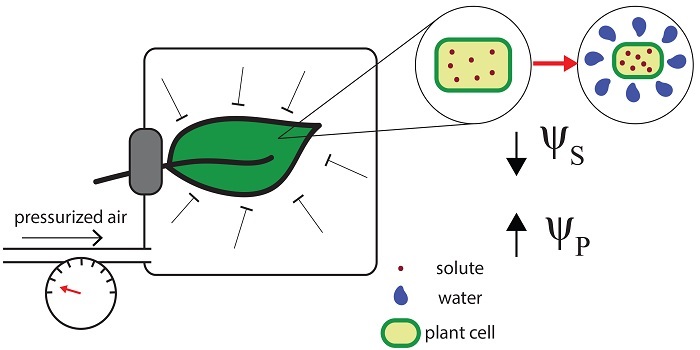
ABA accumulation in dehydrating leaves is associated with decline in cell volume not turgor pressure
Blog, Plant Science Research Weekly, Research, Research BlogDesiccating leaves show increased ABA levels triggered by low turgor – right? Apparently not! The pressure chamber experiments showing increased ABA levels in desiccating leaves are inconsistent when the entire leaves are enclosed in the chamber. Sack et al. proposes that the turgor pressure is increased…
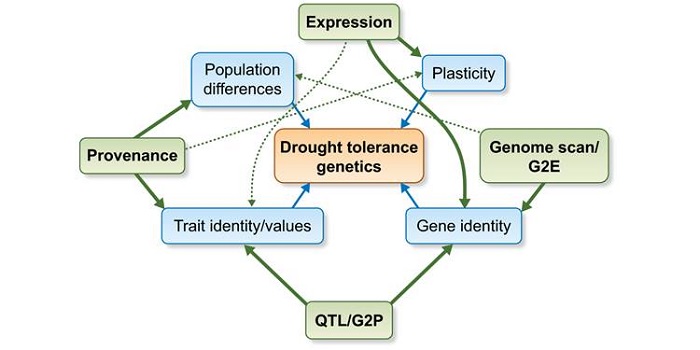
Review: The genetics of drought tolerance in conifers
Blog, Plant Science Research Weekly, Research, Research BlogChanging climates mean changing rainfall patterns, which can have serious consequences for long-lived plants such as conifers. Moran et al. provide a thoughtful and readable overview of the strategies that enable some conifer species to survive drought. They start by discussing the different definitions…
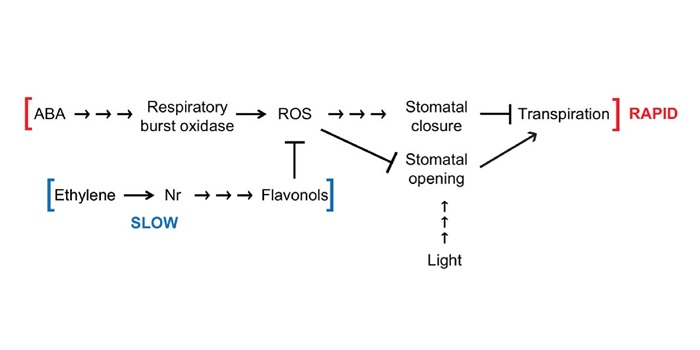
ABA-induced reactive oxygen species are modulated by flavonols to control stomata aperture
Blog, Plant Science Research Weekly, Research, Research BlogMuch of our knowledge concerning ABA-induced stomatal closure comes from genetic models such as Arabidopsis and Vicia faba. Watkins et al. explore the mechanism of ROS production in this abiotic stress pathway in an important agricultural crop: tomatoes (Solanum lycopersicum). Specifically, they are…

How Plants Keep Troublemakers Out and Water In
Research, The Plant Cell, The Plant Cell: In a NutshellKaundal et al. examine how a protein keeps plants safe from invading pathogens and dehydration http://www.plantcell.org/content/29/9/2233
By Amita Kaundal, Vemanna S. Ramu, Kirankumar S. Mysore
Background: To cause disease in plants, bacteria must enter plant tissue and multiply. Bacteria and…

Update on autophagy: Dynamics of autophagosome formation
Blog, Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: Updates, Research, Research BlogBy Junmarie Soto-Burgos, Xiao-Hong Zhuang, Liwen Jiang, and Diane C. Bassham
Autophagy, literally defined as “self-eating”, functions as a degradation process by recycling cytoplasmic contents under stress conditions or during development. Upon activation of autophagy, a membrane structure known…
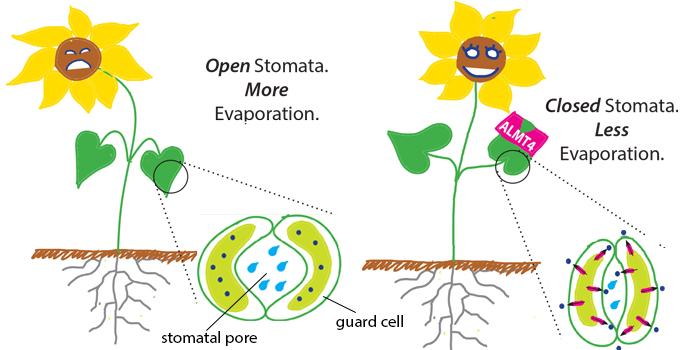
An Ion Channel Active in Plant Drought Response
Research, The Plant Cell, The Plant Cell: In a NutshellEisenach et al. discover A new ion channel of the plant vacuole helps plants react to drought https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.17.00452
By Cornelia Eisenach
Background: Stomata are small pores on plant surfaces that facilitate diffusion of CO2, O2 and water vapor between plant and atmosphere. During…

Photosynthesis in Desert Plants: It’s About Time
Research, The Plant Cell, The Plant Cell: In a NutshellBoxall et al. investigate CAM photosynthesis in Kalanchoë fedtschenkoi The Plant Cell (2017). https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.17.00301
Background: During photosynthesis, most plants use the enzyme Rubisco to capture CO2 during the day. Crassulacean acid metabolism (CAM) plants such as prickly pears,…
To Grow or to Defend: That is the Question for Plant Central Metabolism
Research, The Plant Cell, The Plant Cell: In a NutshellFusari et al. perform GWAS to explore primary plant metabolism https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.17.00232
By Corina M. Fusari and Rik Kooke
Background: Primary metabolites such as sugars, organic acids, and amino acids are essential chemical compounds that drive plant growth and development by providing…

The Cys-Arg/N-end rule pathway is a general sensor of abiotic stress in flowering plants
Blog, Plant Science Research Weekly, Research, Research BlogThe N-end rule pathway is a conserved pathway for the control of protein turnover, through which the clipping or modification of amino acids from the amino-terminus of a protein leads to an interaction with PROTEOLYSIS 6 (PRT6; an N-recognin E3 ligase) and 26S proteasome-mediated proteolysis. Previously,…

