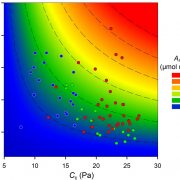
CO2 and O2 as Drivers of Plant Macroevolution
Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: On The InsideThe evolution of photosynthesis and, at a later point, the emergence of land plants resulted in substantial changes in the composition of Earth’s atmosphere. Plant colonization of the land in the early Paleozoic (more than 450 million years ago [mya]) was followed by a rapid drop in atmospheric [CO2],…
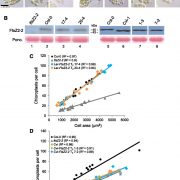
A Gene Affecting Chloroplast Size
Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: On The InsideDuring leaf growth and development, chloroplast numbers increase to maximize photosynthetic capacity. In mesophyll cells, chloroplast division takes place primarily during cell expansion and increases plastid numbers from; 10 to 20 in leaf primordia to; 100 or more in mature mesophyll cells. Chloroplasts…

Regulation of Pavement Cell Morphogenesis
Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: On The InsideSimple plant cell morphologies, such as cylindrical shoot cells, are determined by the extensibility pattern of the primary cell wall, which is thought to be largely dominated by cellulose microfibrils, but the mechanism leading to more complex shapes, such as the brick-shaped or jigsaw-like patterns…

How Carrots Get Their Colors
Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: On The InsideCarrot (Daucus carota ssp. sativus) are classified into two groups: the carotene group (variety sativus) and the anthocyanin group (variety atrorubens). Carotene group members, also known as nonpurple carrots, accumulate massive amounts of carotenoids in their roots. Anthocyanin group members, also known…

A Circadian Clock Protein Regulates Fitness under Water Limitation
Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: On The InsideThe circadian clock of plants coordinates many molecular, physiological and metabolic processes to optimize the plant's health and survival in an ever-changing environment. The core circadian clock component TIMING OF CAB EXPRESSION1 (TOC1) integrates environmental stress responses in plants through…

Systems Analysis of Lignin Mutants
Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: On The InsideLignin is a complex polymer deposited in plant cell walls that provides mechanical support and facilitates the transport of water and solutes through the vascular system, and aids in plant defense. Lignin waterproofs plant cells by providing a hydrophobic environment by chemical bonding with cellulose…
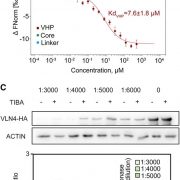
Cytoskeletal Targets of an Auxin Transport Inhibitor
Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: On The InsideThe phytohormone auxin plays critical roles in various plant developmental programs by controlling cell expansion and polarity, as well as organ patterning. Auxin action relies on polar transport through different plant tissues. Auxin transport inhibitors are important tools for understanding auxin-dependent…
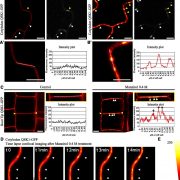
Stress-Induced Kinases Rapidly Relocate to Plasmodesmata
Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: On The InsidePlasmodesmata are membranous pores that span the plant cell wall creating both cytoplasmic and membrane continuums between cells. By interconnecting most cells throughout the entire plant body, plasmodesmata form a symplastic network that supports and controls the movement of molecules from cell to cell,…
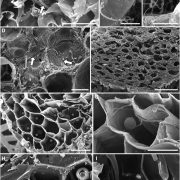
Insights into a Vascular Plant–Fungal Symbiosis
Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: On The InsideThe land invasion by plants more than 500 million years ago was facilitated by the formation of mutualistic symbioses with fungi, through which the earliest plants gained access to mineral nutrients in exchange for photosynthetically fixed carbon (C). It was long hypothesized that this ancient mycorrhiza-like…

