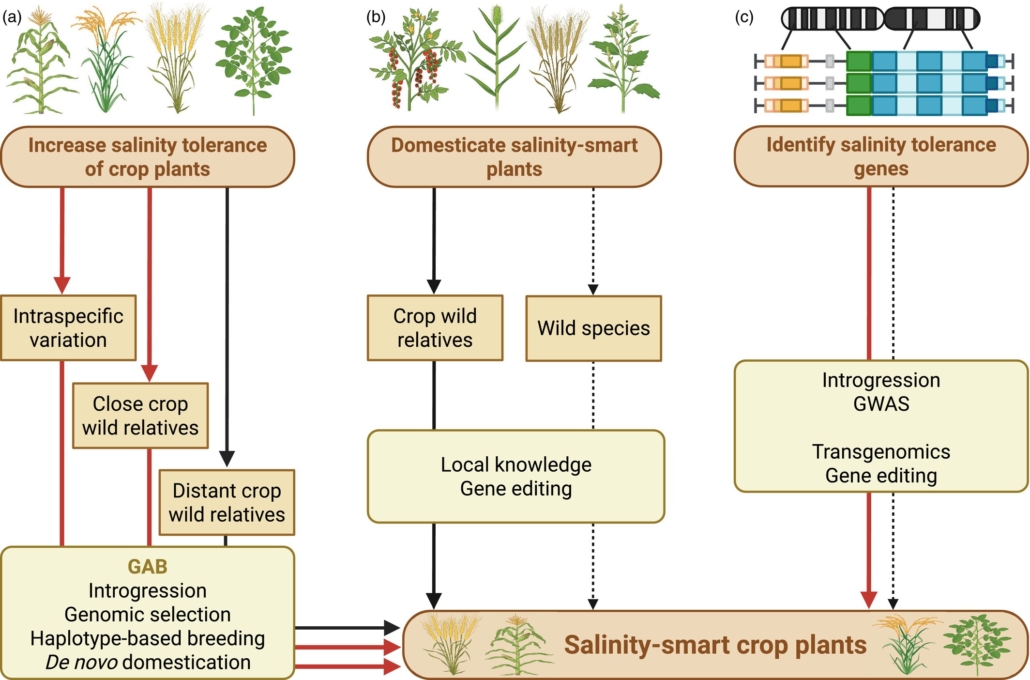
Review: Genomic tools and breeding tools to design salinity-smart food crops
Plant Science Research WeeklyMost food crops are relatively intolerant to soil salinity, yet globally soils are becoming increasingly salinized. This excellent review by Raza et al. pulls together the myriad approaches that are being used to develop salinity-smart crops. It starts with an overview of how soil salinity affects crops…

PPR767 controls mitochondrial RNA editing to regulate growth and drought tolerance in rice
Plant Science Research WeeklyMitochondria are vital energy-producing organelles that depend on precise RNA processing for function. In this study, Peng et al. identify PPR767, a mitochondria-localized E-type pentatricopeptide repeat (PPR) protein in rice, as a key regulator of plant architecture and drought tolerance. Loss-of-function…
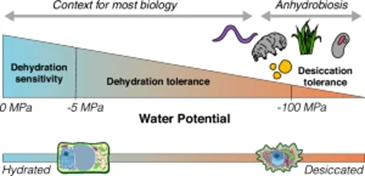
Perspective. The art of drying gracefully: The future for desiccation research
Plant Science Research WeeklyIn their perspective article, “Life on the dry side: a roadmap to understanding desiccation tolerance and accelerating translational applications,” Marks et al. outline the current state and future promise of desiccation tolerance research. They define desiccation tolerance as “the ability to dry…
