Cytokinin regulation in the endoplasmic reticulum (Plant Physiology)
 Cytokinin is a phytohormone involved in many plant processes such as cell proliferation, apical dominance, leaf senescence, tissue patterning, organ initiation, environmental responses… To allow for effective control of all these processes, cytokinin concentrations need to be continuously adjusted.
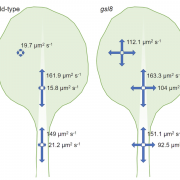
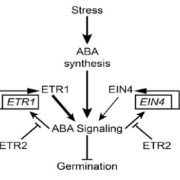
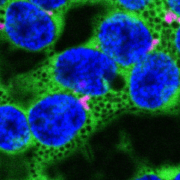
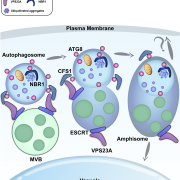
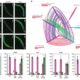
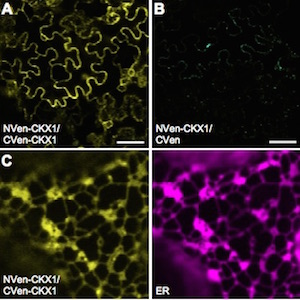
One such control mechanism is the irreversible degradation of cytokinin controlled by CKX (cytokinin oxidase/dehydrogenase) enzymes. Little is known about these proteins’ molecular behaviour and cellular localization. In Arabidopsis thaliana they are encoded by a small gene family of just 7 members. Nieman et al. show that one of them, CKX1, is a type-II integral membrane protein in the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) that forms homooligomeric complexes. According to their results, the N-terminal section of CKX1 is the one responsible for targeting to the ER and, together with the transmembrane domain, responsible for the homooligomerization. (Summary by Isabel Mendoza) Plant Physiol. 10.1104/pp.17.00925
Cytokinin is a phytohormone involved in many plant processes such as cell proliferation, apical dominance, leaf senescence, tissue patterning, organ initiation, environmental responses… To allow for effective control of all these processes, cytokinin concentrations need to be continuously adjusted.
One such control mechanism is the irreversible degradation of cytokinin controlled by CKX (cytokinin oxidase/dehydrogenase) enzymes. Little is known about these proteins’ molecular behaviour and cellular localization. In Arabidopsis thaliana they are encoded by a small gene family of just 7 members. Nieman et al. show that one of them, CKX1, is a type-II integral membrane protein in the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) that forms homooligomeric complexes. According to their results, the N-terminal section of CKX1 is the one responsible for targeting to the ER and, together with the transmembrane domain, responsible for the homooligomerization. (Summary by Isabel Mendoza) Plant Physiol. 10.1104/pp.17.00925