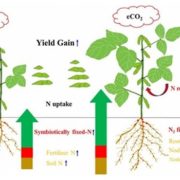
Elevated CO2 increases N2 fixation and contributes to various yield responses of soybean
Blog, Plant Science Research Weekly, Research, Research BlogClimate change is certain to affect our ability to produce food crops and feed a growing global population in the twenty-first century. Free-air CO2 enrichment (FACE) experiments have shown that elevated CO2 (eCO2) levels, a major driver of climate change, have a consistently positive effect on the…
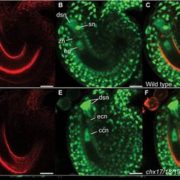
Cation/H+ exchangers affect pollen wall formation, male fertility, and embryo development
Blog, Plant Science Research Weekly, Research, Research BlogCells have developed different mechanisms including control of ion and pH homeostasis to adapt to their constantly changing environment. Such adaption is accomplished by different ion transporters at the membranes. AtCHX17, AtCHX18 and AtCHX20 are members of the cation-H+ exchanger (CHX) family, which…

An acidophilic green algal genome provides insights into adaptation to an acidic environment ($)
Blog, Plant Science Research Weekly, Research, Research BlogHirooka et al. examined the genome of an acid-loving green alga, Chlamydomonas eustigma, to learn how it tolerates its low pH environment. Key differences between the acidophilic species and the neutrophilic species Chlamydomonas reinhardtii include: an increase in expression of genes encoding plasma…
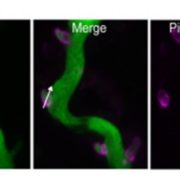
Tracking effector delivery in Irish famine potato pathogen
Blog, Plant Science Research Weekly, Research, Research BlogPathogenic microbes interfere with the host cellular and physiological processes to promote infection. This interaction is monitored by pathogen molecules called effectors that either act in intercellular space or enter the host cells. Mechanisms underlying the uptake of these effectors are not fully…

Special delivery: An independent secretion pathway for the delivery of cytoplasmic pathogen effectors
Blog, Plant Science Research Weekly, Research, Research BlogPathogenic microbes manipulate host plants by secreting effector molecules that interfere with immunity. Bacterial phytopathogens achieve this using specialized secretion apparatuses that act as molecular ‘hypodermic needles’ to inject effector proteins directly into plant cells. In comparison, effector…

Root phonotropism: Early signalling events following sound perception in Arabidopsis roots
Blog, Plant Science Research Weekly, Research, Research BlogPlants can hear. We know plants respond to touch, can perceive day and night, and respond to volatile compounds, water and nutrients. Moreno et al. studied root phonotropism (not phototropism). They showed that roots of Arabidopsis plants can perceive and respond to sound waves. Arabidopsis roots grew…

Stem parasitic plant Cuscuta australis (dodder) transfers herbivory-induced signals among plants
Blog, Plant Science Research Weekly, Research, Research BlogDodders (Cuscuta spp) are parasitic plants, which absorb water and nutrients from their host. Their vines can embrace, and in this way connect, more than one host. Hettenhausen et al. showed that in certain situations these connections serve as communication routes. In their experiment a pair of soybean…
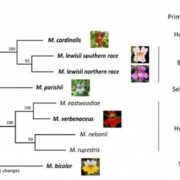
Less is more: Gene loss in flower pollination evolution ($)
Blog, Plant Science Research Weekly, Research, Research BlogThe evolution of flowers solved one of the largest obstacles of plant reproduction, finding a compatible mate. Since plants are sedentary, they are unable to search for a compatible mate like other organisms. Instead they use pollinators to do the searching for them. Flowers use scent and color to attract…

ABA-induced stomatal closure involves ALMT4, a phosphorylation-dependent vacuolar anion channel
Blog, Plant Science Research Weekly, Research, Research BlogChanges in guard cell turgor pressure result in stomatal opening and closing, balancing CO2 uptake with transpiration. These dynamics have been studied as early as the 1800s and much knowledge has been gained regarding the components involved in this process, yet we are still far from a unified model…