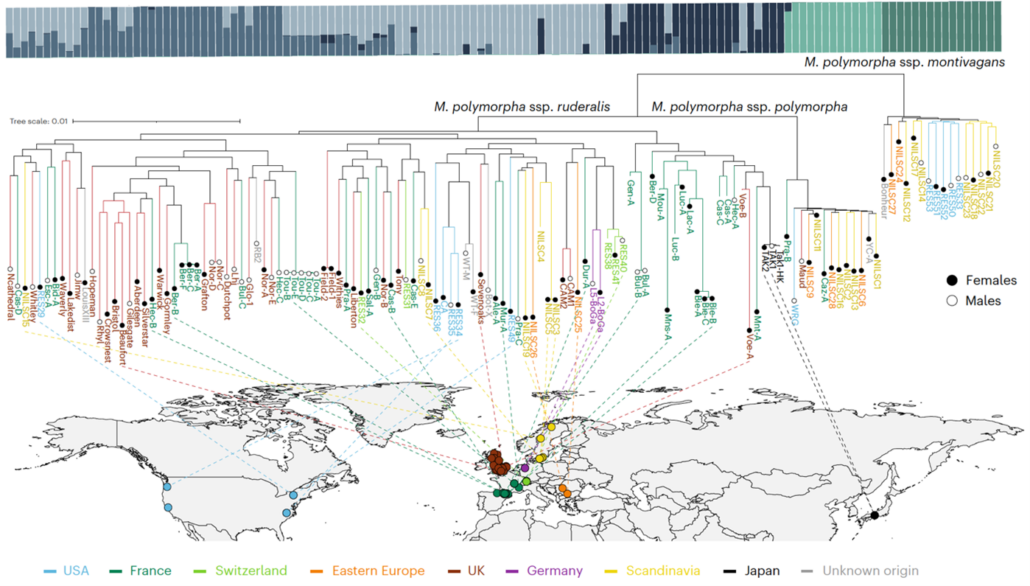
From water to land: What bryophytes reveal about plant evolution and adaptations
Plant Science Research WeeklyThe transition of plants from aquatic to terrestrial environments occurred approximately 400 million years ago, leading to the diversification of two major lineages: tracheophytes (vascular plants) and bryophytes (non-vascular plants). While most studies on plant adaptation to environmental stressors…
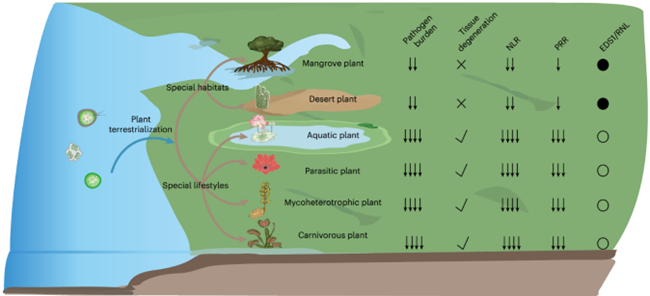
Streamlining the immune system: How plants adapt to reduced pathogen pressure
Plant Science Research WeeklyAlthough plants are sessile organisms unable to escape pathogen invasions, they are well equipped with defense mechanisms. Cell surface-localized pattern-recognition receptors (PRRs) detect extracellular signals and initiate pattern-triggered immunity (PTI), while nucleotide-binding leucine-rich repeat…
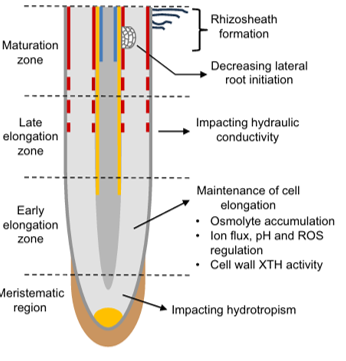
Review: Root growth in response to water stress
Plant Science Research WeeklyMaintaining root growth is a major plant adaptation to water deficit, enabling continued access to soil water. In a recent review, Voothuluru et al. discuss the inherent complexity of root systems in regard to water stress. Different root types, including primary, seminal, and nodal roots, show varying…
