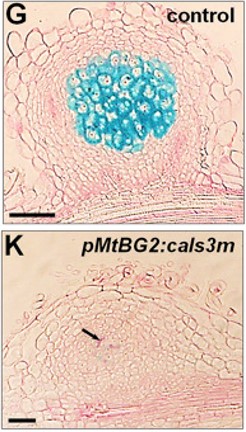
Symplastic coordination of root nodule development (Curr. Biol.)
Plant Science Research WeeklyThe establishment of root nodule symbiosis in legume roots involves the perception, infection, and accommodation of nitrogen-fixing rhizobia. The de novo formation of root nodules relies on complex developmental programs coordinated through different tissues via unknown cellular routes. Gaudioso-Pedraza…

Plant extracellular vesicles contain diverse small RNA species and are enriched in 10-17 nucleotide "tiny" RNAs (bioRxiv)
Plant Science Research WeeklySmall RNAs are known to move between cells and even between organisms. Studies in mammals have shown that extracellular vesicles (EVs) can contribute to small RNA transport, and recently small-RNA containing EVs were identified in plants. Baldrich et al. extend this work with an analysis of the types…
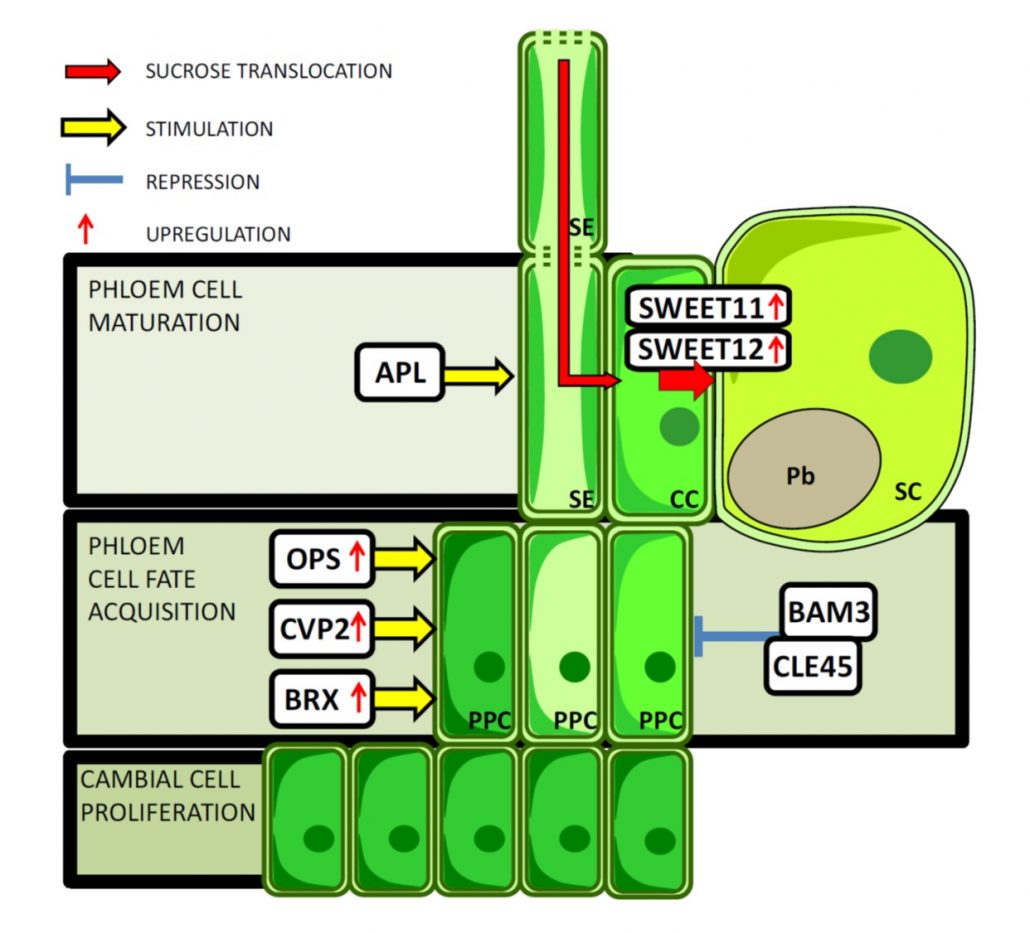
Brassica clubroot disease protist pathogen promotes phloem differentiation and expression of SWEET sucrose transporters (Plant Cell)
Plant Science Research WeeklyClubroot is a disease of brassicas (including oilseed crops and Arabidopsis) caused by the protist Plasmodiophora brassicae. The infection is characterized by the formation of swollen tissues called galls that are metabolic sinks in which the pathogen propagates. Walerowski et al. took advantage of Arabidopsis…

Towards Pathogen-Resistant Apples
Research, The Plant Cell, The Plant Cell: In a NutshellZhang et al. show that a single-nucleotide polymorphism in a hairpin RNA promoter contributes to Alternaria alternata leaf spot resistance in apple and could serve as a marker to distinguish susceptible versus resistant apple cultivars. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.18.00042.
