacuole helps plants react to drought https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.17.00452
By Cornelia Eisenach
Background: Stomata are small pores on plant surfaces that facilitate diffusion of CO2, O2 and water vapor between plant and atmosphere. During…
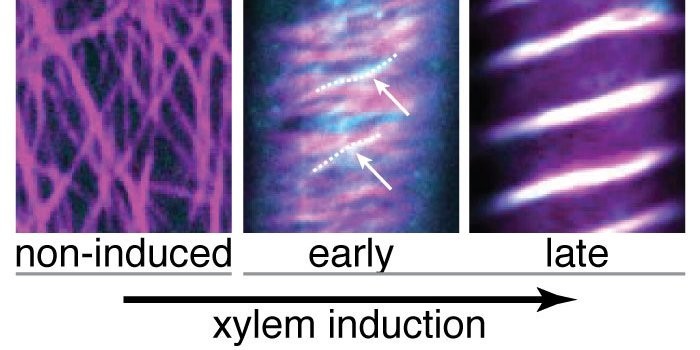
Keeping Walls on Track
Schneider et al. explore how secondary cell walls are made. The Plant Cell 2017. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.17.00309
Background: Plant cells are surrounded by robust cell walls that function as dynamic extracellular skeletons and protect plants against their environment. The cell walls make up…
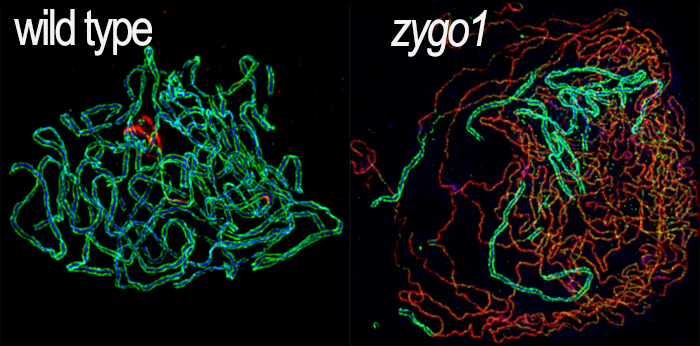
How Meiotic Chromosomes Cluster into a “Bouquet”
Zhang et al. explore the behavior of chromosomes during meiosis. The Plant Cell (2017). https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.17.00287
By Fanfan Zhang
Background: In meiosis, plants, animals, and fungi reduce their chromosome numbers by half to form gametes (sperm and eggs) that can fuse to form a cell…
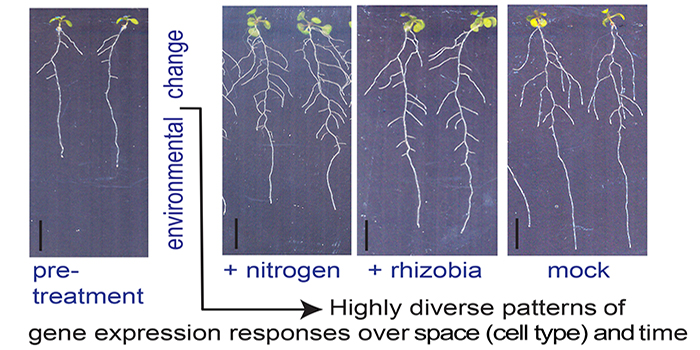
Space-Time Continuum of Gene Expression in Lateral Root Development
Walker et al. explore how the environment shapes root architecture. The Plant Cell 2017. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.16.00961
By Liam Walker
Background: To acquire nutrients and anchor themselves, plant roots spread both vertically and horizontally in soil. Plants typically have a primary root…
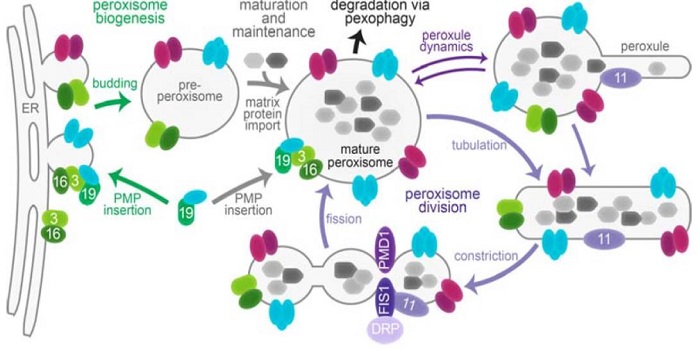
Update: Peroxisome function, biogenesis, and dynamics in plants
