
The genome of Quenopodium quinoa, a halophytic pseudocereal
Blog, Plant Science Research Weekly, Research, Research BlogQuenopodiium quinoa is a highly nutritive and facultative halophyte pseudocereal whose cultivation has increased 10 fold in the last decades. However, the adaption to non-native areas is not easy to achieve and the limited genetic resources do not allow a breeding program. Zou and collaborators have…
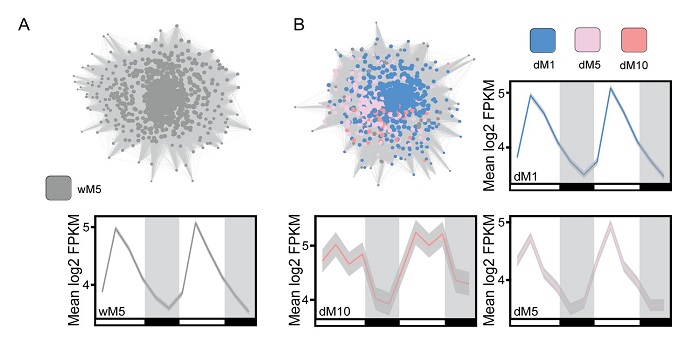
Temporal network analysis of mild drought in Brassica rapa
Blog, Plant Science Research Weekly, Research, Research BlogIf you whithold water from a plant it eventually will wilt, but before this visible change there are other measurable effects and responses. However, many plant processes change cyclically over a 24-hour period independently of early drought responses, so it can be difficult to separate drought-responsive…
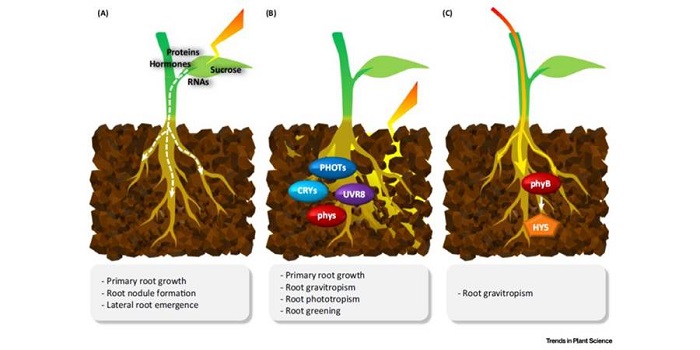
Review: Multiple routes of light signaling during root photomorphogenesis
Blog, Plant Science Research Weekly, Research, Research BlogLight response research in plants has traditionally focused on the shoot, but recent studies have revealed that roots are also light responsive. Lee et al. address the why and how of root photomorphogenesis. They review three ways that light is perceived in roots: via mobile signals from the shoot, direct…
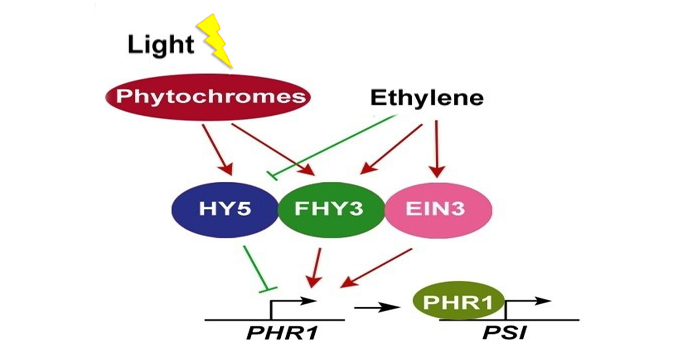
Light Helps Plants Cope with Phosphate Starvation
Research, The Plant Cell, The Plant Cell: In a NutshellLiu et al. focus on transcriptional regulation of PHR1 expression. The Plant Cell 2017. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.17.00268
Phosphorus (P) is an essential micronutrient for plant growth, development, and metabolism. Phosphate (Pi), the major form of P used by plants, is highly immobile in most soils,…
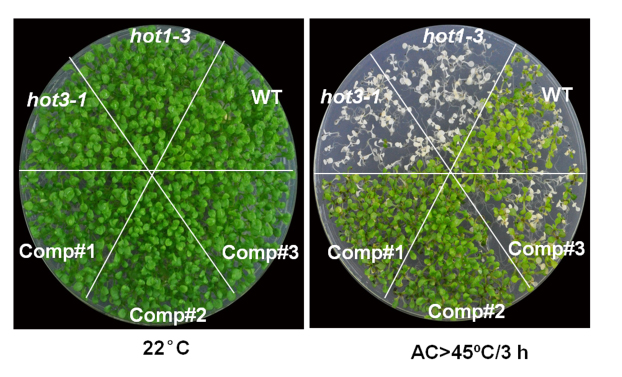
Translating to beat the heat
Research, The Plant Cell, The Plant Cell: In a NutshellZhang et al. investigate protein translation under heat stresss http://www.plantcell.org/content/29/8/1952
