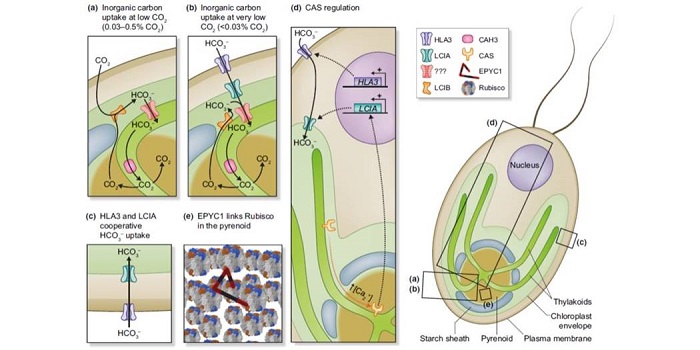
Review: The Chlamydomonas CO2-concentrating mechanism and its potential for engineering photosynthesis in plants
Blog, Plant Science Research Weekly, Research, Research BlogMany green algae have the ability to concentrate CO2 to enhance their photosynthetic performance. Mackinder reviews these algal CO2-concentrating mechanisms (CCMs) and what steps would be required to introduce them into higher plants. He also compares progress and pitfalls towards introducing algal CCMs…

Temporal and spatial transcriptomic and miRNA dynamics of CAM photosynthesis in pineapple ($)
Blog, Plant Science Research Weekly, Research, Research Blog0 Comments
/
CAM (crassulacean acid metabolism) is the form of photosynthesis in which carbon assimilation occurs at night. CAM allows plants, especially those growing in arid regions, to avoid excessive water loss. With the long-term goal of eventually engineering this water-conserving trait into crop plants, Wai…
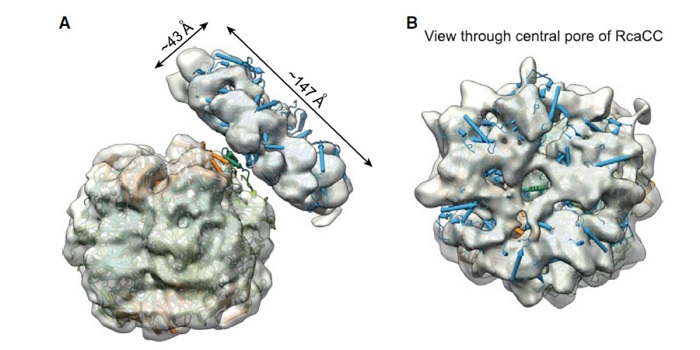
Mechanism of enzyme repair by the AAA+ chaperone Rubisco activase ($)
Blog, Plant Science Research Weekly, Research, Research BlogRubisco is a fascinating enzyme, which in plants is a hexadecamer made up of eight large (RbcL) and eight small (RbcS) subunits. The catalytic sites are buried within the enzyme at the interfaces between pairs of RbcL subunits. Rubisco catalyzes the first step in the carbon-fixing photosynthetic reactions,…
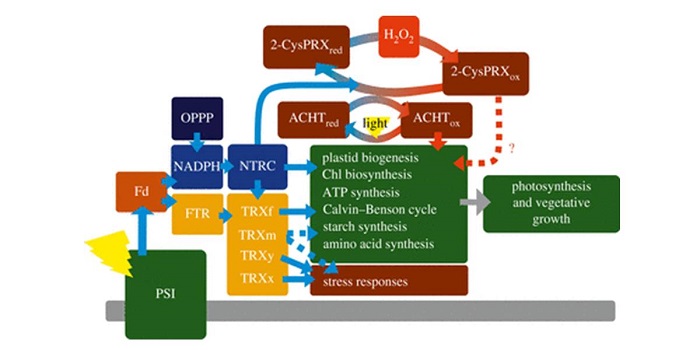
Special meeting issue, “Enhancing photosynthesis in crop plants: targets for improvement” ($)
Blog, Plant Science Research Weekly, Research, Research BlogHere’s a great collection of articles that consider various approaches to increase crop productivity through enhancements to photosynthesis. The authors of the papers in this collection include many of the leading photosynthesis researchers, and the topics include structural and architectural improvements…
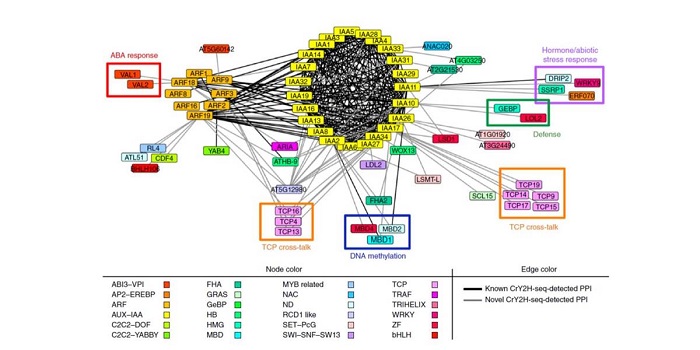
CrY2H-seq: a massively multiplexed assay for deep-coverage interactome mapping ($)
Blog, Plant Science Research Weekly, Research, Research BlogProtein-protein interactions are crucial to our understanding of biology but can be hard to detect. Trigg et al. developed a sophisticated yeast two-hybrid assay augmented with Cre recombinase (CrY2H-seq) to identify the Arabidopsis transcription factor protein-protein interactome. In this method,…

