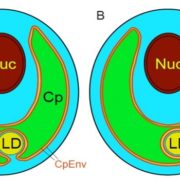
Do Lipid Droplets Exist in the Chloroplast Stroma?
Blog, Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: On The Inside, Research, Research BlogUnderstanding the metabolic pathways underlying oil production and the precise intracellular localization of lipid droplets is crucial for successfully engineering microalgae for biofuel production. The microalga Chlamydomonas reinhardtii accumulates considerable amounts of starch and triacylglycerol…
Actin and Aphid Feeding
Blog, Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: On The Inside, Research, Research BlogRemodeling of the actin network in plant cells involves the severing, depolymerization and polymerization of F-actin. A variety of actin-binding proteins are involved in remodeling of the actin cytoskeleton, including the actin-depolymerizing factor (ADF) family of proteins. As a result of their ability…

Origin and Role of ABA in Stomatal Regulation
Blog, Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: On The Inside, Research, Research BlogWhen the vapor pressure difference (VPD) between a leaf and the atmosphere increases (i.e., when air humidity decreases), guard cells lose turgor, thereby leading to stomatal closure. The evolution of this mechanism was an important step in the colonization of land by plants, since it enabled plants…
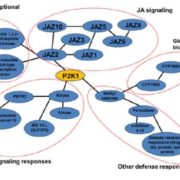
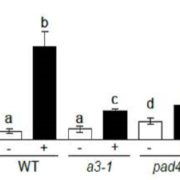
Extracellular ATP Boosts Plant Immunity Via Jasmonate Signaling
Blog, Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: On The Inside, Research, Research BlogDamage-associated molecular patterns (DAMPs) are endogenous chemicals that are released from damaged cells and which play a role as “danger signals.”
Adenosine 5’-triphosphate (ATP) becomes a DAMP signal after release into the extracellular milieu following cellular damage. Extracellular ATP…
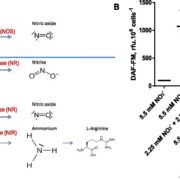
Nitric Oxide and Diatoms
Blog, Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: On The Inside, Research, Research BlogAll gases in the N cycle, including nitric oxide (NO), are present in oceans, either because of gas exchanges at the air-water interface or because they are produced within oceans themselves. NO, a physiologically important gaseous transmitter, is generated in seawater by nonbiological photochemical…

A MicroRNA Affecting Grain Yield in Rice
Blog, Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: On The Inside, Research, Research BlogMicroRNAs (miRNAs), a class of abundant small noncoding RNAs, have been identified as important regulators of gene expression in plants, affecting many aspects of plant development. Recently, several miRNAs have been reported to regulate rice grain yield. A previous study revealed that miR397 regulates…
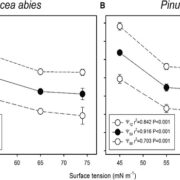
Xylem Sap Surface Tension and Hydraulic Safety
Blog, Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: On The Inside, Research, Research BlogXylem embolisms are induced by drought stress and/or freezing stress by means of “air-seeding,” that is the aspiration of gaseous bubbles into xylem conduits from adjacent gas-filled compartments via the pits. At water potentials less negative than the threshold for air seeding, the air-water interface…
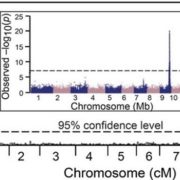
Chemical Defenses of Maize Roots
Blog, Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: On The Inside, Research, Research BlogOf the many classes of natural products produced by plants, terpenoids are the most structurally diverse, with well over 25,000 established compounds. In maize (Zea mays), terpene olefins are nearly ubiquitous components of induced volatile emissions following biotic stress. In contrast to our understanding…
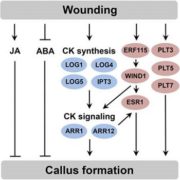
New Insights into Wound-Induced Callus Formation
Blog, Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: On The Inside, Research, Research BlogPlants repair wound sites through the formation of unorganized cell masses called calli, which can also serve as progenitors of new organs. Callus formation and organ regeneration often entail cell cycle re-entry of quiescent cells, which is achieved through the re-activation of core cell cycle regulators…