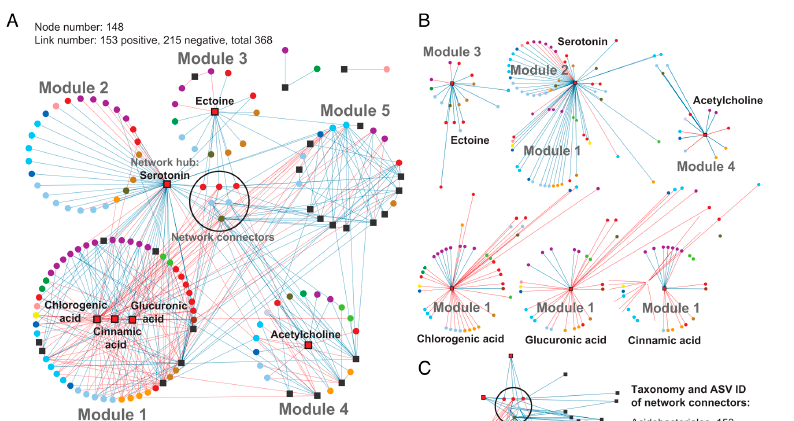
Keystone metabolites influence rhizosphere metabolomes and microbiomes
Plant Science Research Weekly
Rhizosphere interactions between plants and microbes are essential for nitrogen cycling, stress tolerance, and plant health in general. Metabolites secreted by plant roots can greatly influence microbial community composition, although how different environmental conditions impact these interactions…
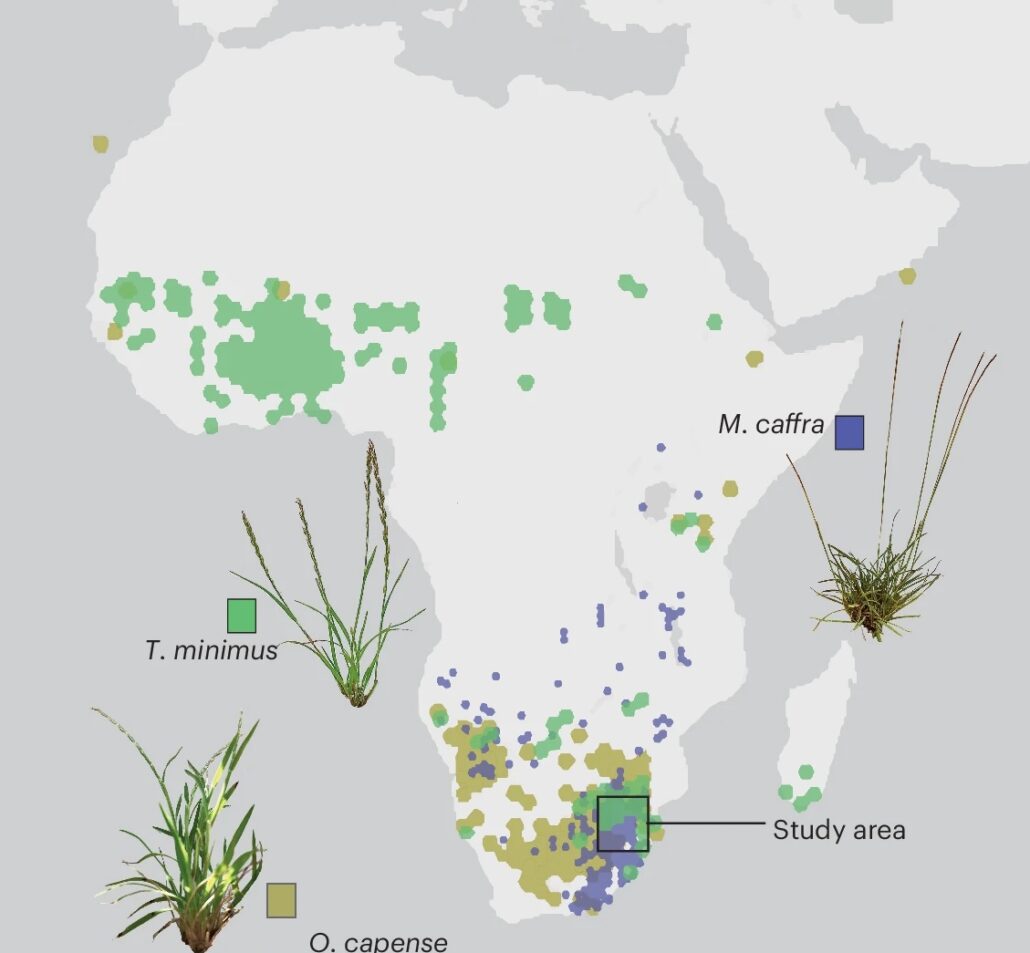
Convergent evolution of desiccation tolerance in grasses
Plant Science Research WeeklyMany bryophytes and other non-seed plants are tolerant to vegetative desiccation, which is thought to have been necessary for colonization of land. By contrast, most seed plants lack this capacity, although they retain desiccation tolerance in their pollen and seeds. However, some seed plants, known…
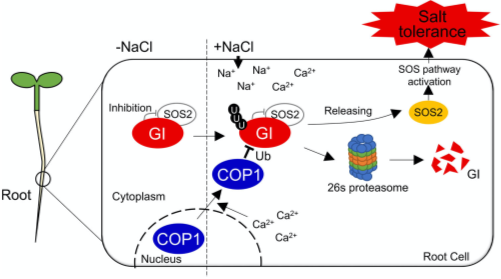
COP1 regulates salt tolerance via GIGANTEA degradation in roots
Plant Science Research WeeklyGlobal climate change affects weather patterns, and excess soil salinity harms plant growth. Previous studies have shown interaction between the circadian clock and salt responses. In normal conditions, the core circadian clock oscillator GIGANTEA (GI) sequesters the SOS2 kinase, part of the salt-overly…