Peroxisomes are endoplasmic reticulum-derived membrane-enclosed organelles in which many oxidative enzymatic reactions are compartmentalized. These reactions and their products contribute to energy production, detoxification, and signaling. Kao et al. review our understanding of the plant peroxisome,…
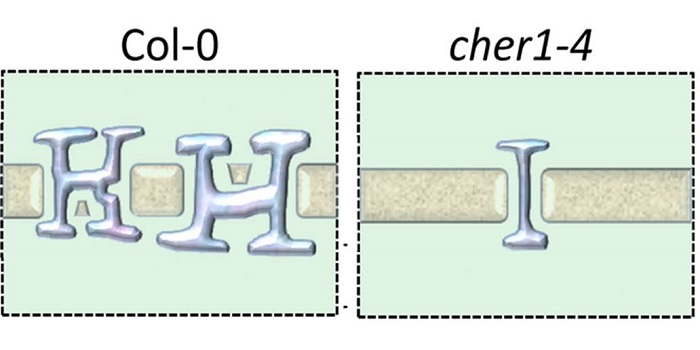
Insights into plasmodesmata composition of fully developed Arabidopsis thaliana leaves
Plasmodesmata (PD) are complex, regulated channels between plant cells that facilitate the movement of signals, metabolites and pathogens, but their small size makes them difficult to study. Previously, Kraner et al. identified an Arabidopsis mutant that produced fewer, simpler plasmodesmata. In their…
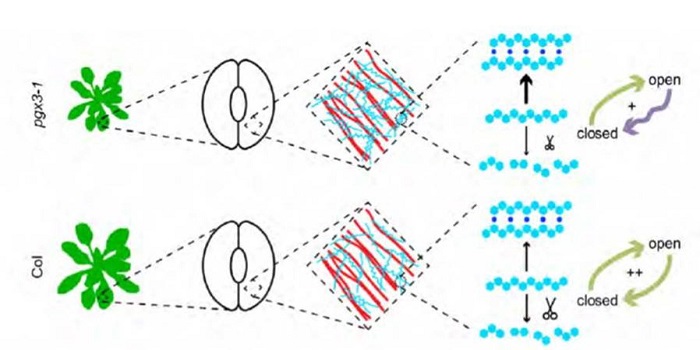
Pectinase function in growth and stomatal dynamics
Pectin is a polymer that holds cell walls together and stiffens the walls, but what happens when those cell walls need to move, for example when cells (including guard cells) expand? Rui et al. started with a guard-cell specific transcriptome to identify genes encoding cell-wall modifying enzymes. They…
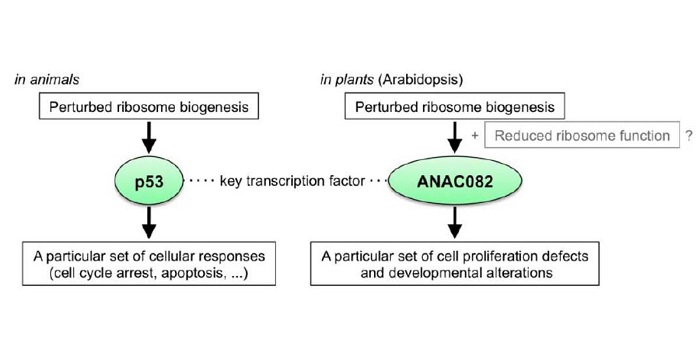
Proliferate at Your Own Risk: Ribosomal Stress and Regeneration
Plant growth and development are extremely adaptable to changes in the external environment, including nutrient status, light quality and intensity, and temperature. Thanks to their developmental plasticity, plants can also initiate new organs from differentiated tissue following wounding, to the benefit…

