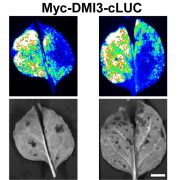
A Partnership for ABA Responses
The Plant Cell: In BriefThe phytohormone abscisic acid (ABA) regulates a variety of processes in plants including seed dormancy, seedling growth, and response to environmental stresses. A fascinating study by Ni et al. (2018) shows that ABA responses in rice are regulated by an interaction between the DMI3 kinase, which activates…
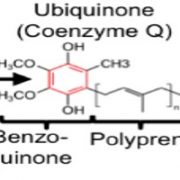
Questions about Coenzyme Q? A New Genetic/Metabolic Study Has Answers
The Plant Cell, The Plant Cell: In BriefAnyone who works on plants should be dazzled by the complexity and versatility of plant metabolism. In fact, why restrict this to plant biologists? We all love plant metabolites, whether we’re enjoying the caffeine in our morning cup of tea, or the capsaicin heat in the pepper flakes on our lunchtime…

How resurrection plants survive being hung out to dry
The Plant Cell, The Plant Cell: In BriefResurrection plants have the unique ability to survive extreme dehydration (desiccation), lying dormant for months or sometimes years until rehydration is possible. This formidable survival strategy has independently evolved several times across the land plant phylogeny, and several phylogenetically…
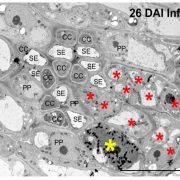
Sugar architect: the Brassicaceae pathogen Clubroot manipulates plants on multiple levels to secure sucrose supply
The Plant Cell, The Plant Cell: In BriefThe soil-borne pathogen Plasmodiophora brassicae can infect most members of the Brassicaceae family. The infections, which can lead to extensive crop losses, typically involve development of galls in the underground tissues of the plant, giving the pathogen its common name, ‘clubroot’.
Although…
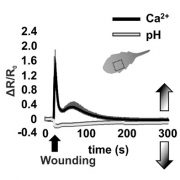
Small Talk: Protons Help Calcium Get the Message Across
The Plant Cell, The Plant Cell: In BriefCalcium (Ca2+) is a versatile second messenger that controls a range of cellular processes—from pollen tube growth to stress responses—by regulating the activity of various proteins. Although Ca2+ is present at millimolar concentrations in the cell wall and vacuole, a set of channels, pumps, and…
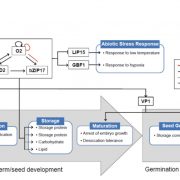
Corn ChIPs and RNA-seq: Researchers Dip into Advanced Tools and Resources to Examine bZIP Transcription Factor Function in the Maize Endosperm
The Plant Cell, The Plant Cell: In BriefThe endosperm of maize (Zea mays) seeds undergoes a complicated developmental program that ends with the production of massive amounts of storage compounds, particularly carbohydrates, but also including zein storage proteins (reviewed in Li and Berger, 2012; Hannah and Boehlein, 2017; Larkins et al.,…
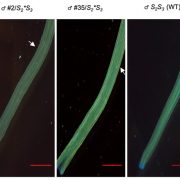
Self Control: SLF Proteins are Essential for Preventing Self-Fertilization in Petunia
Blog, The Plant Cell, The Plant Cell: In BriefA pollen grain lands on a stigma, swells with water, and sprouts a pollen tube, which races through the style to deliver sperm to the ovule below. When the pollen arises from the flower itself, this process often stops in its tracks. Self-incompatibility (SI) between pollen and pistil promotes outcrossing…
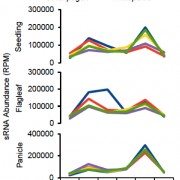
In Brief: Loss of a Silencing Cascade Contributed to Indica Rice Domestication
Blog, The Plant Cell, The Plant Cell: In BriefThousands of years of artificial selection have produced rice plants (Oryza sativa) that are vastly different from their wild progenitor species in terms of architecture, yield, and resilience. Most of the genetic changes linked to rice domestication involved genes encoding transcription factors. However,…
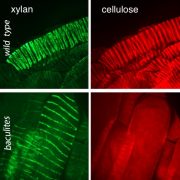
Microtubules Direct Lignin and Xylan Deposition in a Cellulose-Independent Manner
Blog, The Plant Cell, The Plant Cell: In BriefAlthough secondary cell walls represent the bulk of plant biomass, the mechanism by which cellulose, hemicellulose, and lignin assemble into a functional three-dimensional matrix is unknown. Cortical microtubules are thought to guide cellulose deposition in the plasma membrane by defining the trajectories…

