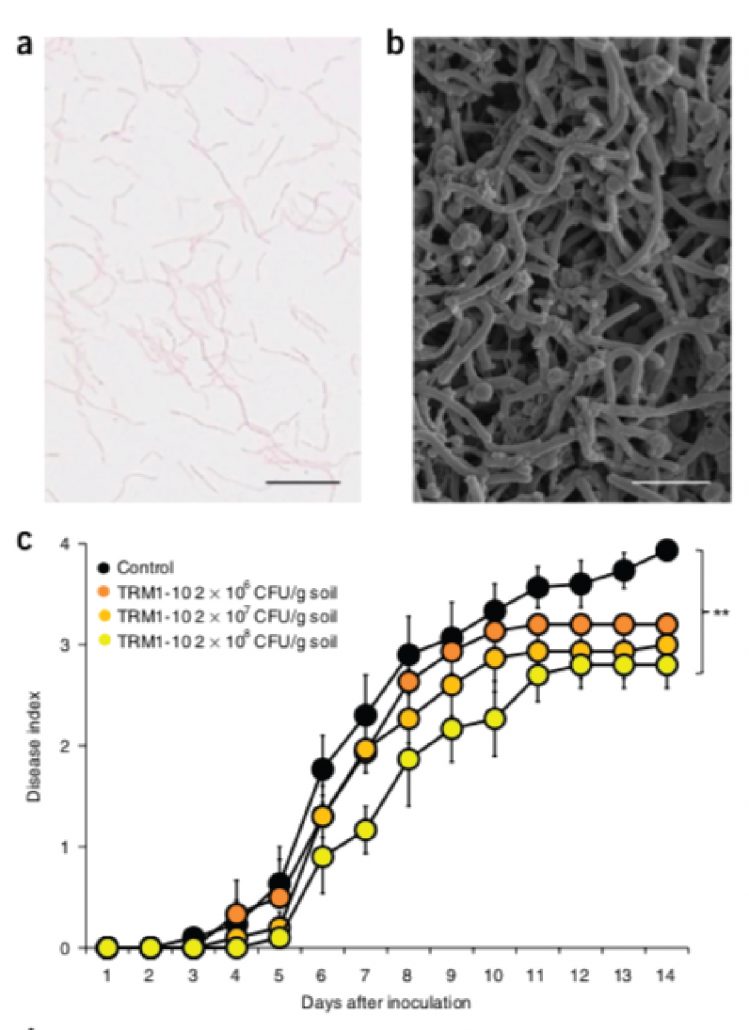
Rhizosphere microbiota structure alters to enable wilt resistance in tomato (Nature Biotech. - $)
Plants are frequently attacked by pathogens, but the pathogen-resistance is often attributed to the host. While interactions between the plant and its microbiota are recognized for their role in plant growth, their role in pathogen resistance is unknown. Kwak et al. studied the effect of soil-borne pathogen Ralstonia…
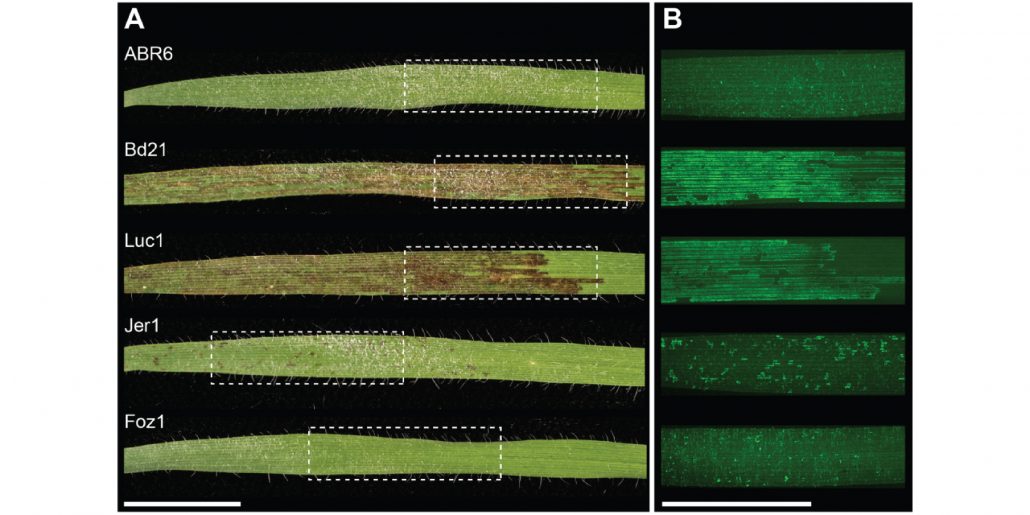
The genetic architecture of colonization resistance in Brachypodium distachyon to non-adapted stripe rust (Puccinia striiformis) isolates (PLOS Gen.)