By Elizabeth Vierling
Plants can’t move to avoid unfavorable growth conditions, such as insufficient water availability or extremes of temperature. When plants are confronted with stressful…
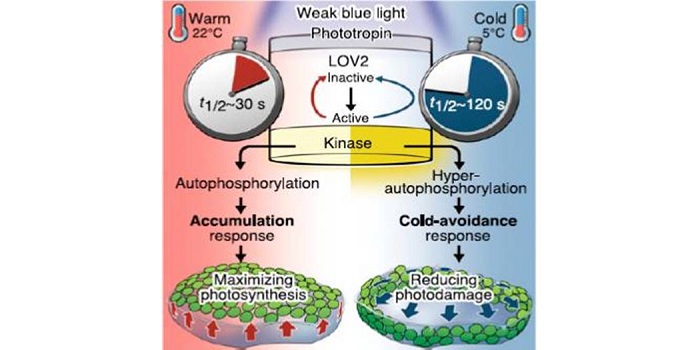
Phototropin perceives temperature based on the lifetime of its photoactivated state
Blog, Plant Science Research Weekly, Research, Research BlogFujii et al. studied the role that blue-light perceiving phototropins play in sensing temperature. They studied the temperature response in the liverwort Marchantia polymorpha, which has only one phototropin. At 5°C, blue-light perception by phototropins induces a cold-avoidance response in which chloroplasts…
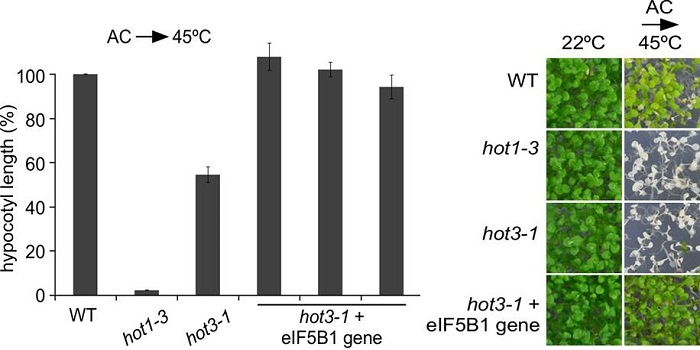
Some Like it HOT: Protein Translation and Heat Stress in Plants
Blog, Research, The Plant Cell: In BriefThe ability to acclimate to high temperatures that are normally lethal is common to virtually all organisms on the planet. A short exposure to milder heat stress informs organisms that they should ready themselves in case they experience even warmer conditions. Acquired thermo-tolerance in plants is…

Phototropin perceives temperature based on the lifetime of its photoactivated state
Blog, Plant Science Research Weekly, Research, Research BlogAlthough plants clearly perceive and respond to changes in temperature, it has not always been clear how they perceive temperature and its changes. Evidence for temperature sensing through membrane fluidity, protein stability and, more recently, the reversion of phytochrome to its inactive form has been…

Temperature increase reduces global yields of major crops in four independent estimates ($)
Blog, Plant Science Research Weekly, Research, Research Blog0 Comments
/
Although future negative impacts on crop yields expected from rising temperature are well known to plant scientists, there are still some members of the broader public that need to be made aware of this problem. Zhao et al. combined four different methods of assessing the impact of increasing temperatures…