Background: Apple Alternaria…

Aphid-borne viral spread is enhanced by virus-induced accumulation of plant reactive oxygen species (Plant Physiol)
Plant Science Research WeeklyAphids are major vectors for viral spread. Guo et al. have identified an interesting interaction that affects aphid feeding behavior and viral spread. They showed that reactive oxygen species (ROS) accumulation in plants infected with cucumber mosaic virus (CMV) affects aphid feeding behavior; specifically,…
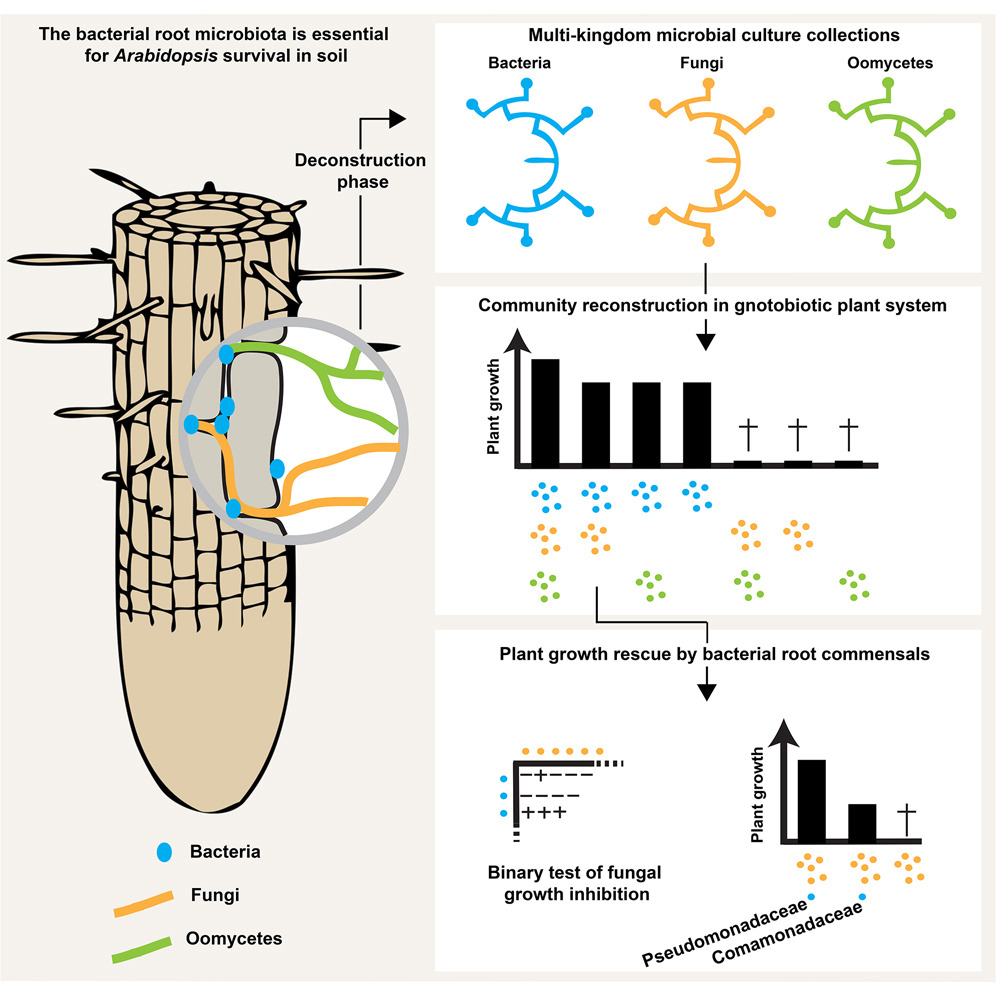
Microbial interkingdom interactions in roots promote Arabidopsis survival (Cell)
Plant Science Research WeeklyPlant roots in soil are surrounded by different microorganisms such as bacteria, fungi and oomycetes. The impact of these organisms on plant health has been known