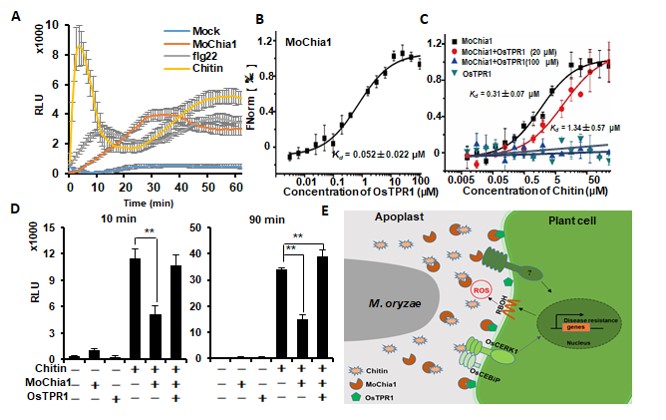
Mechanism of rice blast fungus recognition revealed
The Plant Cell, The Plant Cell: NewsRice is an important food crop in China, but the damage of rice blast fungus is an important factor affecting the high and stable yield of rice. Liu Jun's research group of the Institute of Microbiology, Chinese Academy of Sciences found in the previous study that when rice blast fungus infects rice,…
Volatiles as inducers and suppressors of plant defense and immunity — origins, specificity, perception and signaling (Current Opinion in Plant Biology)
Plant Science Research WeeklyWhen plants are under attack by herbivores and microbes, running away is not an option. As a defence, plants produce volatile organic compounds (VOCs) that repel herbivores, attract enemies of the herbivores, or alarm surrounding plants; VOCs have mostly been viewed as positive regulators in the plant…
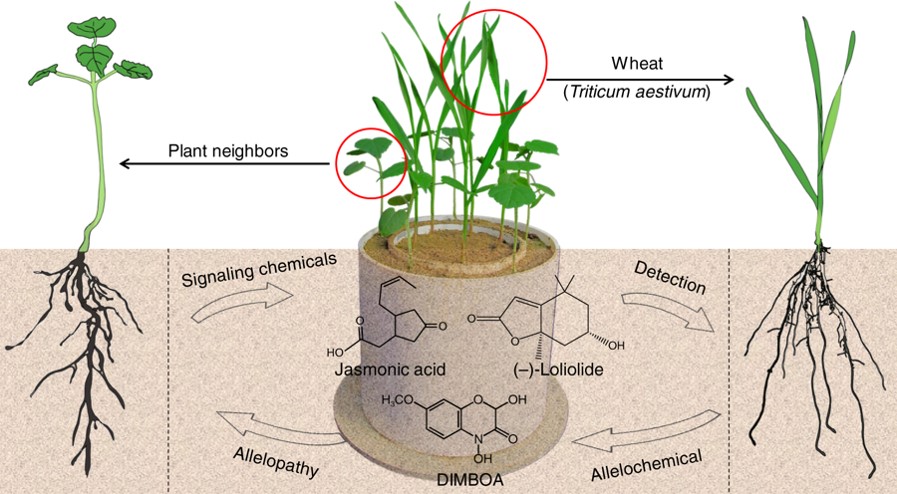
Plant neighbor detection and allelochemical response are driven by root-secreted signaling chemicals (Nature Communications)
Plant Science Research WeeklyPlants are not able to move out of their neighborhood if they are unhappy, but they are capable of recruiting and assembling a community in which they are able to thrive. Plants are also able to initiate defense when they sense that threats are near. To keep tabs on their neighbors, plants utilize both…
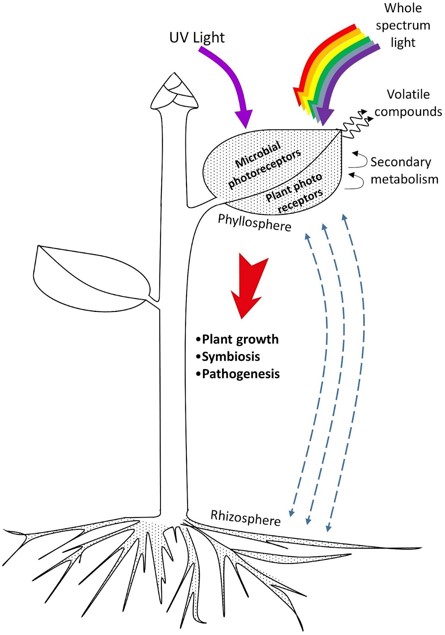
Influence of light on plant–phyllosphere interaction (Frontiers in Plant Science)
Plant Science Research WeeklyThe term “phyllosphere” refers to the world of microbes that interact among themselves and with their plant hosts above ground. In this review, the authors explore what is known about this interesting habitat and how abiotic factors, especially light, influences the interactions and survival of its…
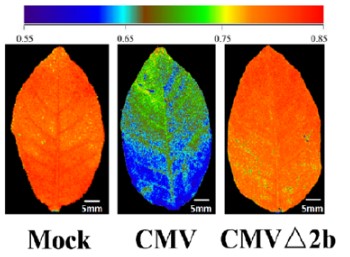
Plant Reactive Oxygen Species Enhance Virus Spread by Aphids
Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: On The InsideHemipterans, a group of phloem-feeding insects that includes aphids, planthoppers, and whiteflies, are responsible for the spread of most plant viruses from plant to plant. Stylet positioning and feeding activities have important consequences for the acquisition and transmission of viruses by insect…

Review: Mechanisms of plant–soil feedback: interactions among biotic and abiotic drivers
Plant Science Research WeeklyWe often think about how the soil environment influences plants, but two new papers focus on how plants influence the soil environment (through abiotic and biotic effects), in turn affecting other plants. These plant-soil feedbacks (PSFs) can be negative (resource depletion, natural enemy accumulation)…
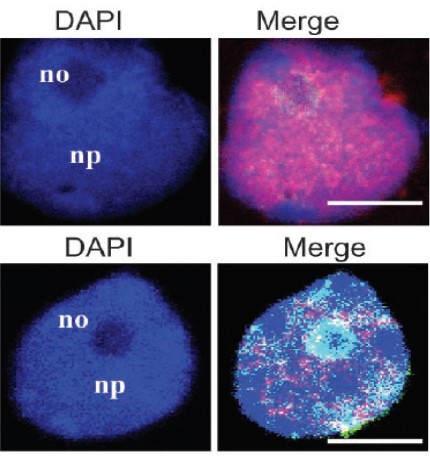
Worming into the Plant Chromatin: A Nematode Effector Influences Host Histone Acetylation
Blog, The Plant CellPlants encounter myriad invaders, including bacteria, fungi, insects, and other parasites. These pathogens generally deliver effector proteins into plants, increasing their virulence and targeting various host processes (Toruño et al., 2016). Although advances in the past two decades have led to significant…
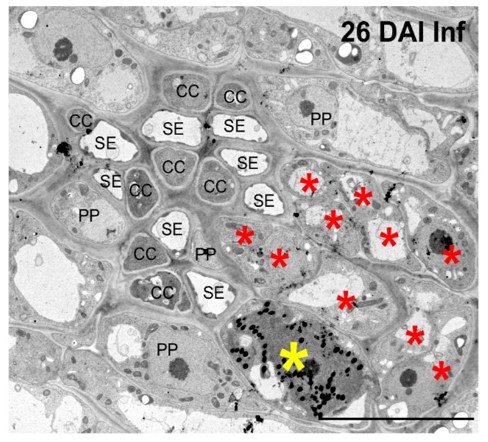
Sugar architect: the Brassicaceae pathogen Clubroot manipulates plants on multiple levels to secure sucrose supply
The Plant Cell, The Plant Cell: In BriefThe soil-borne pathogen Plasmodiophora brassicae can infect most members of the Brassicaceae family. The infections, which can lead to extensive crop losses, typically involve development of galls in the underground tissues of the plant, giving the pathogen its common name, ‘clubroot’.
Although…
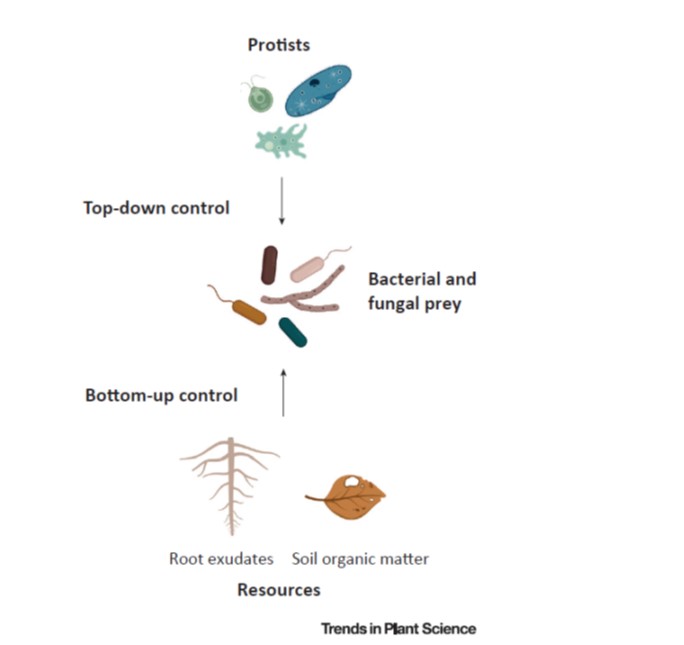
Review. Protists: Puppetmasters of the rhizosphere microbiome ($) TIPS
Plant Science Research WeeklyThe enemy of my enemy is my friend, right? Gao et al. argue that we should be more aware of the beneficial impacts of friendly protists that eat potentially harmful microbes in the rhizosphere (they deliberately exclude plant pathogenic protists in their discussion). Protists are a diverse paraphyletic…

