
Hydrogen Sulfide and Cadmium Stress
Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: On The InsideCadmium (Cd) negatively impacts plant yield by causing growth inhibition, chlorosis, or even the death of entire plants. Cd interferes with the uptake and translocation of other ions, damages protein and DNA/RNA functions, and increases the accumulation of reactive oxygen species (ROS). An increasing…

Calcium Signaling and Sugar Homeostasis
Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: On The InsideThe calcium sensor Calcineurin B-like protein (CBL) participates in calcium signal transduction by interacting with CBL-interacting protein kinase (CIPK). CBL-CIPK pathways have been reported to participate in a range of biological processes. In Arabidopsis (Arabidopsis thaliana), there are 10 CBLs…
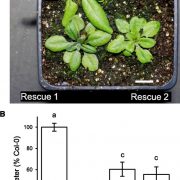
Certain Flippases Are Important for Vegetative Growth
Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: On The InsideLipid flippases hydrolyze ATP to flip lipids across a membrane bilayer toward cytosolic facing leaflets, whether that be from the outer leaflet of the plasma membrane (PM) or luminal leaflet of internal membranes. Flippases are proposed to be involved in multiple processes, such as flipping specific…
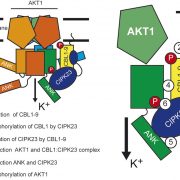
Regulation of a K+ Channel A by Phosphorylation
Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: On The InsidePotassium (K+) serves important roles in plants for the control of cellular pH, regulation of membrane electric potentials and cell turgor, and as a cofactor in essential metabolic processes including protein synthesis. Plasma membrane voltage-gated K+ channels are crucial for K+ uptake, release, and…
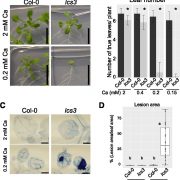
Callose Suppresses Low Calcium-Induced Cell Death
Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: On The InsideCalcium (Ca) deficiency symptoms often occur in crops because Ca is mainly translocated by the transpiration stream, and conditions that affect transpiration can cause Ca deficiency. Because Ca is translocated via the transpiration stream, it tends to accumulate more in older, expanded leaves and less…
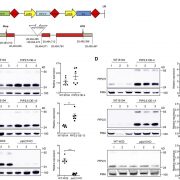
Role of Plasma Membrane Aquaporins in Maize
Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: On The InsideAquaporins belonging to the plasma membrane intrinsic protein (PIP) subfamily are key players in determining membrane water permeability. Since the overall root hydraulic conductivity (Lpr) depends on the integration of conductivity from three pathways (symplastic, apoplastic and transcellular), it…
The Smell of a Peach or Not
Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: On The InsideFruit aromas attract seed-dispersal agents in nature and are critical determinants of human fruit choice. In the process of constructing a peach (Prunus persica) core germplasm collection, Peng et al. (10.1104/pp.19.00964) analyzed the characteristics of peach cultivars in the National Fruit Germplasm…
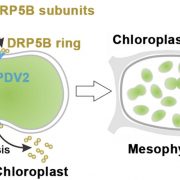
New Insights into Chloroplast Division
Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: On The InsideChloroplasts divide by binary fission, a process that is driven by a ring-like multiprotein complex spanning the inner and outer envelope membranes (OEMs) at the site of division. DYNAMIN-RELATED PROTEIN 5B (DRP5B/ ARC5), a cytosolic component of the chloroplast division machinery, is thought to function…
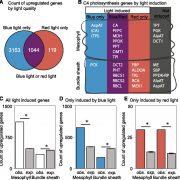
Cell-Specific Light Response in C4 Photosynthesis
Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: On The InsideIn C4 species, the expression of photosynthesis genes is partitioned such that leaf mesophyll and bundle sheath cells accumulate different components of the photosynthetic pathway. The expression of nucleus-encoded photosynthesis genes is modulated both by photoreceptor activity and by a network of…