The host range of a pathogen depends on its ability to overcome various plant defense barriers and successfully complete its life cycle. Although host “jumps” are considered rare, the pathogens are able to infect plants other than their usual host with varying degree of success. Yellow stripe rust…
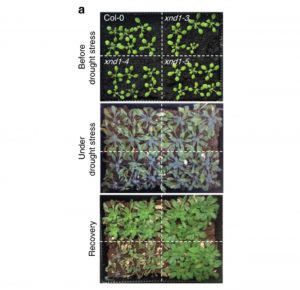
The Arabidopsis negative regulator of root hydraulics XND1 is involved in abiotic and biotic stress responses (Nature Comm.)
Proper uptake and management of water is essential for plant growth and adaptation to stress. However, there are gaps in the understanding of the genetics of root hydraulics, including the regulatory components. Tang et al. used a genome-wide associate analysis approach to identify XYLEM NAC DOMAIN 1 (XND1),…
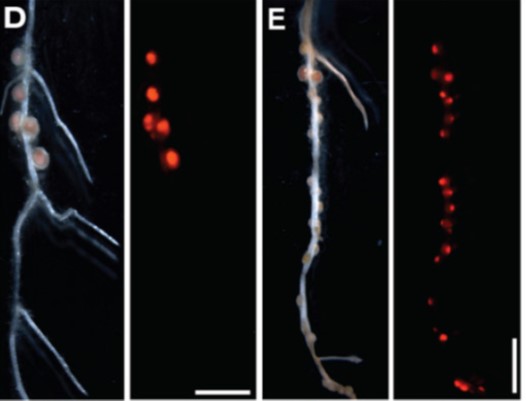
A shoot-derived miRNA ensures susceptibility to beneficial rhizobacteria in legumes (Science)
Nitrogen-fixing rhizobacteria and leguminous plants engage in a tightly controlled root symbiosis resulting from bacteria-to-plant as well as (plant) shoot-to-root communication. This interplay controls the initiation and maintenance of root nodule development while preventing the over-production of…
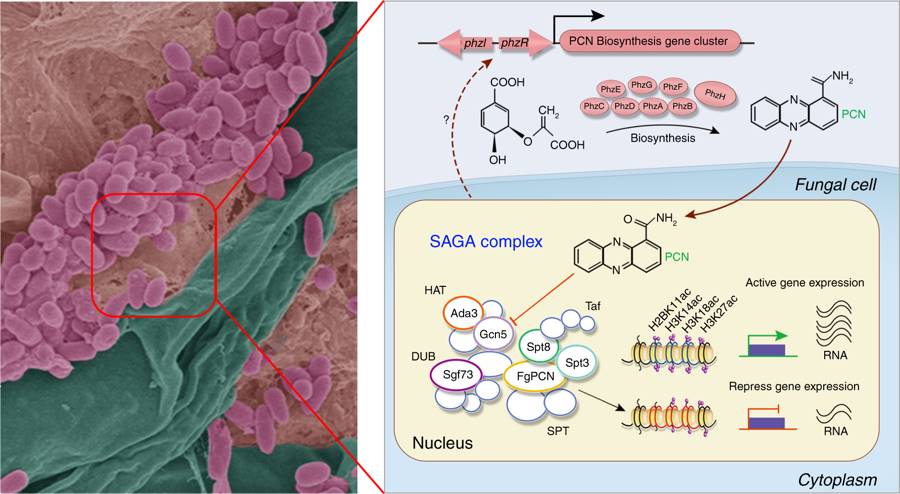
Wheat microbiome bacteria reduce virulence of pathogenic fungus by altering fungal histone acetylation (Nature Comms)
Sometimes the plant is a relatively passive host upon which other organisms engage in dynamic interactions. Chen et al. showed that a wheat head-associated bacterium, Pseudomonas piscium, produces antifungal compounds that inhibit the growth of a plant pathogenic fungus, Fusarium graminearum. The authors…