f0r many decades. However, the interaction network between these organisms is not well understood. By using next generation sequencing as…
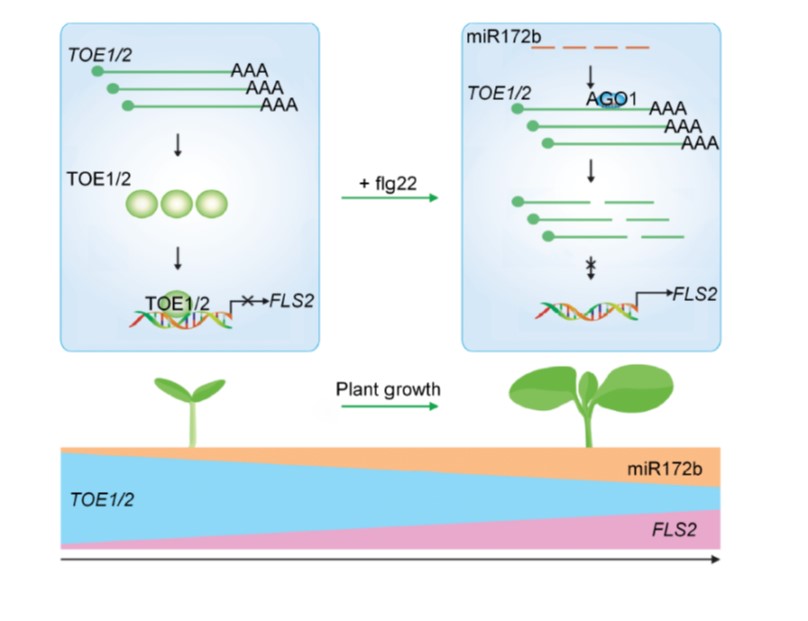
Transcriptional regulation of the immune receptor FLS2 controls the ontogeny of plant innate immunity (Plant Cell)
Plant Science Research WeeklyFLS2 is a well-known cell-surface receptor that triggers plant immune response. Zou et al. asked whether its expression level is age-dependent, and found that FLS2 is expressed at very low levels in newly-emerged seedlings. They identified two closely related transcription factors TOE1 and TOE2 that…
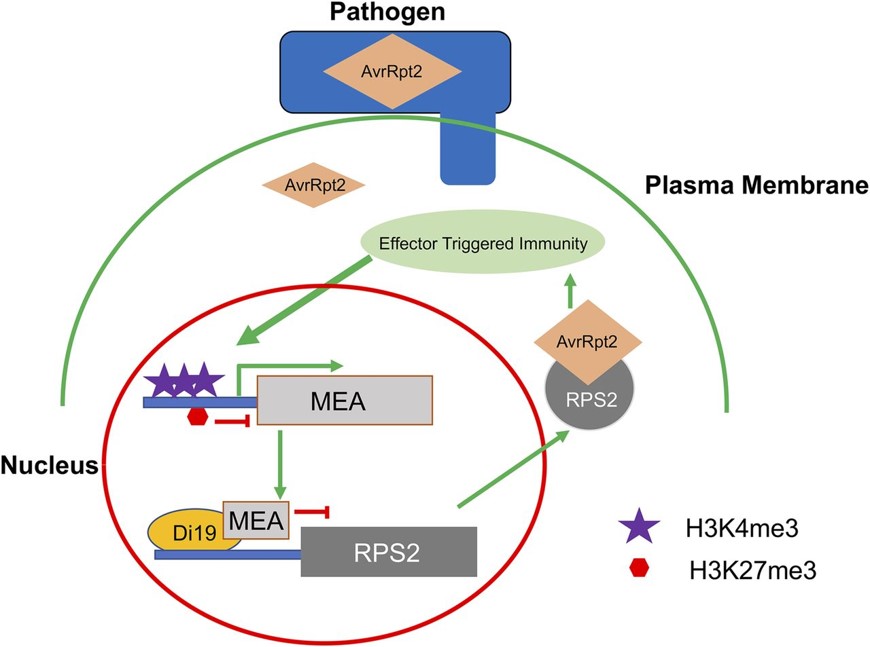
Polycomb Group Transcriptional Repressor: Suppress to Sustain
Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: News and ViewsEvidence of epigenetic gene regulation in plant immunity was first reported in 1975 (Guseinov et al., 1975) with the demonstration that cytosine methylation is altered in response to pathogen infection. Since then, it has been established that pathogen infection influences DNA methylation and histone…
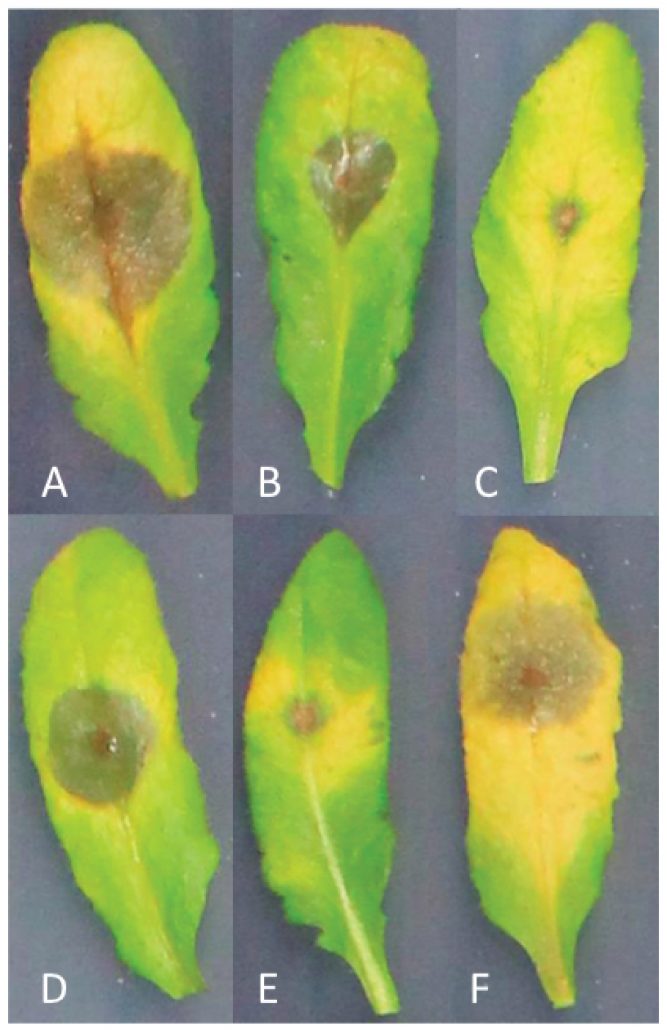

Digital imaging combined with genome-wide association mapping links loci to plant-pathogen interaction traits (Plant Phys.)
Plant Science Research WeeklyResistance to plant pathogens is often studied as a qualitative trait than quantitative, focusing on the lesion size and pathogen numbers. However, resistance to generalist plant pathogens, such as Botrytis cinerea, is known to involve multiple genes. Fordyce et al. used high-throughput phenotyping…