Metabolic engineering of anthocyanin and betalain pigments for health and aesthetics: Purple rice, blue chrysanthemums and violet tomatoes
Blog, Plant Science Research Weekly, Research, Research BlogPigment engineering was featured in three recent papers. Anthocyanins are blue pigments valued for their antioxidant health benefits and for their beauty, but their biosynthesis and chemistry is complex. Noda et al. introduced two genes to produce blue anthocyanins in chrysanthemum petals (Sci Advances…

A Key Enzyme in the Biosynthesis of a Plant-Derived anti-HIV Drug
Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: On The Inside, Research, Research BlogRhododendron dauricum (Ericaceae), a native of northeastern Asia, produces unique secondary metabolites including daurichromenic acid (DCA). DCA has attracted considerable attention as a medicinal resource because this compound is one of the most effective natural products with anti-HIV properties in…
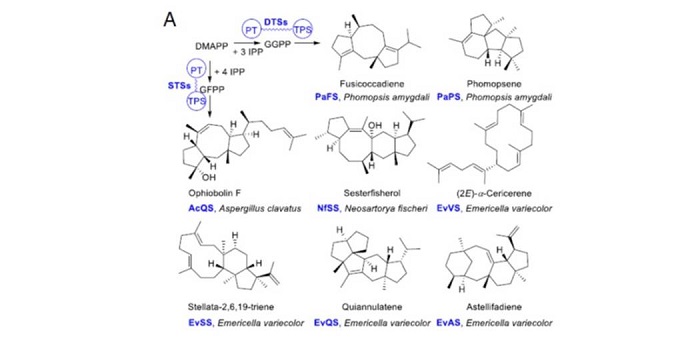
Convergent evolution of sesterterpene biosynthetic repertoire in the Brassicaceae
Plant Science Research WeeklySesterterpenes are a family of natural products; some (derived from corals and fungi) have been shown to have antitumor, antimicrobial and antiinflamatrory activities. Huang et al. used genome mining to identify sesterterpene biosynthetic genes in the Brassicaceae. The first committed step is carried…
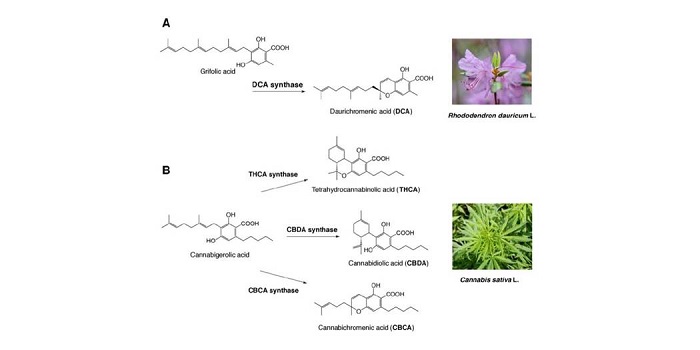
Synthesis of the anti-HIV compound daurichromenic 1 acid in Rhododendron dauricum
Plant Science Research WeeklyDaurichromenic 1 acid (DCA) is a meroterpenoid with anti-HIV properties that is produced in young leaves of Rhododendron dauicum. In this study, Iijimi et al. identified a DCA synthase gene. Starting with their previous observations that this enzyme is a stereoselective meroterpenoid oxidocyclase, similar…

