
Nanopore Sequencing Comes to Plant Genomes
Blog, Research, Research Blog, The Plant Cell, The Plant Cell: In BriefThe next generation of next-generation sequencing is upon us. Third-generation sequencing aims to provide long stretches of sequence – ultimately to the chromosome level – at bargain basement prices. Progress is being made toward those goals with the emergence of long-read sequencing techniques and…
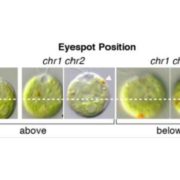
Clipping Chlamy Genes: Improved Methods for Targeted Gene Editing in Chlamydomonas
Blog, Research, Research Blog, The Plant Cell, The Plant Cell: In BriefA beam of sunlight sends Chlamydomonas reinhardtii scrambling. This tiny, biflagellate alga senses light with its eyespot and adjusts its movements accordingly, depending on photosynthetic needs. In the eyespot, a membranous structure of reddish, carotenoid-filled granules that reflect light and two…

Making Connections: MAC Function in Splicing and MicroRNA Biogenesis
Blog, Research, Research Blog, The Plant Cell, The Plant Cell: In BriefFans of the television show The Magic Schoolbus might remember that the teacher/heroine, Ms. Frizzle used to tell her students “Your job, as scientists, is to look for connections!” Ms. Frizzle would love the Mos4-associated Complex (MAC), because MAC has connections all over the place. Indeed, research…
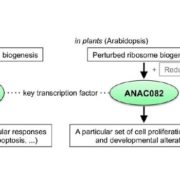
Proliferate at Your Own Risk: Ribosomal Stress and Regeneration
Blog, Research, Research Blog, The Plant Cell, The Plant Cell: In BriefPlant growth and development are extremely adaptable to changes in the external environment, including nutrient status, light quality and intensity, and temperature. Thanks to their developmental plasticity, plants can also initiate new organs from differentiated tissue following wounding, to the benefit…
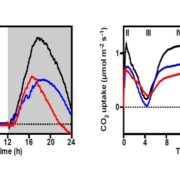
Stop the Clock: Optimized Carbon Fixation and Circadian Rhythm in a CAM Plant
Blog, Research, Research Blog, The Plant Cell, The Plant Cell: In BriefThe energetically costly tendency of the carbon fixing enzyme RuBisCO to, every now and then, fix oxygen instead of carbon dioxide has led to the evolution of various carbon concentrating mechanisms in plants and algae. One such mechanism, Crassulacean acid metabolism (CAM), involves primary CO2 fixation…

A Phloem Protein Contributes to Aphid Resistance and Heat Stress Tolerance
Blog, Research, Research Blog, The Plant Cell, The Plant Cell: In BriefAphids are highly destructive insect pests—in addition to robbing plants of sugar-rich phloem sap, they carry viruses that can be deadly to the plant. To reach the phloem sap, aphids must penetrate the plasma membrane of sieve elements. Mature sieve elements, which are virtually empty, translocate…
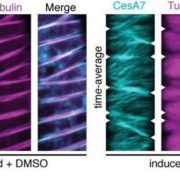
Evidence for Two Distinct Stages in Secondary Cell Wall Formation of Xylem
Blog, Research, Research Blog, The Plant Cell, The Plant Cell: In BriefA hallmark of xylem development is the deposition of secondary cell wall material in specific patterns (reviewed in Patrick et al, 2007). These cell wall deposits structurally reinforce the xylem to withstand negative pressure during water transport and differ in different xylem cell types. While it…

Thrown for a Loop: How RNase H1 and DNA Gyrases Limit R-loops and Maintain Genome Stability in Chloroplasts
Blog, Research, Research Blog, The Plant Cell, The Plant Cell: In BriefWe all know that DNA is the stable nucleic acid, in comparison to its flighty, unstable cousin RNA, right? Well, unusual things happen when metabolic processes require DNA to unwind from its stable, redundant double-helical form. For example, during transcription, the RNA that exits RNA polymerase can…
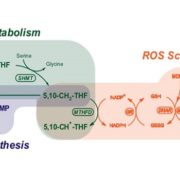
Folate Metabolism Linked to Redox Balance in Arabidopsis
Blog, Research, Research Blog, The Plant Cell, The Plant Cell: In BriefFolates are soluble B9 vitamins with essential functions in all kingdoms of life—both in organisms that produce these vitamins de novo (fungi, plants, and most microorganisms) and in those that do not (animals). As essential cofactors in one-carbon transfers, different folate species mediate the biosynthesis…

