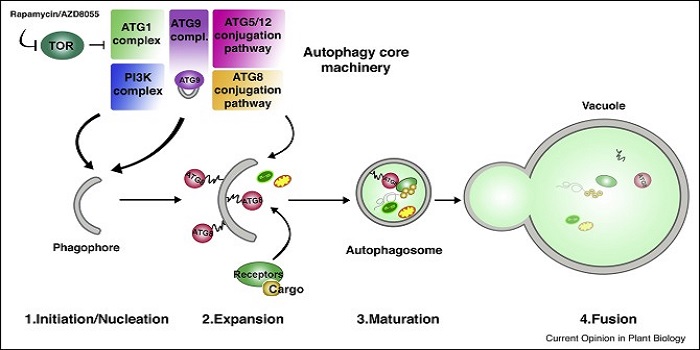
Review: Autophagy as a mediator of life and death in plants ($)
Autophagy is a major pathway involved in degradation and recycling of the cytoplasmic components in a cell. This pathway is functionally well conserved in maintaining cellular homeostasis and modulation of stress responses among yeast, plants and animals. Recent evidence suggests that autophagy targets…

Mechanochemical polarization of contiguous cell walls shapes plant pavement cells
The jigsaw-puzzle shape of the epidermis layer has been puzzling the scientists for some time now. Majda et al. examine the shape of the epidermis cells from the cell wall perspective. Mutations leading to even minor changes in cell wall composition significantly affected pavement cell geometry.…
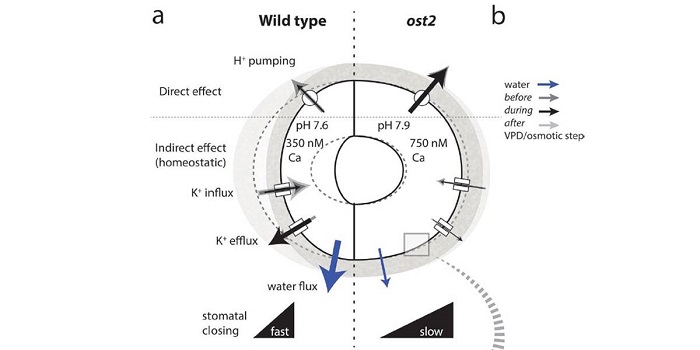
Modeling guard cell-to-leaf scales with OnGuard2
While much is known about the processes involved in stomatal movement and the processes involved in the transpiration of leaves, there has been no framework to bridge this micro-macro divide. Wang and colleagues bridge this divide through OnGuard2, a quantitative systems platform that uses the molecular…

Update: Root plasticity and internal aeration
By Takaki Yamauchi, Timothy D Colmer, Ole Pedersen, Mikio Nakazono
Introduction
Root acquisition of water and nutrients is essential for plant growth and crop productivity (Lynch, 2015). An improved understanding of root system development and functioning, to identify root traits contributing to…

