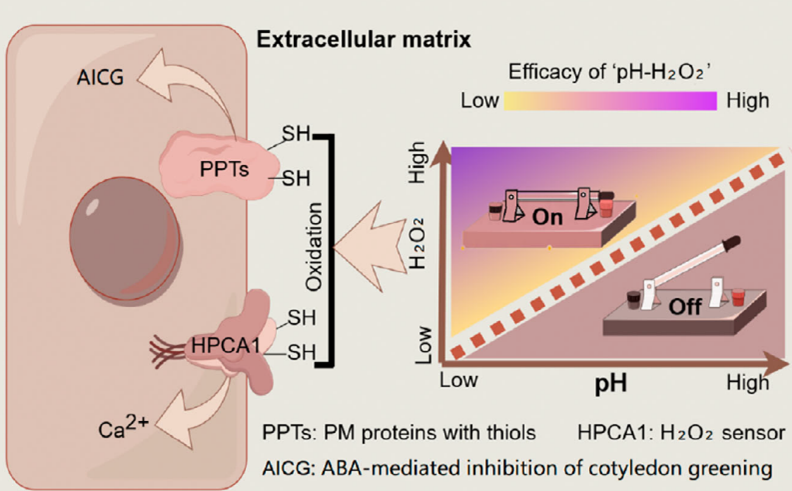
Apoplastic pH acts as a chemical switch in plants by modulating H2O2 redox potential
Plant Science Research WeeklyEnvironmental stimuli, such as drought and salinity, alter cellular conditions including apoplastic pH (pHApo) in plants. These stimuli often lead to an elevation in pHApo which is closely associated with cell functions and plant growth. However, the mechanism behind is largely unexplored. A recent study…
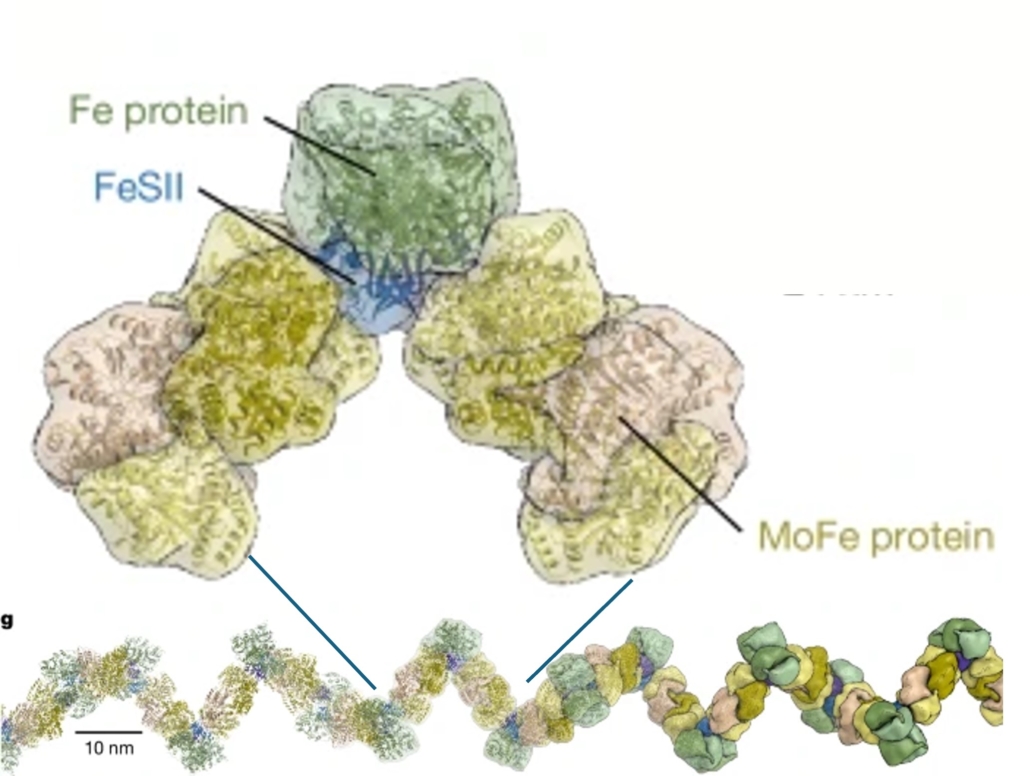
How nitrogenase stays active
Plant Science Research WeeklyOne of the great dilemmas of science is the fact that nitrogen gas, though very abundant in the atmosphere, is limiting for most forms of life. Of course, this lack of availability is because N2 gas has an extremely strong triple bond holding the two nitrogen atoms together; it’s so strong that N2…

Single cell transcriptomics aids gene discovery of complex natural product biosynthesis
Plant Science Research WeeklyFrom an ancient Greek cure-all to a modern treatment for mild depression, Hypericum perforatum (St. John’s wort) is a fascinating weed. Its leaves and flowers produce hyperforin, a metabolite derived from the isoprenoid pathway, which acts as a serotonin reuptake inhibitor. Despite partial genome and…
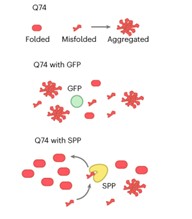
Chloroplast proteostasis prevents aggregation of Huntington’s disease-causing human polyQ protein
Plant Science Research WeeklyCertain human neurodegenerative disorders are caused by aggregation of disordered proteins. In particular, Huntington’s disease is caused by aggregation of a protein called huntingtin, which contains long stretches of glutamine (Q). Llama et al. observed that proteins with long stretches of glutamine…

Using cryo-EM to solve the structures of proteins involved in starch degradation
Plant Science Research WeeklyStarch is synthesized in the chloroplasts of leaves during the day and degraded at night. BAM1 (β-AMYLASE 1) catalyzes starch degradation and interacts with the non-catalytic glucan phosphatase called LSF1 (LIKE SEX FOUR 1) and the plastid localised MDH (MALATE DEHYDROGENASE). However, we don’t fully…

Spotlight: Salt and Peppers
Plant Science Research WeeklyIn my cruise around the internet looking for fascinating plant science, I found this tasty morsel. It’s a Spotlight feature of new paper on the effects of salt stress on plants of the genus Capsicum. I don’t want to detract from author Robert Calderon’s fine writing, so head over to Physiologia…

Soluble and insoluble α-glucan synthesis in yeast by enzyme suites derived from maize endosperm
Plant Science Research WeeklyStarch is a polymer of α-glucose which is assembled into insoluble, semi-crystalline granules in plants. It is not known why we see only insoluble starch granules in plants and no soluble α-glucan polymers. To investigate this, Boehlein et al. took a synthetic biology approach. Eleven starch metabolism…

Review: Stress-related biomolecular condensates in plants
Plant Science Research WeeklyBiomolecular condensates are non-membrane-bound compartments containing proteins and RNAs with key functions in stress responses. In plants, they occur as several types with different properties and components, including stress granules and processing bodies. Protein domains such as prion-like domains…

Review: One plant’s poison
Plant Science Research WeeklyPlants synthesize interesting chemicals that attract, deter, amuse, and harm their predators. Some of the most harmful to humans have been selectively eliminated through the process of domestication, but others render potential food sources inedible. This review by Liu et al. discusses four approaches…