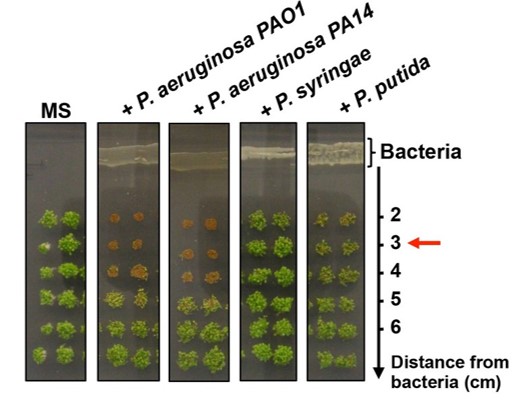
Arabidopsis seeds delay germination in the presence of pathogens (eLIFE)
The rhizosphere represents a complex and dynamic environment that poses many challenges for seed germination and seedling establishment. While a number of well-characterized abiotic factors and hormone signaling pathways are known to contribute to the initiation of seed germination, our current understanding…
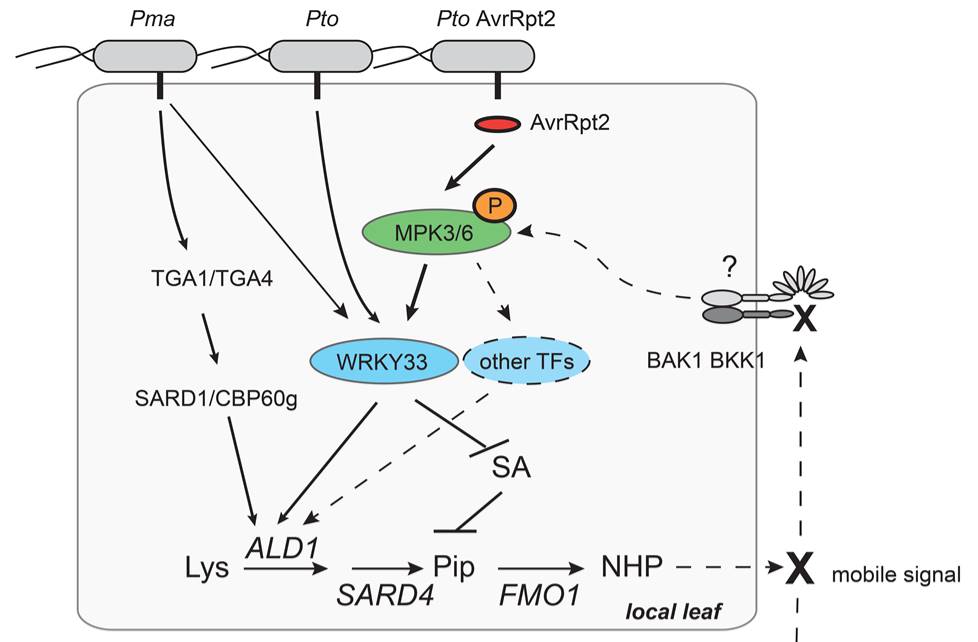
Plant Systemic Immunity Comes Full Circle: A Positive Regulatory Loop for Defense Amplification
The plant immune system is effective in conferring resistance to various invading pathogens and pests. Membrane-localized pattern recognition receptors (PRRs) and intracellular nucleotide-binding domain, leucine-rich repeat proteins (NLRs) recognize pathogen-associated molecular patterns and pathogen…
Review. Xylella fastidiosa: Insights into an emerging plant pathogen ($) (Annu. Rev. Plant Phytopathol.)
The plant pathogenic bacterium Xylella fastidiosa occurs widely and often asymptomatically, yet it is associated with a few seriously bad disease outbreaks, the most recent affecting olive trees in southern Italy and adjoining regions. It also is the causal agent of Pierce’s Disease of grapevine, citrus…

A single transcription factor promotes both yield and immunity in rice ($) (Science)
Plants regularly prioritize either growth or defense, leading to reduced growth rate when the plant is under attack. Wang et al. have identified a simple switch in rice that demonstrates this principle beautifully. The Ideal Plant Architecture 1 (IPA1) transcription factor is involved in controlling…