Update. Inroads into Internalization: Five Years of Endocytic Exploration
By Gregory D. Reynolds, Chao Wang, Jianwei Pan, Sebastian Bednarek
Introduction
The plasma membrane (PM) serves as the interface between the cell and its environment. Accordingly, cells have the capacity to modulate their complement of PM-associated receptors, transporters, channels, lipids, and…
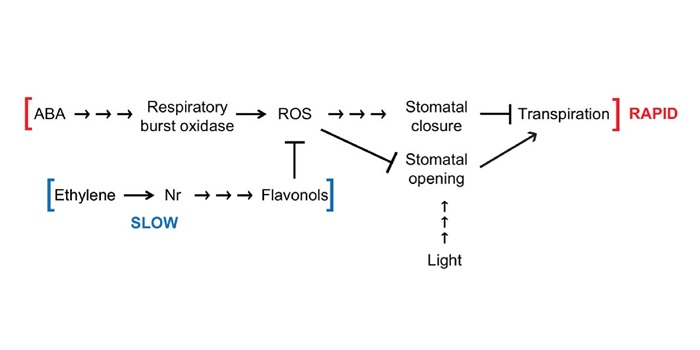
ABA-induced reactive oxygen species are modulated by flavonols to control stomata aperture
Much of our knowledge concerning ABA-induced stomatal closure comes from genetic models such as Arabidopsis and Vicia faba. Watkins et al. explore the mechanism of ROS production in this abiotic stress pathway in an important agricultural crop: tomatoes (Solanum lycopersicum). Specifically, they are…
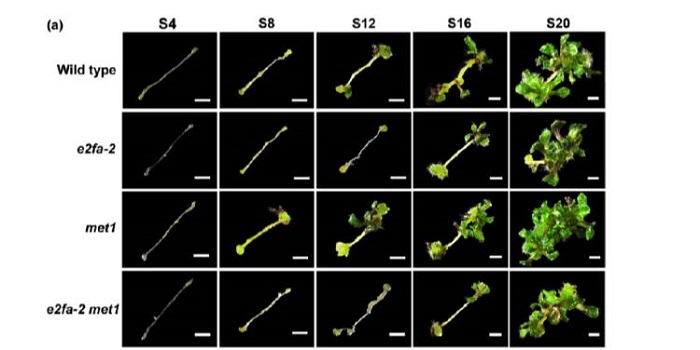
Cytokinin-induced cell cycle regulates MET1 activity during shoot regeneration ($)
The capacity of plants to regenerate new shoots from differentiated tissue – a process called de novo shoot regeneration – confers plasticity to plant development and has also important agricultural applications. Previous studies revealed that DNA METHYLTRANSFERASE1 (MET1) inhibits shoot regeneration…
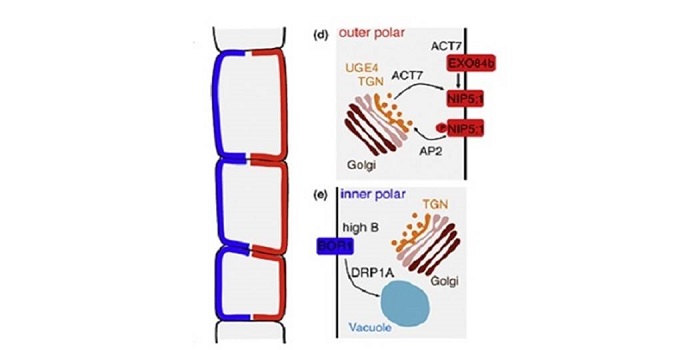
Review: Outer, inner and planar polarity in the Arabidopsis root
Despite vast differences across all living organisms, most eukaryotes display some form of cellular polarity which enables them to carry out specialized functions. The coordination of cell polarity within a single tissue layer is known as planar polarity. Nakamura and Grebe highlight the unique execution…
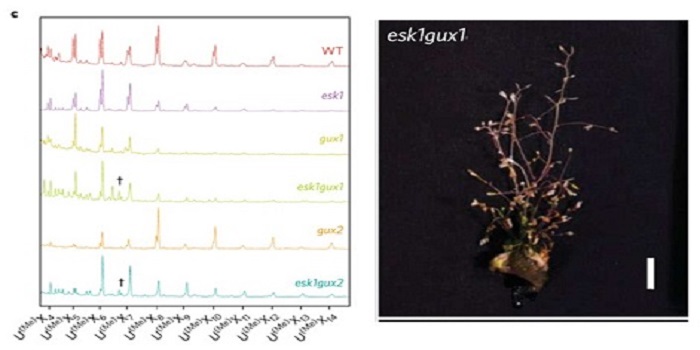
An even pattern of xylan substitution is critical for interaction with cellulose in plant cell walls
Plant cell wall architecture is a very complex specific design and the interaction between xylan and cellulose is believed to be that way too. Grantham et al. reveal the details of the association between xylan and cellulose using mass spectrometry and NMR in Arabidopsis. ESKIMO1 (ESK1) is a xylan-specific…

